Over the past several years, the Chinese government has been taking steps towards promoting green energy projects and building eco-friendly New Energy Vehicles (NEVs). Since 2008-2009, investments in green sector projects in China have witnessed tremendous growth, which is pushing development of the Chinese NEV industry. As China is slowly shifting focus from fossil fuel vehicles to electric vehicles, its involvement in developing technologies such as green energy and NEVs has equipped the country to compete at global level with western giants such as the USA, Germany, France, etc. While currently China is the largest producer of NEVs globally, it is still debatable whether in the future it will be able to sustain this growth to stay competitive and lead the global EV industry.
China has always aimed to become one of the global leaders in automobile industry similarly to its neighbors, Japan and South Korea, but for the longest time it was not able to produce vehicles that would be globally competitive in terms of quality and safety. In 2009, the Beijing government introduced Automotive Industry Readjustment and Revitalization Plan to strengthen China’s position in the global automotive market. The key objectives of the plan were to support domestic auto manufacturers, commercially as well as technologically, and allocate more resources to environmental friendly vehicles’ research and promotion. The government started promoting electric cars to tackle the environmental threats that China was facing. Electric and hybrid cars were relatively new concepts in 2009-2010, but this did not dissuade China and it started building strategies to increase production of such vehicles to compete and lead in the NEV market.
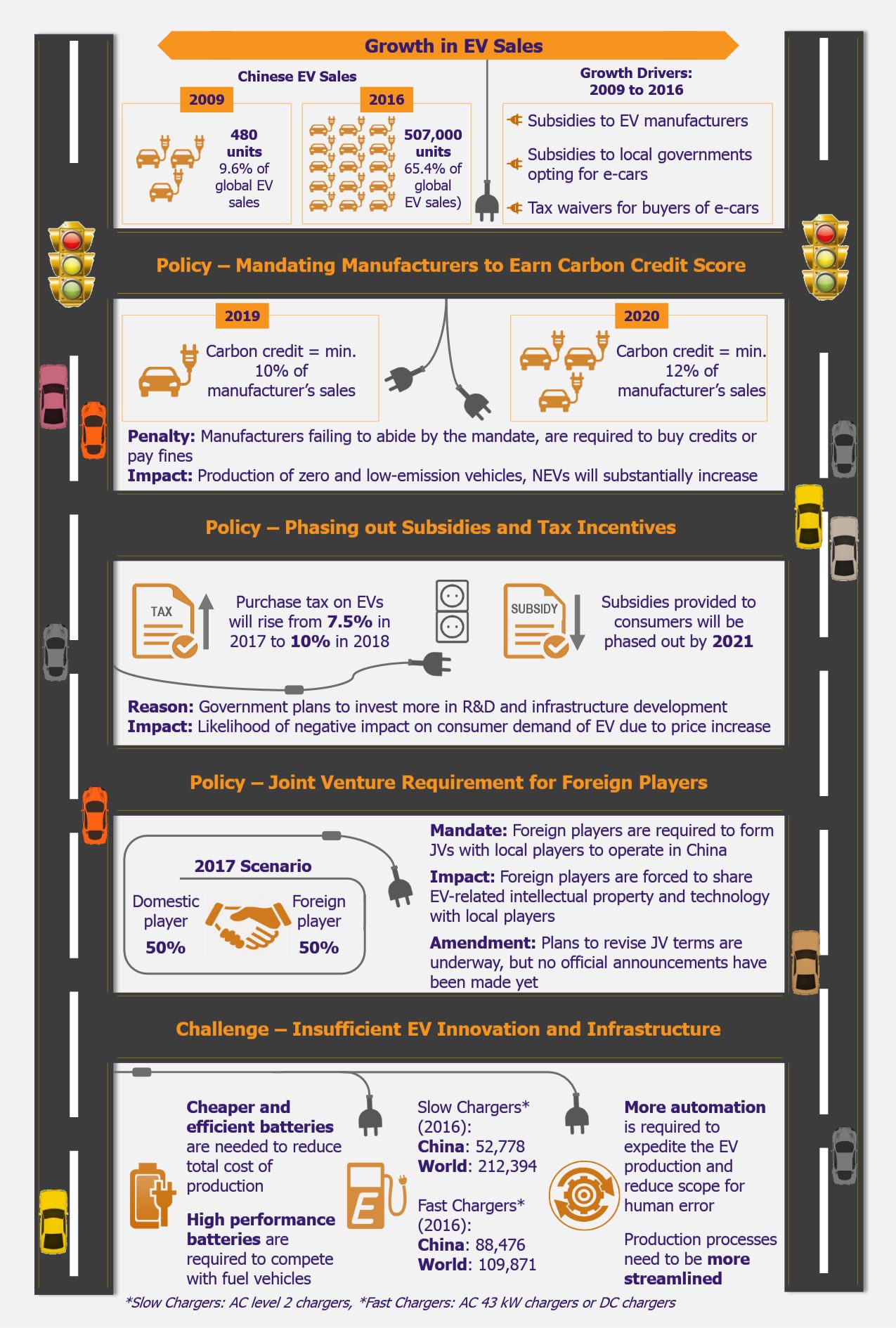
Since 2010, the Chinese government has been providing incentives, in various forms, for the NEV sector. For instance, the government introduced direct subsidies for NEV manufacturers, deductions for local authorities opting for green cars, and tax waivers and free registration incentives for consumers purchasing electric cars. These incentives accelerated the growth of NEV industry, which sold around 507,000 units in 2016 as compared with 480 units in 2009. Currently, the top ten global EV manufacturers are all Chinese producers. China aims to sell around two million electric cars annually and introduce a fleet of five million electric cars on the country’s roads by 2020. China’s goal, in terms of NEV sales, is quite ambitious but also necessary, as the country aims to limit its carbon emission rate by 2030 and curtail air pollution.
With the Chinese government shifting its focus on promoting green energy and green vehicles, changes have been made in various policies laid down for the auto sector. For instance, the 13th Five Year Plan, introduced in 2016, promotes adoption of NEVs. Government is also considering to ban gasoline and diesel vehicles, indicating that in near future, automakers may have to redesign their production and shift to green vehicle manufacturing.
In June 2017, the Chinese government made it compulsory for automakers selling more than or equal to 30,000 cars annually to increase share of EVs in their total auto sales. China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) introduced the carbon credit trading program, which mandates manufacturers to earn carbon credit score on their automobile production and sales. The policy is aimed to encourage production of various types of zero and low-emission vehicles. Effective 2019, manufacturers will be required to earn EV credits equivalent to 10% of sales, which would eventually rise to 12% in 2020. The credit score will be calculated on the basis of electrification level of the cars produced, indicating that fully electric cars will earn more credits than plug-in hybrid cars. Manufacturers not complying with these quotas will either have to buy credits or pay penalties. A credit score equivalent to 12% of sales will be equal to about 4-5% of EV sales, which could lead to the production of more than a million green energy vehicles in China in 2020. Certainly, this policy will be beneficial to the domestic EV manufacturers, who have massive EV production, as their income from credit sales will increase.
In January 2017, the Chinese government introduced another change in EV policy to subsequently phase out the tax benefits on purchase of EVs by 2021. The announcement has resulted in slight decline in consumer demand for EVs in China.
Further, the government has mandated the foreign players to form a 50-50 joint venture (JV) with domestic firms to operate in China. Consequently, the foreign players are forced to share their intellectual property and technology with local Chinese automakers. Some of the countries perceive this move as intellectual property theft by China. In the future, the Chinese government is likely to relax the JV terms and increase the foreign player’s percentage share in a JV.
EOS Perspective
Currently, China holds a bright spot in the global electric vehicle industry. Fuel-run vehicles are expected to lose their dominant position in a couple of decades if the EV industry continues to grow at the anticipated rates. Being the largest market for NEVs globally, China is likely to play a major role in this progress. But to continue leading the EV market, foremost requisite is to solve issues such as the price to performance ratio of batteries, and lack of sufficient charging stations and EV infrastructure in China.
In near-term, undoubtedly, China will remain a huge market for NEVs with foreign players aiming to be a part of it. It is yet to be seen what changes the Chinese government makes in JV terms for foreign players, but they will surely face a stiff competition from the well-settled domestic EV manufacturers. Selling in the competitive environment of China will surely affect their profits, but the main concern for them will be sharing their intellectual property with Chinese OEMs. Another challenge for all players would be to understand whether consumer demand for EVs will continue to thrive after the price increase related to the gradual withdrawal of subsidies and tax benefits. China has strategically kept NEV prices low to increase popularity and awareness of EVs amongst consumers. However, the government does not plan to sustain the low-priced regime, with the recent policy changes and subsidy phase outs likely to gradually increase EV prices in China, which might impact demand for EVs (it is likely to still remain high as compared with demand in other countries). The government plans to focus more on research and innovation to supply EVs at lower prices without any subsidies as well as to build robust infrastructure to support growth of the industry.
China also plans to export EVs to other major markets such as the USA, Norway, the UK, Germany, and Korea. With the current low quality and performance of domestically manufactured EVs, local Chinese players are not getting many buyers in these countries. But forging JVs with foreign players to produce EVs at lower rates and better quality may improve the export figures in future.
China has definitely raised the bar for other countries with its aggressive EV policies launched in 2017, which are future-centric and focused on ushering in a revolution in the auto industry by promoting EV vehicles over the traditional diesel/gasoline-based vehicles. In the future, NEV manufacturers in China are likely to focus on building economical and efficient vehicles, and with foreign players bringing in their latest EV manufacturing technologies, the future drive looks smooth for Chinese NEVs.



