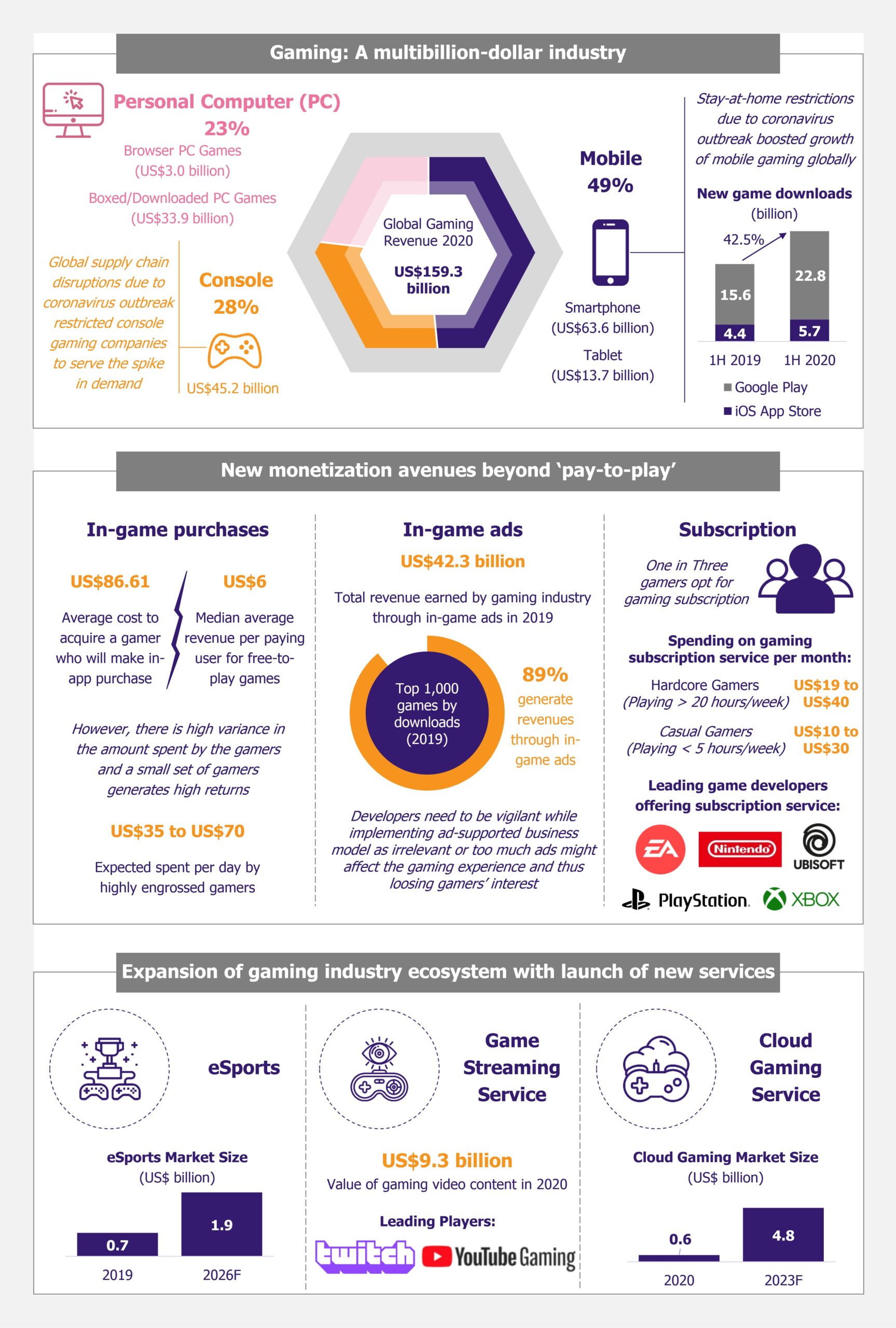
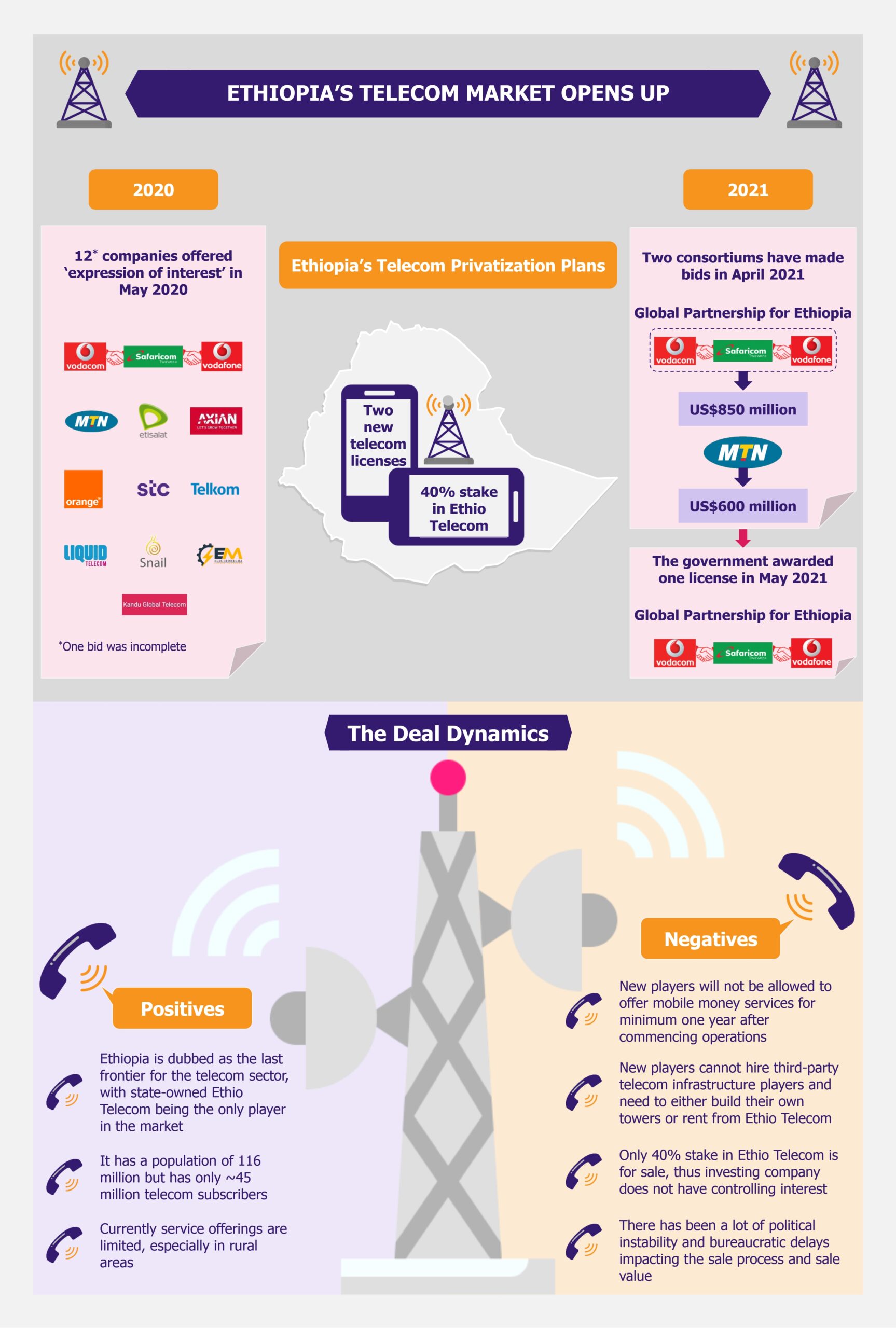
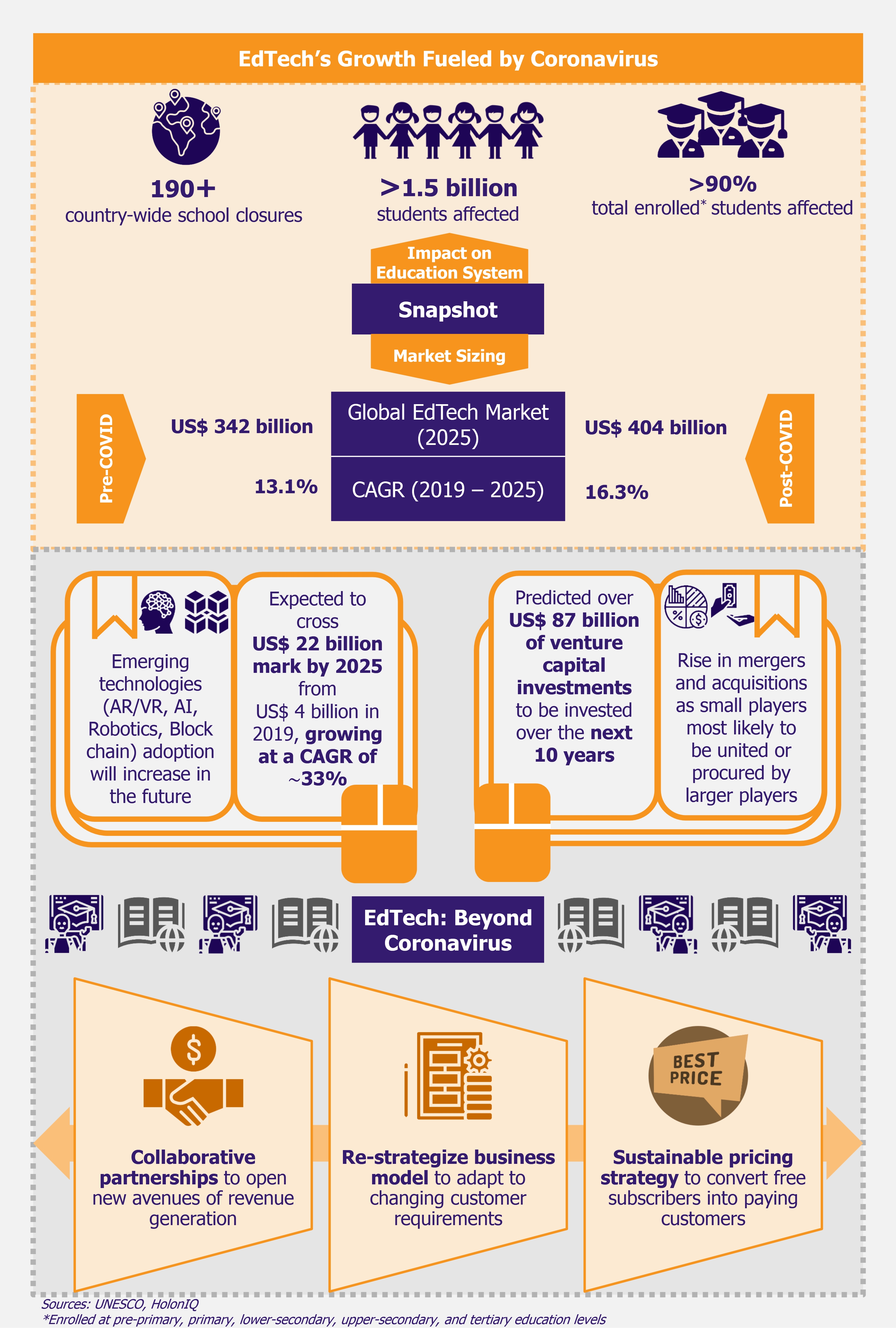
First conceptualized over 40 years ago, 3D printing is still rapidly developing. The technology has been used in various industries ranging from 3D-printed human organs for implants to printing numerous customized products as per the customers’ requirement. There are several interesting applications of this technology in the Food & Beverage (F&B) industry as well. While currently they mostly pertain to creating visually complex geometrical food structures, there are also ongoing innovations with regard to using 3D printing for nutritional controllability and sustainability. However, most of these projects are one-off and 3D printing still remains a niche application in the F&B space.
3D printing is an evolving technology, offering F&B industry players benefits such as efficiency and customization. 3D printers are mostly used by F&B producers to make foods using the extrusion technique. In this method, the edible is in the form of a paste and is extruded from syringe-like containers onto a plate based on a 3D computer model. The process is similar to icing a cake using a piping bag, except with robotic precision, as the printer layers edible filament in desired shapes.
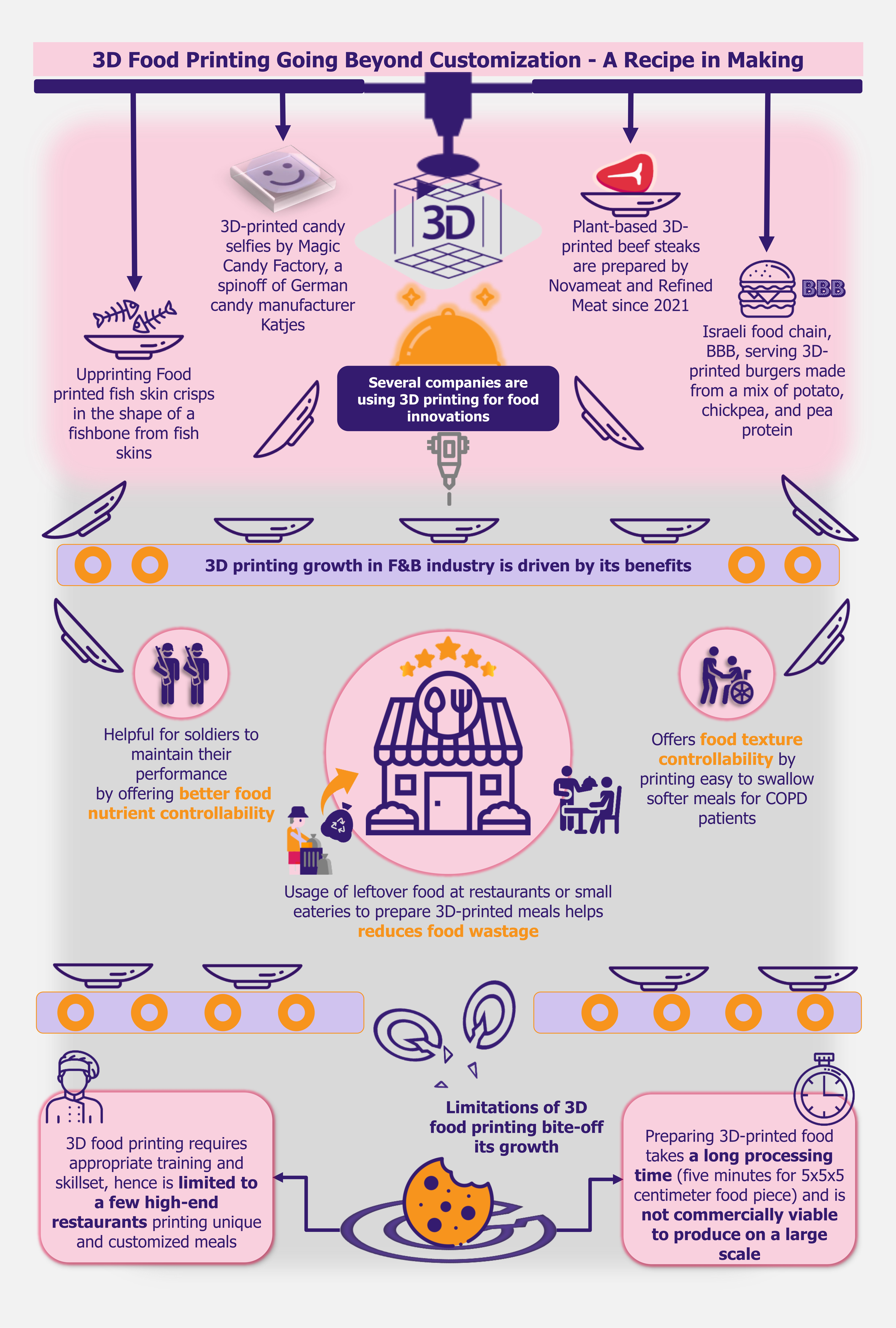
Traditionally, 3D food printing has been used to architect intricate shapes and designs that are difficult to achieve manually. It has been mostly confined to desserts such as chocolates and sweets as 3D printing offers huge potential for customization.
That being said, there is a gradual shift to adopt this technology in preparing more complex foods such as 3D-printed pizzas, spaghetti, burgers, and meat alternatives. For instance, since January 2022, BBB, an Israeli food chain has been serving 3D-printed burgers prepared from a mix of potato, chickpea, and pea protein. Similarly, since 2021, companies such as Spain-based Novameat and Israel-based Redefine Meat have been preparing 3D-printed beef steaks and other products using unique plant-based compounds that taste like blood, fat, and muscle that make up traditional meat flavors.
Printing beyond customization
While currently the main advantage of 3D printing in food is its ability to customize complex shapes and designs (thereby making it popular for creating chocolates, cakes, and cookies), it is also extending to customizing the level of nutrients in a meal. 3D printing offers the possibility to produce high-quality food concepts such as developing personalized meals by adding specific nutrients or flavors, ultimately giving more control over the food’s nutritional and flavor value.
With this idea in mind, a Netherland-based Digital Food Processing Initiative (DFPI) is testing this concept and trying to come up with a flexible food production system using 3D printing technology that will allow personalizing food at any time based on individual dietary choices. The collaboration is an ongoing project between the Dutch institution, Wageningen University & Research (WUR), global food and beverage companies GEA Group, General Mills, Tate & Lyle, and pharmaceutical company Solipharma B.V., together with Ministerie van Defensie, and a Netherland-based research organization, TNO, whose aim is to bring commercially viable personalized food products to the market, especially for military personnel and COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) patients.
Another potential use of 3D printers is to reduce food wastage. The Netherland-based food-tech startup, Upprinting Food, which specializes in recycling organic food waste through 3D printing, has offered design services to various chefs and is also training restaurants to utilize their 3D printers to reduce food wastage. The company specializes in creating dishes out of any food left at restaurants and currently focuses only on high-end restaurants. They plan to expand their work towards retail and wholesalers in the future to reduce food wastage on a larger scale.
While 3D food printing seems to have a lot of unique uses, commercializing 3D-printed foods on a large scale has always been a challenge. For instance, printing a small piece (5x5x5 centimeter) of a food item takes around four to five minutes. Thinking about producing large-scale printed food would be difficult at this rate. In 2015, a project called the PERFORMANCE project (PERsonalized FOod using Rapid MAnufacturing for the Nutrition of elderly ConsumErs ) was shut down because it could not produce at a scale large enough to provide meals at nursing homes. The project focused on creating customizable meals for the elderly who had difficulties in chewing and swallowing. Thus, while customization of food products has immense use and strong growth potential in theory, it still needs a lot of work on improving speed and costs to facilitate its commercialization and feasibility.
Despite several advantages and functionalities, the market does not seem to use 3D printers for printing food as much as it could. It is mostly limited to confectionaries and very high-profile restaurants where quantities are small and prices are high. For instance, Natural Machines 3D printer, Foodini, is being used at Spain-based Michelin-star restaurant, La Enoteca, to prepare seafood, where food puree is printed into a flower-like shape, topped with caviar, sea urchins, hollandaise sauce, and carrot foam.
As per industry experts, 3D printing in F&B is still at an initial stage of development and will be more accepted once people see it being extensively adopted at restaurants. For now, 3D printing can be used to produce food with unique functionalities related to shape, taste, and texture such as printed pasta shapes of unique designs as offered by Italian food giant Barilla, through its spinoff business BluRhapsody as well as 3D-printed candy selfies by Magic Candy Factory, a spinoff of German candy manufacturer Katjes.
EOS Perspective
At present, 3D printing in food is largely limited to confectionaries. It is an evolving technology that offers considerable benefits of saving time and improving efficiency. It can potentially bring other advantages to the table, including reduction of food wastage, but such applications still require more research, investment, and trials, as well as attempts of expansion across food service formats, including small eateries and larger restaurants.
A 3D printing machine requires skill and appropriate training to print a meal. 3D food printing machines may not seem attractive for personal usage at this point but several food and beverage industry players have already moved in to adopt and exploit this innovative technology for various customized and attractive food options, although still largely at a pilot or experimental scale.
Most 3D food printers currently only cater to single restaurants or personal kitchens and are not very popular. For the technology to enter mainstream use and become attractive to broader audience, the printers need to be able print at large volumes. At the moment, there is a huge gap between what could be achieved with 3D printers in the F&B space and what has been actually tested and implemented. While several companies are working towards using this technology in innovative ways, there is a large space open for market disruption.