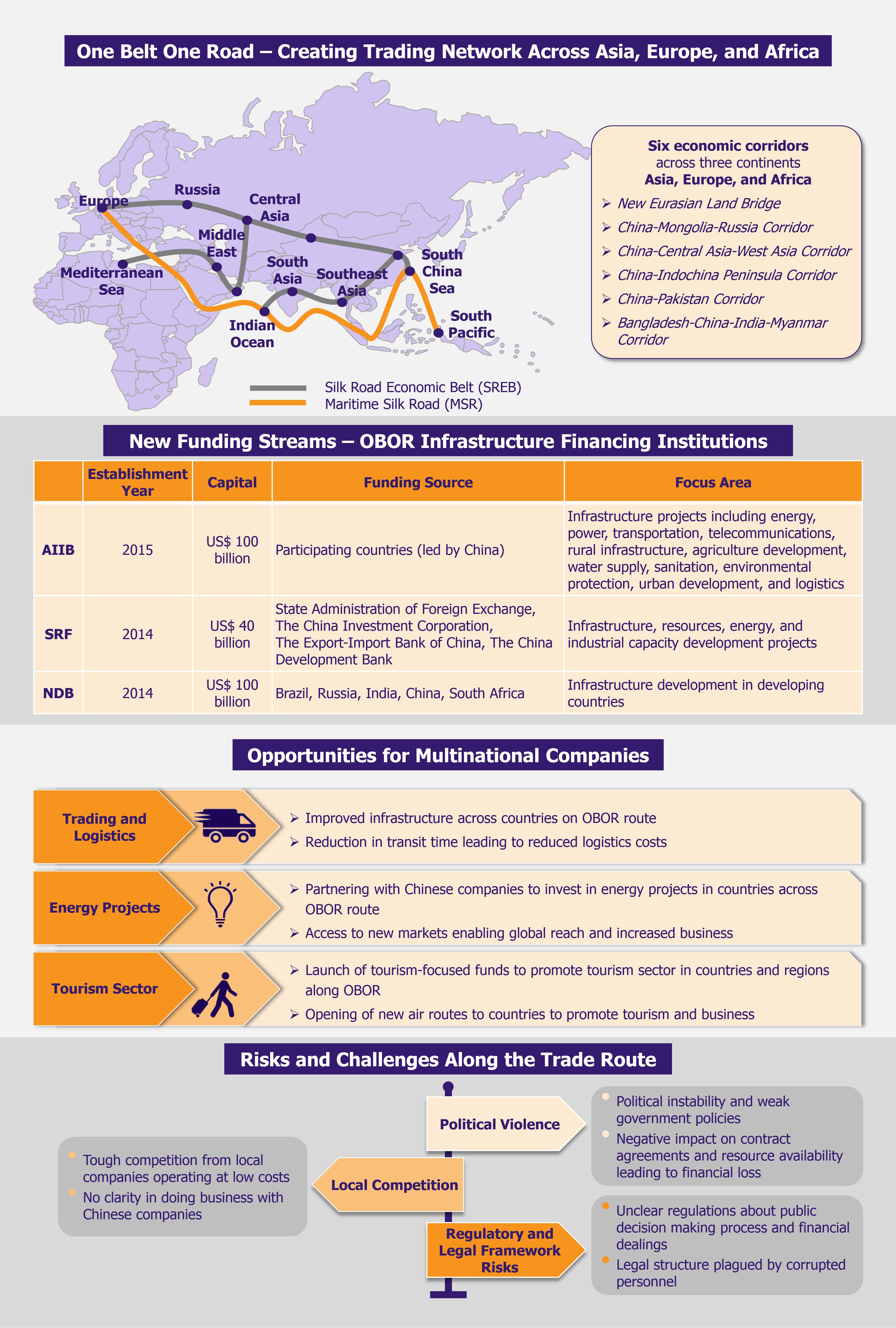
Connecting nearly 70 countries through an extensive land network and sea routes across Asia, Europe, and Africa, the One Belt, One Road (OBOR) Initiative is the focal point of China’s foreign policy that is publicized as providing various economic developmental opportunities. Proposed by China’s President, Xi Jinping, in September 2013, the action plan and framework of the OBOR, also known as Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) was officially presented in March 2015. Since the unveiling, the initiative has gained huge momentum in certain parts of the world. Africa is one such region that has witnessed major infrastructural development across road and rail network, telecommunication, and energy sectors in the early stages of BRI.
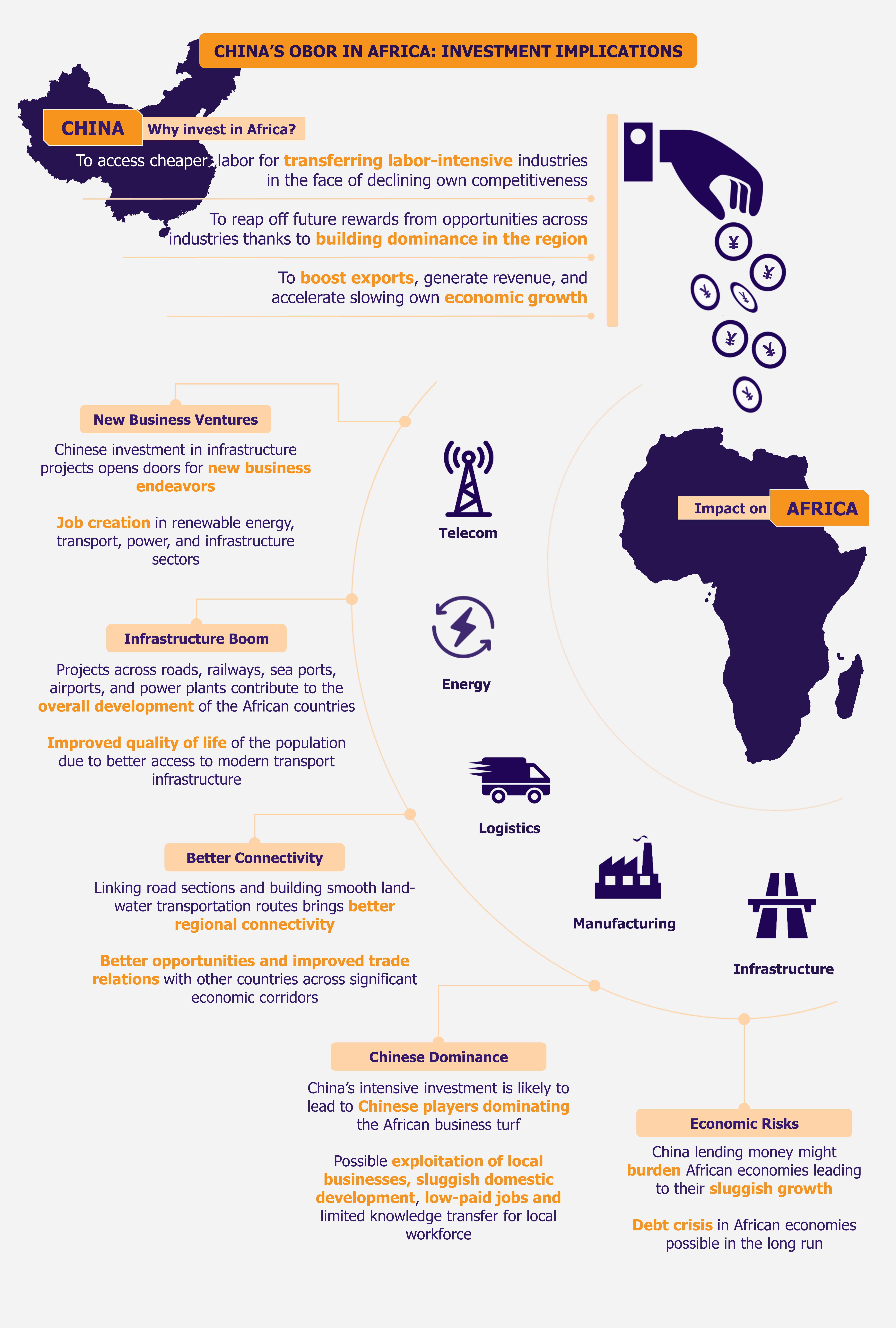
Africa is keen on receiving investment from China to boost its economic development. Owing to its location, the continent, as such, is placed perfectly on the sea route as part of China’s global plan. Although the continent lies on the Maritime Silk Road, the sea route that connects Indian Ocean to Suez Canal via Red Sea, only few African countries are of direct strategic importance to China along the OBOR route (including Egypt, Kenya, Tanzania, Ethiopia, and Djibouti). However, in its growth strategy, China is involved in several projects to increase its presence across other African nations as well.
Focus on strategic sectors
China is focusing intensely on infrastructure projects in the initial years of this initiative, as strengthening the railway and road network across the countries and developing sea ports is crucial for the success of the project. However, the expansion plans are not only limited to logistics. China is also investing heavily in other sectors, such as energy, mining, and telecommunications.
Logistics and industrial zones
China is involved in a number of mega infrastructure projects in Africa. Railway projects rolled out by Chinese companies across Africa are amongst the ones (along with road network and sea ports projects) that have gained momentum in terms of execution and become operational ahead of scheduled time. The Mombasa-Nairobi Standard Gauge Railway (Madaraka Express) in Kenya at a cost of US$3.2 billion, built by China Road and Bridge Corporation (a Chinese state-owned construction and engineering company) and funded by China Exim Bank (90% funding by the bank and remaining 10% by Kenya government) connecting Mombasa to Nairobi, became operational in June 2017 (construction of the railway line began in January 2015) as against the timeline of four years. In due course, the line will link Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, and South Sudan to Ethiopia’s Addis Ababa Light Rail Transit (AA-LRT) built by China Railway Group Limited, a Chinese construction company. Initiatives such as this, when married with port connectivity across sea-based countries, will not only improve trade amongst nations within the continent but will also boost Africa’s commerce market by opening new trade routes with other continents.
Some of the railway projects initiated by China were planned long before OBOR came to play, however, they could still form a crucial part of the initiative. For instance, the Tanzania-Zambia railway line built in 1970 with the technical and financial aid from China, is now being revived again with the help of Chinese companies Plans are underway to link it with other ports and build an industrial economic belt along the railway line to utilize the line more effectively. Chinese government has given Tanzania-Zambia Railway Authority (TAZARA) a US$22.4 million interest-free loan to not only improve the operations but also to extend the line to other countries that include Malawi, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Rwanda, and Burundi. This line is of strategic importance to China in terms of better connectivity, which could lead to improved trade partnerships in the future, as this is the only railway line in Africa that connects three economic blocs, namely East African Community, Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA), and Southern African Development Community (SADC).
China is effectively planning for future stability of its position in the continent, as evident from its plan to build Africa’s largest free trade zone in Djibouti, considered as China’s gateway to the continent.
China is effectively planning for future stability of its position in the continent, as evident from its 2016 announcement to build Africa’s largest free trade zone in Djibouti, considered as China’s gateway to the continent, spread over an area of 48 sq. km. The port will be built by Dalian Port Corporation Limited, Chinese largest port operator, and is expected to handle US$7 billion in trade within two years of becoming operational. About 15,000 direct and indirect jobs are expected to be created from the project. Strengthening Djibouti air transport sector is also of crucial importance to China and in light of this, two new airports – Hassan Gouled Aptidon International Airport and Ahmed Dini Ahmed International Airport – are also being set up to boost connectivity between the two countries. Funded by the China Civil Engineering Construction Corporation (CCECC), a Chinese construction engineering company, at a combined cost of US$599 million, this paves way for the country’s economic growth and development by making it a trade hub.
Telecommunications
China Communications Services Corporation Limited (also known as China Comservice), a subsidiary of China Telecommunications Corporation, is planning to revamp the original Africa Information Superhighway to Trans Africa Information Superhighway, an information and communication technology (ICT) project. The 20,000 km long optical cable is expected to pass through 48 African countries and involves an investment of US$10 billion. With growing internet penetration in many African countries (as per World Bank report, Kenya had an internet penetration rate of 45.6% in 2015 which was above the world’s average of 44%), the ICT project offers huge potential.
Mining and energy
China has already been heavily investing in energy, power, and mining sectors in Africa as part of its FDI policy, and now under the OBOR initiative the investments are expected to rise further. China General Nuclear Power Holding Corporation (CGNPC), a Chinese player that develops, constructs, and operates power plants, started mining uranium in the western-central part of Namibia in 2016. Known as the Husab Uranium Project or Husab Mine, it is amongst China’s largest projects in Africa, and has received investment worth US$2 billion, expected to produce 6.8 million kilograms of uranium oxide every year.
Although China has been investing in Africa for development of renewable energy projects, China’s focal point on the energy and power sector under OBOR initiative is still diluted. However, investments across this sector can be expected to happen in the near future owing to abundance of natural resources in the continent.
EOS Perspective
China’s OBOR initiative seems to be successfully transitioning from a theoretical plan to reality, at least within African continent. It provides developing countries across Africa what they need the most – infrastructure (roads, railways, sea ports, airports, power plants, refineries) along with supporting various other sectors such as information technology, telecom, and financial services. Apart from streamlining infrastructural development in Africa, African countries can also benefit in terms of better trade within the continent as China plans to build high speed rails, ports, and roads across the continent as indicated in the memorandum of understanding (MoU) with the African Union (AU), signed in 2015. Though this means some good news in terms of job creation, infrastructural development, and overall growth, African nations need to strategically think and analyze how they can emerge truly stronger in the run for economic development, without the threat of being increasingly dominated by the Chinese influence.
Projects undertaken as part of OBOR are of great size and offer growth opportunities, but also involve large amount of investment, long periods of construction, and associated operational risks – we wrote about it in our article OBOR – What’s in Store for Multinational Companies? in July 2017. African domestic stakeholders should wisely chalk out their approach tactics and secure participation in implementation plans when partnering with Chinese companies, in order to favor their own economic and sustainable development as well as share in benefits. Governments and local leaders of each African country will have to play an active and important role in negotiating and finalizing business terms with Chinese companies, if they want these partnerships to benefit their country and local population in the long run.
African stakeholders should secure participation when partnering with Chinese companies, in order to favor their own economic and sustainable development as well as share in benefits.
While it cannot be denied that African countries are surely bound to benefit from the OBOR initiative, it is the Chinese companies leading these projects that will reap the largest benefits as well as China that will intensify and strengthen its economic hold in the region. Starting off with successful road and railway projects in Africa, Chinese companies are going to focus on sectors such as manufacturing and real estate in the coming years. Presence of natural resources in the continent is also likely to attract Chinese players in the mining sector. And with so much investment already happening in the initial phase of OBOR, Chinese players are planning for the long haul by developing large industrial zones to avoid issues related with labor costs and tariffs.
This sudden inclination of China towards developing and helping African nations seems overwhelming. It draws attention to the fact that China may try to overpower and dominate the economic and geo-political scenario across Africa in disguise of offering the countries development opportunities. With easy loans, with no stringent clauses related to intellectual property, legal matters, and human rights policies, all of which are conditions far more attractive than those that would be offered by China’s Western counterparts, China makes sure to have an upper hand in all the projects that are undertaken as part of the OBOR initiative.
With loans from Chinese banks and projects led by Chinese companies, there is no doubt that the Chinese influence in the continent is already on the rise. While the immediate effect of growing Chinese dominance in Africa will first be realized in the countries that fall directly on the OBOR sea route (or are easily connected to these sea routes via road and rail), other regions, that are currently not on the OBOR map, are highly likely to also witness the rising control of Chinese companies in less than a decade.
It is also being speculated that if Chinese investment continues to grow at this speed, it can be expected that in relatively near future many sectors will be dominated by Chinese companies, leaving no room for African players to grow. This could lead to exploitation of African players by the Chinese side, local governments finding themselves under huge debt with Chinese banks hampering plans for domestic development, and leaving local people to deal with meaner jobs as all the high paid jobs would be retained with the Chinese – these are just a few of possible immediate repercussions, but the list might not end here.
If Chinese investment continues to grow at this speed, it can be expected that in relatively near future many sectors will be dominated by Chinese companies.
A drive such as OBOR definitely seems to greatly contribute to putting the African economy on a growth path by pouring the much needed billions of dollars to link China’s trade route to African countries through a strategized set-up of railways, roads, sea ports, and airports thus opening doors for investment in other sectors as well. In the short term, it is clear that African countries have more to gain than to lose when receiving huge investments from China as this drives the continent towards economic prosperity. But China’s intentions behind investing in developing African economies, under the disguise of OBOR initiative, might be more than meets the eye. In the long run, Africa’s economic scene may be China-dominated, not only reshaping the continents’ infrastructural and business scenario, but also initiating a new phase of globalization and development, which most of the African nations have been void off for a long time.
Amid these discussions of the extent to which African nations will let China take control in the name of growth, one thing is clear that China is a strong ally for African nations and the association can only be expected to strengthen under OBOR. Both China and Africa stand to gain from this association – China to notch up a step to reach its goal for global expansion by leaving an imprint on the continent that will be clearly visible for decades to come, and Africa, with regular investment from China, to work on the development and economic upliftment of the continent.