A new era of mobile communication and data services is set to begin as telecom operators across the world are priming for roll out of 5G. As per the estimates by Hadden Telecoms, a UK-based consultancy firm, as of August 2019, 287 telecom operators have invested in 5G deployment across 105 countries. Investments span across various facets of 5G technology including ongoing 5G base-station deployment and other infrastructure development, commercial service launches, future commitments or contracts to deploy 5G networks, pilot testing and trials, and research studies. As 5G seems to be an inevitable leap to the future of internet technology, the pressing question for telecom operators is how they can monetize the 5G opportunities.
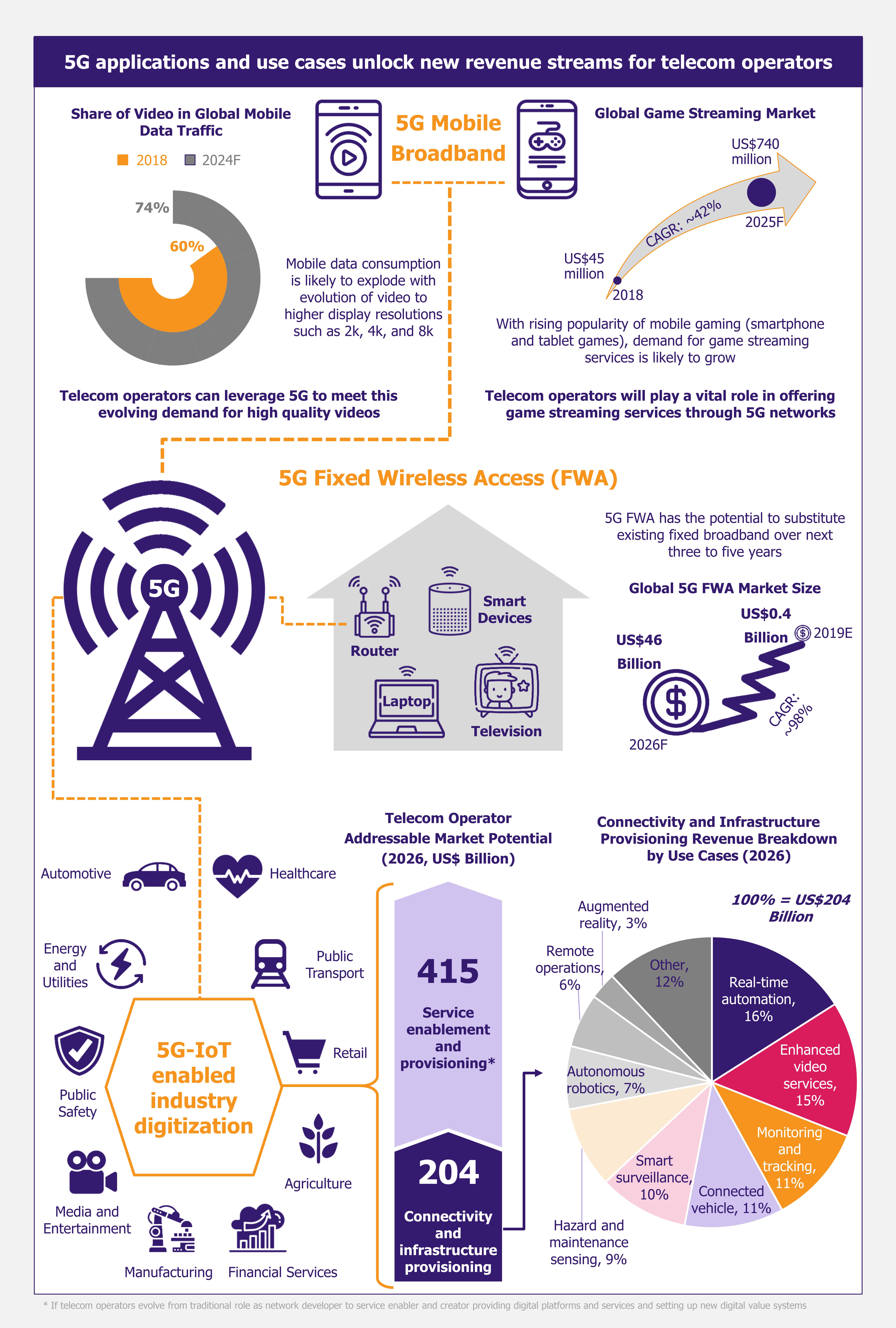
5G mobile broadband is expected to become the key driver of revenue growth in consumer segment
Telecom operators will be primarily banking on 5G-enabled high-speed mobile broadband which is a natural progression from 4G mobile broadband internet services. An annual industry survey (2018), conducted by Telecom.com Intelligence – an information source for global telecom industry, indicated that 45% of the respondents (i.e. 1,500 telecom industry professionals across the world) recognized mobile broadband as the 5G service with greatest commercial potential. Based on 35,000 online interviews conducted with people across 22 countries in May 2019, Ericsson estimated that, with 5G, the average monthly mobile data consumption will increase 10 -14 times. Rising demand for data-intensive applications offering high quality video viewing and immersive gaming experience will be the key impetus for 5G mobile broadband.
5G to make dream of high-quality video streaming come true
Video accounts for the lion’s share of telecom operator’s network traffic today and it is likely to become the key driver of 5G mobile broadband service. Based on survey of 30 telecom operators across the world, Openwave Mobility (a mobile data traffic management solution provider) indicated that video on mobile broadband has registered average growth of 50%-60% year-on-year during 2014-2018. In many developing countries, this growth was over 100%. As per Ericsson’s estimates, video’s share in global mobile data traffic is forecasted to rise from 60% in 2018 to 74% in 2024, witnessing a 35% growth annually.
The growth in mobile video from 2010 to 2015 was attributed mainly to increased watch times. Interestingly, since 2015, growth in mobile video was mainly driven by consumer’s move towards high definition (HD) content. Further, video is expected to evolve from HD to higher display resolution such as 2k, 4K, and even 8K in the future. HD video consumes about 0.9GB per hour, while 2k and 4k would consume about 3GB and 7GB, respectively, thereby demanding higher bandwidth capacity and speed – which only 5G will be able to fulfil. This is because 5G is expected to be 100 times faster and have 1,000 times more capacity than 4G, thus enabling smooth streaming of 4k or 8k video without any buffering or lag. 5G will also become backbone for emerging technologies such as 360-degree video, virtual reality, and augmented reality.
5G will push for convergence of communications and media, opening up new avenues for telecom operators by integration of video content and media into their offerings. For instance, in May 2019, US-based telecom operator Verizon hinted that partnerships with content providers such as NFL, The New York Times, and YouTube TV, are part of the company’s 5G video strategy.
Anytime, anywhere gaming gets closer to reality with 5G
Just as 4G enabled video streaming services to go mainstream, 5G is expected to do the same for game streaming (also known as cloud gaming, meaning the game runs on a cloud platform instead of consumer’s devices). As per estimates of Newzoo, a gaming research company, the global gaming market is expected to reach US$152.1 billion in 2019, out of which 45% i.e. US$68.5 billion will be generated from mobile gaming (games on smartphones and tablets). This indicates that smartphones and tablets have already become most commonly used devices for gaming. 5G is expected to push mobile gaming to a next level by enabling game streaming. This is because 5G’s low latency (i.e. time taken to upload data from consumer’s device to target network) will allow consumers to stream games with virtually no lag. Currently, with 4G technology, the average latency is about 50 milliseconds (ms) because of which the response time between player-cloud server-player is too long. But latency could be reduced to 1ms with 5G, thus providing uninterrupted gaming experience to the players.
With advent of 5G, majority of the leading game developers, including Nvidia, Sony, Microsoft, EA, and Google, have already launched or plan to include game streaming as a part of their service offerings. The game streaming market is expected to grow at CAGR of 41.9% during 2019-2025, to reach US$740 million in 2025 from US$45 million in 2018. Telecom operators could tap into this growing demand for game streaming by partnering with game developers. For instance, in March 2019, Nvidia’s CEO indicated that the company will cash in on delivering game streaming service via telecom operators’ 5G offering and in return, telecom operators will get to keep more than half of the gaming subscription fee collected from the players (i.e. consumers). Such partnerships are already seen to be materializing; for instance, in September 2019, SK Telecom (South Korea’s largest telecom operator) paired up with Microsoft to deliver xCloud (Microsoft’s game streaming service) in South Korea over its 5G network.
5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) provides telecom operators with scope of market expansion
While 5G mobile broadband provides internet connectivity to smartphones, 5G FWA offers wireless broadband to homes and businesses through 5G networks. 5G FWA is expected to be a better alternative to fixed wired broadband including DSL (Digital Subscriber Line – internet delivered through existing copper telephone lines), cable (internet provided by cable operators through coaxial cables), and FTTH (Fibre-to-the-Home – the latest broadband technology using fibre optic cables). In January 2019, CEO of a US-based telecom operator AT&T emphasized that 5G FWA will evolve as a replacement product for existing fixed broadband over next three to five years.
5G FWA will be able to compete head on with fixed broadband. 5G FWA can provide faster speed and higher bandwidth, while also remaining more cost-effective compared to fixed wired broadband. To be specific, an article published in October 2018 on Inside Tower, an information source for wireless infrastructure industry, indicated that total capex per subscriber to deploy FTTH was about US$2,000-US$2,500, while 5G FWA capex could be estimated at US$1,000-US$1,500 per subscriber (representing nearly 50%-60% cost reduction over FTTH). Earlier, in August 2017, a Dubai-based research firm SNS Telecom estimated that 5G FWA can reduce the initial cost of installing last-mile connectivity by 40% when compared to FTTH.
Explore our other Perspectives on 5G
5G FWA is expected to become one of the first commercial use cases of 5G technology. SNS Telecom estimates 5G FWA revenues to reach US$1 billion globally by the end of 2019, and the market is forecast to grow at a CAGR of over 84% between 2019 and 2025, to reach US$40 billion in 2025. Another research firm MarketsandMarkets predicts that the global 5G FWA market will grow from US$396 million in 2019 to US$46,366 million by 2026, at a CAGR of 97.5% between 2019 and 2026.
Push for industry digitization by leveraging 5G-IoT technology opens up new market opportunities for telecom operators in business-to-business (B2B) segment
Digital transformation driven by 5G-enabled IoT applications is the key focus for most industries including automotive, healthcare, media and entertainment, retail, energy and utilities, manufacturing, agriculture, public transport, public safety, and financial services. Based on analysis of 400 digitization use cases from ten industries (mentioned above), Ericsson in association with Arthur D. Little (a management consultancy firm) released a report in October 2017 suggesting that the connectivity and infrastructure provisioning to enable industry digitization is expected to generate US$230 billion in 2026. Telecom operators, in their traditional role of operating network infrastructure, have the potential to address 89% of connectivity and infrastructure provisioning opportunity, representing US$204 billion in revenues. As per the Ericsson report, the telecom operators’ potential business from connectivity and infrastructure provisioning is anticipated from number of use cases including real-time automation, enhanced video services, monitoring and tracking, connected vehicle, hazard and maintenance sensing, smart surveillance, autonomous robotics, remote operations, and augmented reality, among others.
Further, many telecom operators are expected to evolve from being network developers to service enablers providing digital platforms catering to industry-specific digitization requirements. Service enablement to address industry digitization is forecast to generate US$646 in revenues in 2026, of which telecom-operator-addressable share is estimated at 52%, translating to US$337 billion.
Moreover, telecom operators also have the opportunity to take on the role of a service creator by developing new digital service and setting up new digital value systems. In this role, telecom operators have the potential to earn US$79 billion in 2026 (representing 18% of the total revenue generated through application and service provisioning).
Thus, if telecom operators partake in every step of industry digitization value chain by adapting the role of a network developer, service enabler, as well as service creator, the total addressable revenue opportunity from industry digitization could reach US$619 billion in 2026.
EOS Perspective
Traditionally, telecom operators’ business model revolved mainly around providing voice and data services to consumers. Advent of 5G will not only allow telecom operators to unlock new revenue streams in consumer side of business but also expand the addressable market to B2B space.
The onset of 5G will enable telecom operators to explore new use cases and develop corresponding service offerings. For this, telecom operators will need support and cooperation from different players across the ecosystem.
Telecom operators will need to collaborate with application developers, device manufacturers, as well as third-party technology solution providers to co-create services as per the requirement of specific industries. Ericsson research report (based on survey of 50 executives working with 37 telecom operators globally), released in 2017, pointed out that 77% of the respondents believed that third-party collaboration would be vital in monetizing 5G. Realizing the importance of industry collaboration to cultivate commercially viable 5G use cases, most of the leading telecom operators have started building their partnership network. For instance, Japanese telecom operator NTT Docomo indicated that total number of partners in its 5G Open Partner Program (launched in 2018) reached 2,700 by June 2019.
Further, telecom operators will need to modify and tailor their offerings to address the evolving consumer demands and expectations. To be successful, telecom operators will need to strive to develop and offer a complete solution to the consumers. For instance, 74% of the 35,000 respondents (that participated in Ericsson survey in May 2019), indicated that they find the idea of moving away from cable TV and shifting to 5G FWA bundled with 5G TV services very appealing. In view of this, most telecom operators are experimenting with bundling strategy, starting with inclusion of streaming services as a part of their package. Ovum estimates that streaming services (including, video, live sports, music, and game) billed through 5G network bundles offered by telecom operators will grow from US$6 million in 2019 to US$4.87 billion in 2024.
Moreover, telecom operators will need to develop completely new revenue models for enterprises. Telecom operators may adopt a business model widely used by consultants, wherein they can collaborate with enterprises for specific projects and receive a one-time fixed fee or share of project-associated profits or cost savings. Or, like application developers, telecom operators can develop standard solutions for specific industries and adapt licensing model permitting enterprises to integrate the solution into their end-product or subscription-based model allowing the enterprises to use the solution for a specific period of time.
5G’s functionalities and characteristics entice telecom operators to develop new use cases and capitalize on corresponding revenue opportunities. However, the use cases, particularly in enterprise segment, still need to stand the test of practicality and commercial viability. Though 5G offers plethora of opportunities for the telecom operators, it is advisable to focus on a few business cases that best fit to their capabilities and develop the ecosystem (including application developers, device manufacturers, and third-party solution providers) required to take the final solution to prospective consumers.