Robotic-assisted surgeries, being minimally invasive, have been an excellent alternative for conventional open surgeries for quite some time now. Surgical robots use small incisions with broader 3D visualization of the operating area and precision-guided wrist movements. Players in the industry aim to develop solutions that combine medical device technology with robotic systems to provide patients with rapid post-surgery healing and reduced trauma. As surgeons perform an increasing number of procedures worldwide using these robots, the surgical robots market is growing along with the popularity of minimal-invasive surgeries.
Robotic-assisted surgeries have been rapidly adopted by hospitals in the USA, especially since 2000, when the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the da Vinci Surgery System by Intuitive Surgical for general laparoscopic surgeries.
The system excelled its predecessors, such as PUMA 560 robotic surgical arm, which was used for non-laparoscopic surgeries in the late 1980s, by its 3D magnified high-resolution imaging and one centimeter diameter surgical arms to move freely inside the operating area.
These and other variants of surgical robots started to enter the market, enabling surgeons to operate complex minimally-invasive surgeries with improved precision, superior operative ergonomics, enhanced adroitness, and visualization compared to traditional laparoscopy.
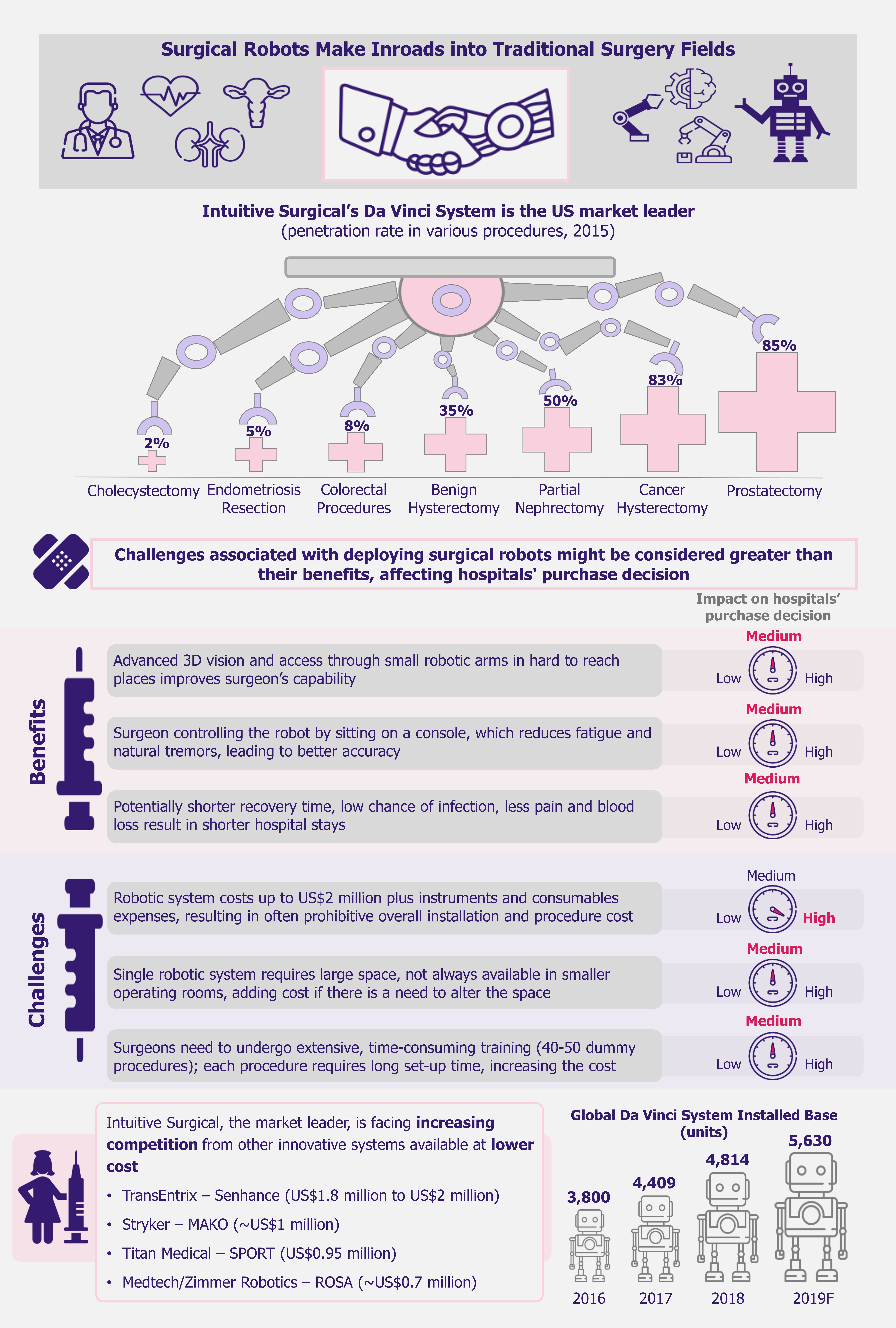
Robotics adoption focused on selected specialties
Even though robotic surgeries have been performed for quite some time, are still in the early stages of adoption in surgeries.
The adoption rate of robotic systems is uneven across various specialties with most robotic surgeries being performed in urology, gynecology, and general specialties. These fields also enjoy the fastest rate of adoption, example of which has been found in a 2017 study, in which researchers at Stanford University School of Medicine (California) analyzed data compiled by 416 hospitals on kidney removal procedures from 2013 to 2015. According to the study, robotic-assisted surgeries accounted for just 1.5% of all kidney removal surgeries in 2013, ration that increased to 27% by 2015.
Competition strengthens, challenges the market leader
In 2017, according to international market research and consulting firm, iData Research, surgical robotic systems market was valued over US$2.4 billion with over 693,000 robotic-assisted procedures performed in the USA alone. US-based Intuitive Surgical has long dominated the robotic surgery market with more than 4,800 da Vinci units installed around the globe, and approximately 877,000 surgical procedures performed with the da Vinci Surgical System in 2017. Intuitives’ da Vinci System is the only surgical robotic system which has been approved by FDA for various surgeries in gynecology, urology, cardiothoracic, thoracoscopic, and general surgeries.
In comparison, Intuitive’s competitor TransEntrix’s Sehnhance Robotic Surgical system received a nod from FDA in 2017 specifically for inguinal hernia and gall bladder removal laparoscopic surgeries, while also in the same year a robotic system for spinal surgeries, Mazor X by Mazor Robotics received FDA clearance.
Though Intuitive Surgical is the market leader, other players are not far from getting their products FDA-approved, a fact that has the potential to affect Intuitives’ leadership position.
Cost remains the main challenge for adoption
One major challenge for the robotic systems manufacturers is to convince hospitals to purchase their systems costing millions. For instance, a single da Vinci Surgical System costs around US$0.5 million to US$2.5 million, with additional disposable instruments whose costs range from US$700 to US$3,500 per procedure. Apart from the initial cost, there are other associated costs such as installation, service, and training fees that a hospital has to bear.
Players in this market started to realize that in order to strengthen their position and competitiveness, cost-effectiveness of their systems is the key requirement. Recently, several companies have increased their focus on developing cost-effective surgical robots, attempting not to compromise system’s performance.
Players in this market started to realize that in order to strengthen their position and competitiveness, cost-effectiveness of their systems is the key requirement
Examples of products competing on cost-effectiveness include Titan Medical’s SPORT surgical robotic system that is designed to perform various surgeries such as gynecology, urology, and general surgeries. At the outset, the system costs approximately US$0.95 million (da Vinci: ~US$1.8 million). Further the company claims the robotic system is cost-effective by driving down annual service and per procedure cost by increasing the number of times its disposable and reusable components can be used for various surgeries.
The market leader, Intuitive, also understands the costs pressures and has already established its presence with its low-cost robotic surgical system, da Vinci X, that costs approximately US$1.42 million, which is around US$780,000 cheaper as compared with Intuitive’s most advanced surgical robotic system da Vinci Xi which comes at a price of around US$2.2 million.
Other players are also entering the space, with Alphabet (Google) partnering with Ethicon (a subsidiary of Johnson and Johnson) to manufacture lower-cost surgical robot, planning to introduce it into the market by 2020.
Hospitals’ limited budgets trigger simpler products development
Considering that cost burden is the key challenge to robotics adoption even in large healthcare institutions, small hospitals are generally completely outside of the potential customer base, due to far lower budgets they have to work with.
At the same time, small hospitals feel the pressure to retain surgical patients, and in that they often want to turn to robot-assisted laparoscopic surgeries. As a result of this need paired with limited budgets, certain low-cost substitutes start to arrive to the market, at times indirectly challenging systems offered by the leading players in this area.
Examples of this include Olympus’ ENDOEYE FLEX 3D camera system and FlexDex, tools used for minimally invasive surgeries that allow for wristed-laparoscopy, giving robot-like dexterity without computers and no annual maintenance services.
According to a case presented at SAGES’ World Congress of Endoscopic Surgery in 2018 by Dr. Kent Bowden from Munson Cadillac Hospital, USA, contribution margin (portion of hospital revenue remaining after the variable cost to pay off hospital salaries, service contract, and other fixed costs) for a ventral hernia using da Vinci was US$ 8 per procedure while when using FlexDex it was US$2,605. For an inguinal hernia the contribution margin using da Vinci ranged from US$596 to US$698 whereas by using FlexDex, hospital contribution margin increased to US$1,601-US$1,115 per procedure.
Another example of such a substitute system is the FreeHand robotic arm produced by UK’s OR Productivity. FreeHand is a system that allows the surgeon to hold and control the laparoscope using his own head movements and a foot pedal. The system was developed to provide a range of benefits (stable image, reduced staff count, high precision) at an affordable installation and running cost. The producer promises a fixed per-procedure cost, whose rough estimation points to around US$197 per procedure (unachievable for procedures conducted with advanced systems).
It is clear that these simpler systems are not able to fully replace the higher-end products. However, these substitutes claim to be dexterous, cost-effective robotic solutions sufficient for certain procedures, thus can be perceived as an alternative (and competition) to expensive robots in some cases.
These substitutes claim to be dexterous, cost-effective robotic solutions sufficient for certain procedures, thus can be perceived as an alternative (and competition) to expensive robots in some cases
Robotic surgeries offer many advantages both for surgeons and patients, however, the equipment comes with certain challenges and limitations, which, apart from cost, include increased operating time in some cases, lack of tactile feeling for the surgeon, large space requirement, and long set-up time required for the robotic system. Having said that, cost-effectiveness is (and will continue to be) the main challenge players face while developing and marketing their systems.
EOS Perspective
Advancements in surgical robots are emerging by adding intelligence into the robotic systems with refined haptic feedback and versatility in robots’ arms. Companies are diving deep in this industry by improving their products and coming up with next-generation surgical robotic systems that could perform different types of minimally invasive surgeries.
Nevertheless, huge investment is needed for development of advanced and multi-skilled robots. Gaining investment for such projects is difficult, hence for the time being, it can be expected that the existing players are likely to consider forming partnerships to improve their products and increase their market share.
Gaining investment for such projects is difficult, hence for the time being, it can be expected that the existing players are likely to consider forming partnerships to improve their products and increase their market share
On the other hand, the market might see arrival of new systems based on existing technologies and solutions. They can be sourced from several of Intuitive’s patents that expired in 2016. These included some basic robotic concepts implemented in the robotic system, such as robotic arms control and imaging functionality. Several other patents developed by the company are expected to expire by 2022 (under the US patent law, a solution is protected for a relatively short period of time, generally 20 years).
Such availability of patent-free solutions will encourage other players in the industry to enter the market with similar products, probably at lower price points. This is likely to intensify the competition, which is already tightening, as Senhance robotic systems by TransEntrix got FDA received approval in 2018 for hernia repair and gallbladder removal, while SPORT by Titan Medical is expecting its approval in 2019, giving competition to da Vinci. Furthermore, a new partnership by Google and Johnson & Johnson is on the horizon, likely to bring some form of cost-effective alternative to the existing, more expensive systems, further adding pressure on the solutions offered by existing players.
Such availability of patent-free solutions will encourage other players in the industry to enter the market with similar products, probably at lower price points
The outlook for the robotic systems looks promising with mergers and partnerships among players that could drive innovation in this industry. Collaborating with hospitals to invest in training and application of robotic systems in growing number of procedures should also remain in the competitors’ focus area, as high number of robot-assisted procedures performed regularly provides opportunities for increasing the cost-efficiency and generating revenues that could be directed towards further R&D.
Players in the market need to focus on such high-volume procedures that will be likely to ultimately increase their sales, and allow them to focus on improving their products to deal with current challenges such as cost-effectiveness, limited portability and complex controls of the robotic systems, improving of which can help producers gain a competitive edge.
However, the players in this industry also need to identify new growth avenues – targeting areas where traditional laparoscopic surgeries are still predominantly performed but where robotic assistance could find its place, such as in colorectal and cholecystectomy procedures. There is still a considerable space in the market with opportunities. They can be tapped by putting emphasis on continuous investment in R&D aiming to innovate and develop new solutions that would find application in under-served therapeutic areas or offer new functionalities in order to cover as many therapeutic subsegments of the market as possible.