For the past decade, China has been on the forefront of the New Energy Vehicles (NEVs) revolution. Although most of its focus has been on battery-powered electric vehicles (BEVs), the government has recently also begun to put its financial might behind hydrogen fuel cells for vehicles. Unlike battery-powered vehicles that need regular and long-periods of charging (therefore are more suitable for personal-use vehicles), hydrogen fueled vehicles do not need frequent refueling and their refueling is quick. This makes them ideal for long-distance buses, taxis, and long-haul transport. However, the existing infrastructure to support fuel cell-powered cars is limited. Thus, despite having inherent benefits over electric vehicles (especially in case of commercial vehicles), fuel cell vehicles fight an uphill battle to build a market for themselves in China, owing to the challenges in acceptability, infrastructure availability, and sheer economies of scale.
Over the last decade, the Chinese government heavily backed the production and sale of electric vehicles through substantial subsidies, investment in infrastructure, and favorable policies. This resulted in the sector picking up rapidly and reaching 1.2 million vehicles sold in 2018. However, the government has begun to reduce the subsidies provided to the sector and the focus is slowly shifting to fuel cell vehicles.
| How do fuel cell vehicles work?
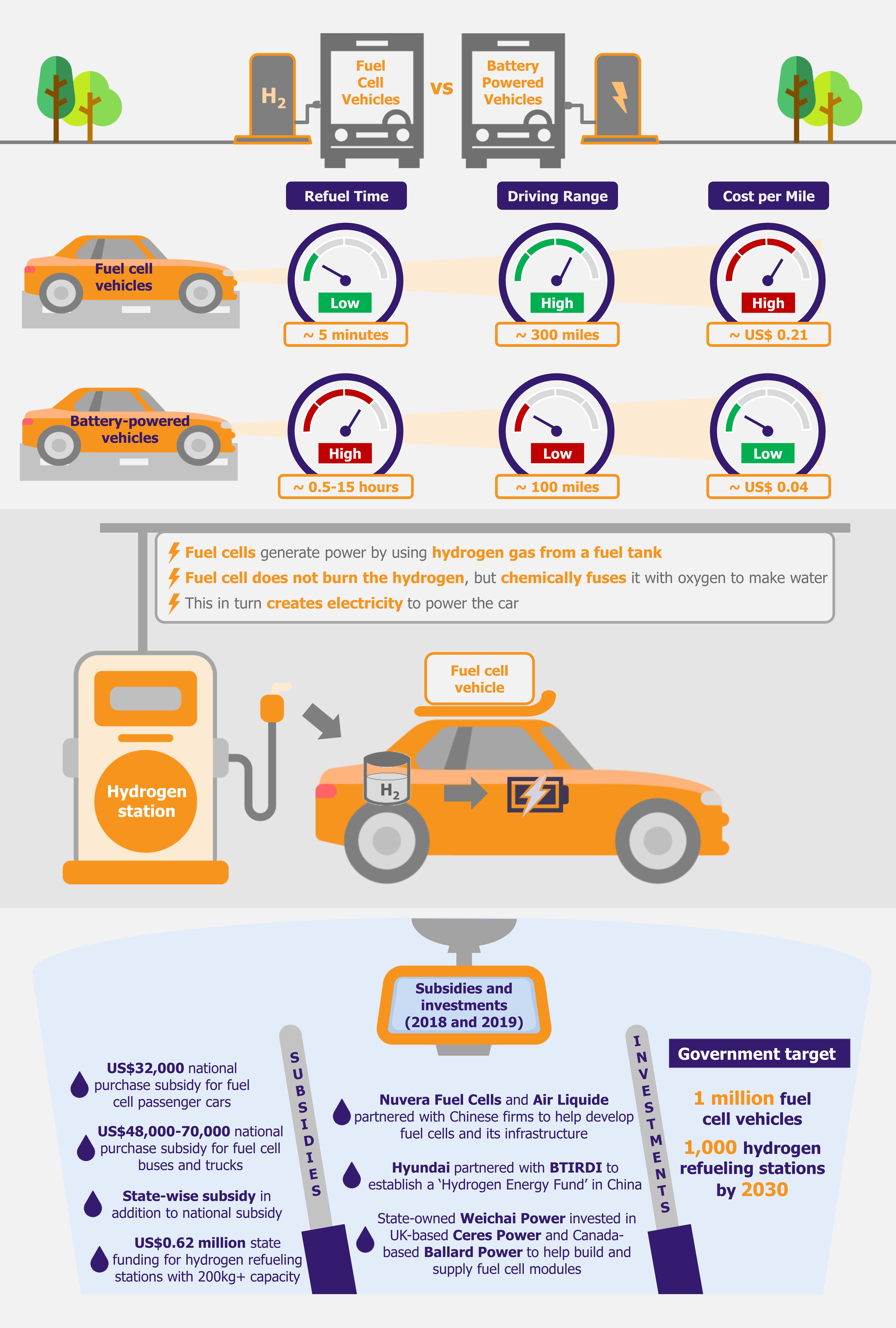
Fuel cell vehicles use hydrogen gas to power their electric motor. Fuel cells are considered somewhat a crossover between battery and conventional engines in their working. Similar to conventional engines, fuel cells generate power by using fuel (i.e. pressurized hydrogen gas) from a fuel tank. However, unlike traditional internal-combustion engines, a fuel cell does not burn the hydrogen, but instead it is chemically fused with oxygen from the air to make water. This process, which is in turn similar to what happens in a battery, creates electricity, which is used to power the electric motor. Thus, while fuel cell vehicles are electric vehicles (since they are solely powered by electricity), they are similar to conventional vehicles with regards to their range, refueling process, and needs. This makes them ideal for long-haul commercial vehicles. |
Chinese government bets big on fuel cell vehicles
Under China’s 13th Five-Year Plan, the government has laid out a Fuel Cell Technology Roadmap, in which it aims to operate over 1,000 hydrogen refueling stations by 2030, with at least 50% of all hydrogen production to be obtained from renewable resources. In addition, it has set a target for the sale of 1 million fuel cell vehicles by 2030.
To achieve these ambitious targets, the Chinese government plans to roll-out a program similar to its 2009 program – Ten Cities, Thousand Vehicles, which promoted the development and sale of battery electric vehicles and hybrid vehicles. It currently plans to promote fuel cell vehicles in Beijing, Shanghai, and Chengdu. Considering the vast success garnered by this program, it is likely that the government will also be successful in achieving similar targets for fuel cells.
Moreover, while the government is phasing out subsidies for BEVs, it is continuing them for fuel cells. As per the government guidelines issued in June 2018, US$32,000 purchase subsidy is available for fuel cell passenger vehicles, while US$48,000-US$70,000 purchase subsidies are available for fuel cell buses and trucks. However, for the buses to receive subsidy, they are required to drive a minimum of 200,000 km in a year.
While the government is phasing out subsidies for BEVs, it is continuing them for fuel cells. As per the government guidelines issued in June 2018, US$32,000 purchase subsidy is available for fuel cell passenger vehicles, while US$48,000-US$70,000 purchase subsidies are available for fuel cell buses and trucks.
Moreover, the government also provides subsidy for the development of hydrogen refueling stations. A funding of US$0.62 million is available for hydrogen refueling stations having a minimum of 200kg capacity.
In addition to these national subsidies, state-wise subsidies are also available for several regions such as Guangdong, Wuhan, Hainan, Shandong, Tianjin, Henan, Foshan, and Dalian. Local subsidies differ from region to region and are given as a ratio of the national subsidy. For instance, it equals 1:1 in Wuhan, while it is 1:0.3 in Henan province. On the other hand, local or state subsidies are cancelled for BEVs (except buses).
Apart from subsidies given to fuel cell infrastructure and vehicle manufacturers, the price of hydrogen is also heavily subsidized, making it cheaper than diesel in many cases.
China’s fuel cell vehicle market picks up steam
The government’s backing and subsidies have stirred interest of several international players towards China’s fuel cell vehicle market. Considering its success and dominance of the BEV market, these players are placing their bets on China achieving similar volumes and success in the fuel cell sphere.
Chinese companies have also begun to invest heavily in fuel cell technology companies globally. In May, 2018, Weichai Power, a Chinese leading automobile and equipment manufacturer, purchased a 20% stake in UK-based solid oxide fuel cell producer, Ceres Power. Similarly, in August 2018, Weichai Power entered into a strategic partnership with Canada-based fuel cell and clean energy solutions provider, Ballard Power Systems. As part of the strategic partnership, the company purchased 19.9% stake in Ballard Power Systems for US$163.3 million. In addition, they entered into a JV to support China’s Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle market, in which Ballard holds 49% ownership. Through this partnership, Weichai aims to build and supply about 2,000 fuel cell modules for commercial vehicles (that use Ballard’s technology) by 2021.
Global leader in industrial gases, Air Liquide, has also partnered with companies in China to be a part of the fuel cell movement. In November 2018, the company entered into an agreement with Sichuan Houpu Excellent Hydrogen Energy Technology, a wholly-owned affiliate of Chengdu Huaqi Houpu Holding (HOUPU), to develop, manufacture, and commercialize hydrogen stations for fuel cell vehicles in China. In January 2019, the company also partnered with Yankuang Group, a Chinese state-owned energy company, to develop hydrogen energy infrastructure in China’s Shandong province to support fuel cell vehicles in that region.
Another global player, Nuvera Fuel Cells (US-based fuel cell power solutions provider) has also engaged with local companies to foster growth in China’s fuel cell vehicle market. In August 2018, the company entered into an agreement with Zhejiang Runfeng Hydrogen Engine Ltd. (ZHRE), a subsidiary of Zhejiang Runfeng Energy Group based in Hangzhou. Under the agreement, Nuvera will provide a product license to ZHRE to manufacture the company’s 45kW fuel cell engines for sale in China. While the fuel cells will be initially manufactured in Massachusetts, it is expected that they will be locally manufactured by 2020.
In December 2018, the company signed another agreement with the government of Fuyang, a district in Hangzhou (in Zhejiang province), to start manufacturing fuel cell stacks locally in 2019. The agreement also includes an investment by Nuvera to establish a production facility in Fuyang region. These fuel cell stacks will be used to power zero-emissions heavy duty vehicles (such as delivery vans and transit buses), which comprise 10% of on-road vehicle fleet, but account for 50% fuel consumption.
In addition to the fuel cell energy producers, global car manufactures have also shifted their attention to fuel cell vehicles market in China. In October 2018, Korean car manufacturer, Hyundai, entered into a MoU with Beijing-Tsinghua Industrial R&D Institute (BTIRDI) to jointly establish a ‘Hydrogen Energy Fund’. The fund aims to raise US$100 million from leading venture capital firms across the globe to spur investments in the hydrogen-powered vehicle value chain. This agreement will help the Korean automobile manufacturer identify and act upon new hydrogen-related business opportunities in China and will eventually help pave the way for Hyundai Motors to make a foray into the Chinese fuel cell vehicle market in the future.
A bumpy road ahead for fuel cell vehicles
While the industry players are working along with the government to meet the ambitious targets set by the latter, fuel cell vehicles must overcome several challenges for them to be a realistic alternative to conventional and electric vehicles.
Currently, the infrastructure for fuel cell vehicles is by far insufficient. More so, it is extremely costly to develop, costing about US$2 million to build a refueling station with a capacity of about 1,000 kg/day. While the government is investing heavily in developing hydrogen refueling stations (for instance, China Energy, China’s largest power company, has been building one of China’s largest hydrogen refueling stations in Rugao City, Jiangsu Province), it requires long term partnerships and investments from private and global players to meet its own targets. Until an adequate number of refueling stations is constructed, especially on highway routes (facilitating truck and bus transportation), fuel cell vehicles will remain in a sphere of concept rather than commercial and mass use.
Another challenge faced by the industry is that hydrogen, the main fuel, is also considered to be highly hazardous, and storing and transporting it is currently difficult. Moreover, it is difficult to convince customers to purchase hydrogen-powered vehicles because of this perceived notion of hydrogen being unsafe. In addition to providing subsidies and incentives for building fuel cell vehicles, the government must also invest in marketing campaigns and enact policies that raise awareness about hydrogen in fuel cell vehicles as a safe and green energy.
In addition to providing subsidies and incentives for building fuel cell vehicles, the government must also invest in marketing campaigns and enact policies that raise awareness about hydrogen in fuel cell vehicles as a safe and green energy.
A lot of new technologies are also being explored to further make transporting and storing hydrogen safer. A German company, Hydrogenious Technologies, has developed a carrier oil that can carry hydrogen in a safe manner. This oil is non-toxic and non-explosive and thus makes transporting, storing, and refueling hydrogen safe. Moreover, using hydrogen mixed with this carrier oil to refuel fuel cell cars follows a similar refueling process as that of a conventional car, with one cubic meter of the oil carrying about 57kg hydrogen, which in turn is expected to give a car a driving range of 5,700km. However, the carrier oil is still in its nascent stage of development and would take time and resources to gain commercial applicability.
However, one of the largest challenges that fuel cell vehicles face is direct competition from battery electric vehicles. BEVs have a 10-year head start over fuel cell vehicles whether it comes to government support, technological development, infrastructure, or acceptability. Moreover, BEVs are cheaper both in terms of cars price and cost of running, which is an important factor for consumers. In addition, BEV players are constantly working towards reducing charging time and increasing driving range. Since both are green technologies, it is likely that the consumer prefers the one which has now proven to be a successful alternative to conventional vehicles in terms of pricing and supporting infrastructure. Although higher subsidies for fuel cell vehicles may help bridge the gap, it is yet to be seen if fuel cell cars will be able to give stiff competition to their green counterparts.
EOS Perspective
There is no doubt that the Chinese government intends to throw its weight behind the fuel cell technology for automobiles. In 2018 alone, the central and local governments spent a total of US$12.4 billion in supporting fuel cell vehicles. This has helped attract the attention of several local and international companies that want a share of this growing market.
It also helps that hydrogen as a fuel has several benefits when compared with battery power, the key advantages being short refueling time and long driving range. Moreover, some consider hydrogen to be a cleaner fuel when compared with battery power as the electricity required to create hydrogen (which is created by pumping electricity into water to split it into hydrogen and oxygen) can be derived from renewable sources from China’s northern region, which are currently going to waste.
Despite these inherent benefits, it will be difficult for fuel cell vehicles to catch up with battery-powered vehicles as the latter have significantly advanced over the past decade (leaving fuel cell vehicles behind).
Moreover, China’s model of promoting green energy is yet to pass its ultimate test, i.e., to sustain and flourish without government support. Since the government has now begun to phase out its support to BEVs, it is to be seen if the large group of domestic electric vehicle makers can survive in the long run or the market will face significant consolidation along with slower growth. Thus it becomes extremely critical for the Chinese government and companies in this sector to understand the feasibility of the market post the subsidy phase. Fuel cell vehicle market should take advantage of learning from the experience of battery powered vehicles sector, which was the pioneer of alternatives to conventional combustion vehicles.