Several sectors, such as banking, F&B, automotive, and healthcare have seen major transformations at the hands of artificial intelligence (AI) ‒ we discussed benefits of AI in fast food industry in our previous article – Artificial Intelligence Finds its Way into Your Favorite Fast Food Chain in November 2017. AI has become an integral part of a large number of industries, providing new solutions and facilitating greater back-end efficiency as well as customer engagement and management. Insurance sector, on the other hand, has been largely slow to react to this disruptive trend. In 2017, only about 1.3% of insurance companies invested in AI (as compared with 32% insurance companies that invested in software and information technologies). However, this is expected to change as insurance companies have begun to realize the untapped potential that AI unearths in all aspects of their business, i.e. policy pricing, customer purchase experience, application processing and underwriting, and claim settlement.
Insurance industry has been one of the sectors that have operated in their traditional form for several decades, without undergoing much of substantial transformation. This is also one of the reasons why the insurance sector has been relatively late in jumping on the AI bandwagon.
Artificial intelligence, which has significantly transformed the way several industries such as automotive, healthcare, and manufacturing operate, also presents a host of benefits to the insurance sector. Moreover, it is expected to drive savings not only for insurance companies but also brokers and policy holders.
Streamlining internal processes
AI has the ability to streamline several internal processes within insurance companies. There is a host of duplicating business operations in the insurance sector. Automation and digitization can result in about 40% cost cutting, and this can be achieved by automating about 30% of the operations.
This can be seen in the case of Fukoku Mutual Life Insurance. In 2017, this Tokyo-based insurance company replaced 34 employees with IBM’s Watson Explorer AI system that can calculate payouts to policyholders in faster and more precise manner. The company expects to boost productivity by 30% and is expected to save close to US$1.26 million (JPY 140 million) in the first year of operations. To put this in a perspective, the AI system cost the company, US$1.8 million (JPY 200 million), and its maintenance is expected to cost US$130,000 (JPY 15 million) per year. Therefore, Fukoku seems optimistic about achieving its return on investment within less than two years of installing the AI system.
In addition to providing automation of processes, AI can bring out disruptive transformation throughout the insurance value chain. Some of the most substantial benefits of using AI in the insurance sector are expected to be seen in policy pricing, offering of personalized insurance plans, as well as claim management.
Policy pricing
Traditionally, insurance companies used to price their policies by creating risk pools based on statistical sampling, thereby all insurance policies were based on proxy data.
AI is transforming this by moving policy pricing analysis from proxy data to real-time source data. Internet of Things (IoT) device sensors, such as telematics and wearable sensor data, enable insurance firms to price coverage based on real events and real-time data of the individuals that they are insuring.
An example of this is usage-based or pay-per-mile auto insurance, wherein a telematics sensor box (a black box for a car), is installed into a car to track information such as speed, driving distances, breaking habits, and other qualitative and quantitative driving data. Using this data, insurance companies can offer a customized policy to the car owner, charging lower premium from safe drivers or offering less-used cars the pay-per-mile option. It also helps insurance companies charge suitable premium from reckless drivers and long-distance drivers.
In February 2017, UK-based mobile network brand, O2, expanded into the auto insurance space with a telematics product called the O2 Drive. The device tracks different aspects of a user’s driving habits and offers discounts and personalized insurance policies based on it. The company is positioning its products to attract teen and young drivers as they are most likely to be open to sharing their driving data.
In addition to auto insurance, IoT devices such as wearable devices and smart home solutions also help in setting policy pricing in health and home insurance. US-based Beam Insurance Services uses a smart toothbrush to offer dental insurance. The company uses data accrued from the smart toothbrush, such as number of times a person brushes their teeth, duration of brushing, etc., to offer a personalized insurance policy. It claims to offer up to 25% lower rates in comparison with its competitors.
In another example, UK-based Neos Ventures offers IoT-powered home insurance based on a smart home monitoring and emergency assistance device. The device and its accompanying app helps users reduce instances of fire and water-based damages as well as break-ins and thefts. The premise of the company is that if they can successfully reduce the chances of any mishaps, they can offer cheaper premiums to the insured.
While IoT devices can greatly personalize insurance pricing, the largest caveat to the success of this pricing mechanism remains that customers must be willing to share their personal data with insurance providers to attain savings in the form of lower premium. As per Deloitte – EMEA Insurance Data Analytics Study 2017, about 40% of customers surveyed seemed open to track their behavior and share the data with insurers for more accurate premiums for health insurance, while 38% and 48% customers were open to tracking and sharing data in case of home and auto insurance, respectively.
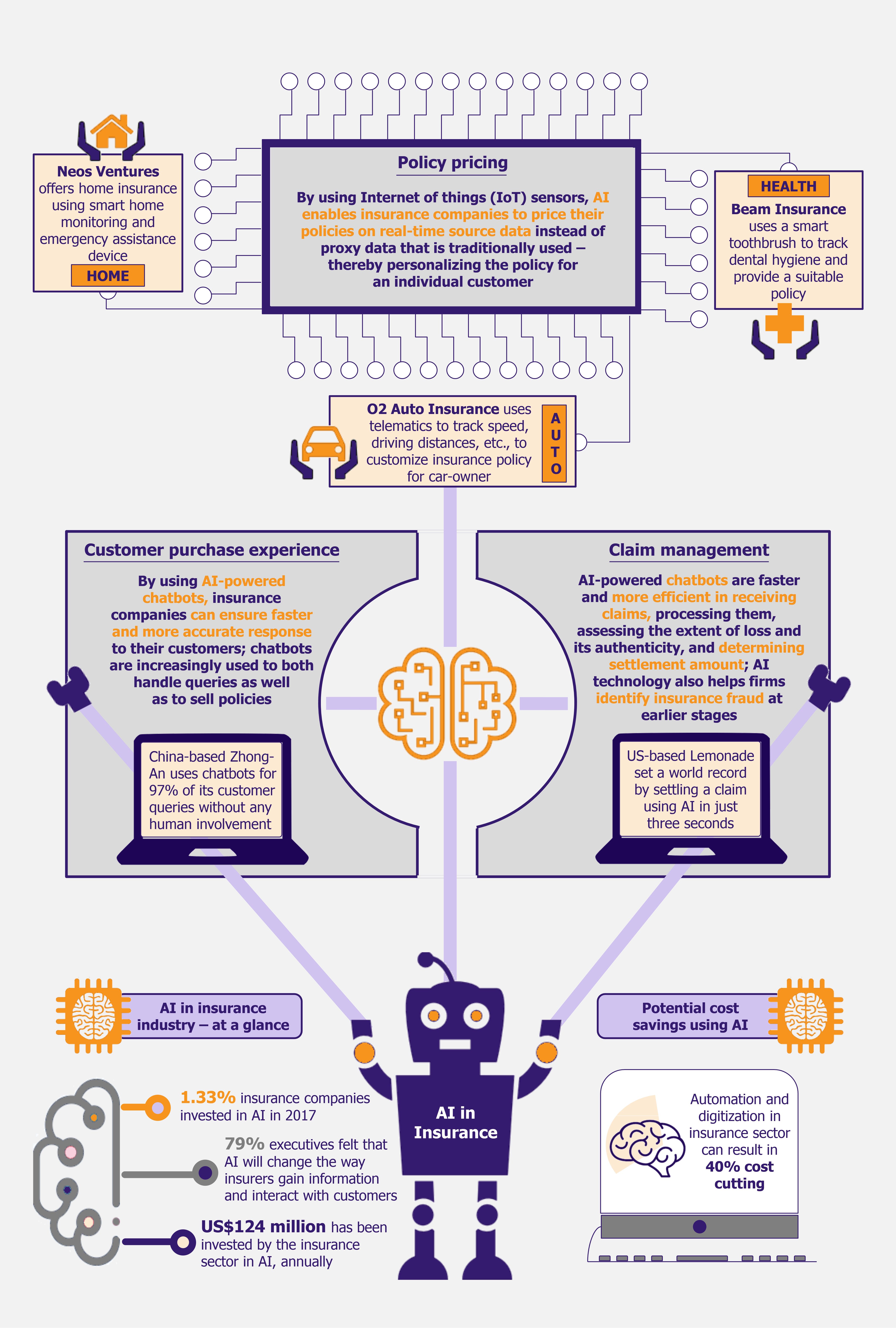
Customer purchase experience and underwriting of applications
The relationship between an insurance agent and the customer is an extremely important one for insurance companies. Many times the customer is dissatisfied with its interaction/experience with the insurance agent as they feel that the agent does not have their best interest at heart or the agent is not available for them as and when required.
This issue is effectively addressed with the use of AI-powered chatbots or virtual assistants. Advanced chatbots use image recognition and social data to personalize sales conversations and provide a better customer experience. Thus, agents and insurance representatives are being replaced by chatbots, which deliver faster and more efficient customer experience.
ZhongAn, a China-based pure online insurance company uses chatbots for 97% of its customer queries without any human involvement. It also uses AI to offer innovative insurance products, such as cracked mobile screen insurance. It uses image recognition technology to detect whether the image shows the mobile screen is cracked or intact. It can also decipher if the picture has been photoshopped or altered to ensure the claim is genuine. Since its inception in 2013, the company has sold about 8 billion policies to 500 million customers (these include cracked mobile insurance as well as the company’s other popular products).
To blend the human experience with chatbots, companies have started branding their chatbots with human names. New York-based P2P insurance company, Lemonade, uses exclusively chatbots named Maya and Jim to interact with customers and create personalized insurance options in less than a minute within the Lemonade app. The chatbots Maya and Jim are alter-egos of the company’s real-life employees with the same names.
Similarly, in December 2016, ICICI Lombard General Insurance launched a chatbot called MyRA. Within six months of operations the virtual assistance platform sold 750 policies without any human intervention, while it was used by 60,000 consumers for queries.
In addition to elevating customer’s purchase experience, AI also helps in reducing insurance underwriting/processing time and ensuring higher quality. The underwriting process traditionally has a range of manual tasks that make the process slow and also prone to human errors. However, AI helps achieve quicker and more reliable data analysis. AI tools such as Machine Learning and Natural Language Processing (NLP) help underwriters scan a customer’s social profile to gather important data, trends, and behavioral patterns that can result in more accurate assessment of the application.
New-York based Haven Life (a subsidiary of MassMutual), leverages AI technology to underwrite its life insurance policies. It requires its customers to submit a 30-question application (which is more conversational in nature as compared with the detailed traditional life insurance forms) and upload few documents such as medical records, motor vehicle driving records, etc. The AI technology analyzes the provided information along with historical life insurance data and asks additional questions if required. In several cases, it also offers coverage without the mandated medical test. Through AI, the company has reduced its underwriting time from the typical 1-2 weeks to as low as 20 minutes.
Claim management
AI can play a significant role in two of the most critical aspects of claim management, i.e. the time to settle a claim and fraud detection.
The time to settle a claim is one of the performance metrics that customers care most about. Using AI, companies can expedite the claim process. Chatbots are used to address the First Notice of Loss (FNOL), wherein customers submit their claims by sending pictures of the damaged goods along with answering few questions. The chatbot then processes the claim and assesses the extent of loss and its authenticity, to determine the correct amount for claim settlement.
Lemonade set a world record in December 2016 by settling a claim using its AI bot, Jim, in only three seconds. The AI bot reviewed the claim, cross-referenced it against the policy, ran several anti-fraud algorithms, approved the claim, sent wiring instructions to the bank, and informed the customer in the three-second window.
Another interesting area of application is in agriculture, where machine learning can also help quickly analyze claims (pertaining to loss spread over a wide area) using satellite imaging, which would otherwise take humans significantly greater time and costs to ascertain.
As mentioned earlier, AI can bring massive savings to insurance firms by reducing fraudulent claims. As per US-based Coalition Against Insurance Fraud (CAIF) estimates, insurance carriers lose about US$80 billion annually in fraudulent claims. AI technologies provide insurance firms with real-time data to identify duplicate and inflated claims as well as fake diagnoses.
In addition, many companies use AI to run algorithms on historical data to identify sequences and patterns of fraudulent claims to identify traits and trends that may be missed by the human eye during the initial stages of claim processing.
According to CAIF, in November 2016, about 75% of insurance firms used automated fraud detection systems to detect false claims. Paris-based Shift Technologies is one of the leading players in this domain, claiming to have a 250% better fraud identification rate as compared with the market average. The company had analyzed more than 100 million claims from its inception in 2013 up till October 2017.
EOS Perspective
There is no denying that AI has the capability to transform the insurance industry (as it has transformed many other industries). Although, initially slow at reacting to the AI trend, insurance companies have realized its potential.
As per an April 2017 Accenture survey, about 79% of the insurance executives believed that AI will revolutionize the way insurers gain information from and interact with their customers. This is also visible in the recent level of investments made in AI by the insurance sector. TCS’s Global Trend Study on AI 2017 stated that the insurance sector outspent all the other 12 sectors surveyed (including travel, consumer packaged goods, hospitality, media, etc.) by investing an average of US$124 million annually in AI systems. The cross industry average of the 13 sectors stood at US$70 million.
Thus, it is very important for insurance players to get on board the AI trend now. Since they are already late (in comparison to some other industries) in reacting to the trend, it is critical that they adapt to it to remain relevant and competitive.
However, the key barrier to AI implementation are the complex and outdated legacy systems that hold back innovation and digitization. The companies that do not manage to implement tech innovations in their legacy systems due to high cost might just be acting penny wise, pound foolish.



