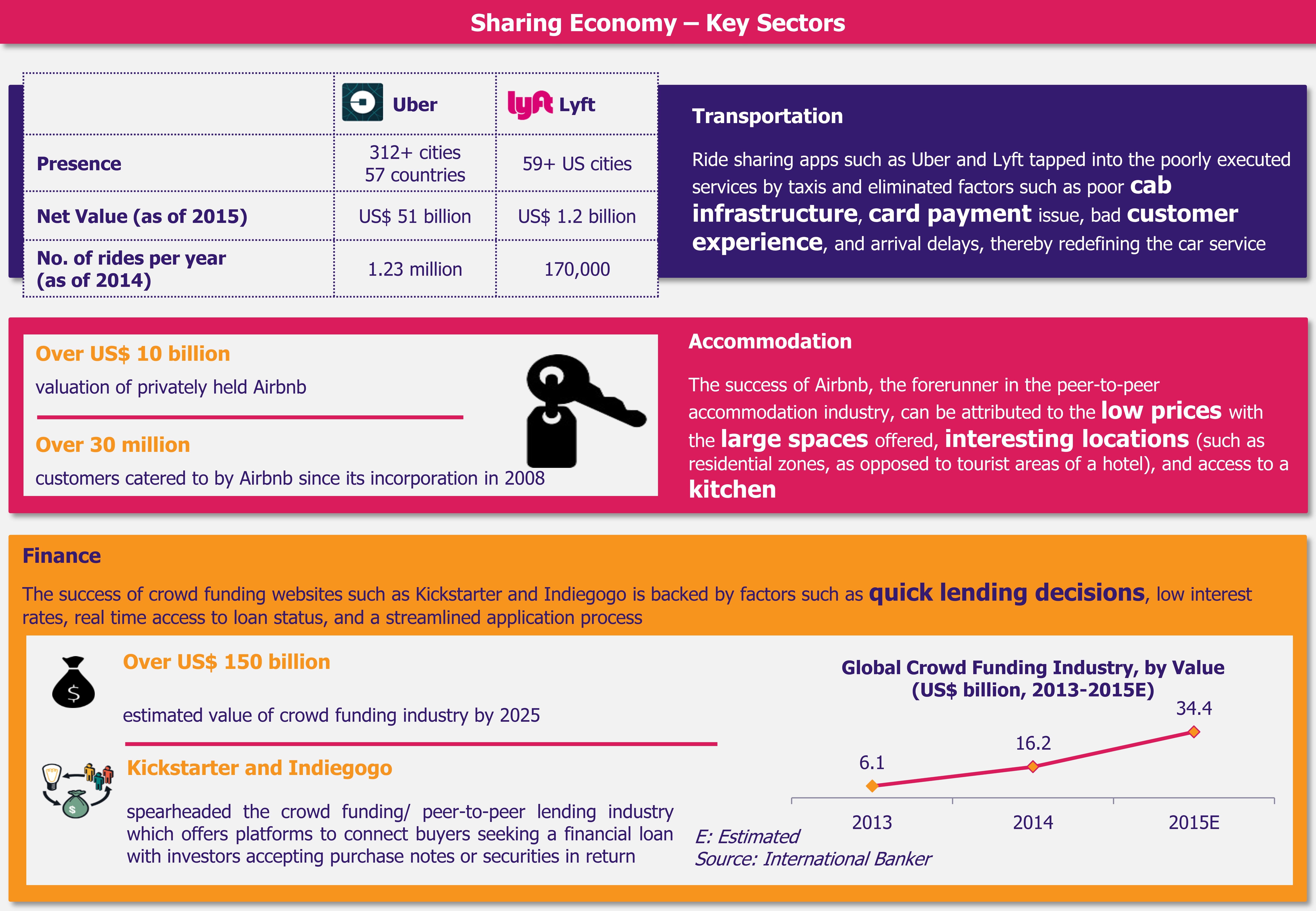
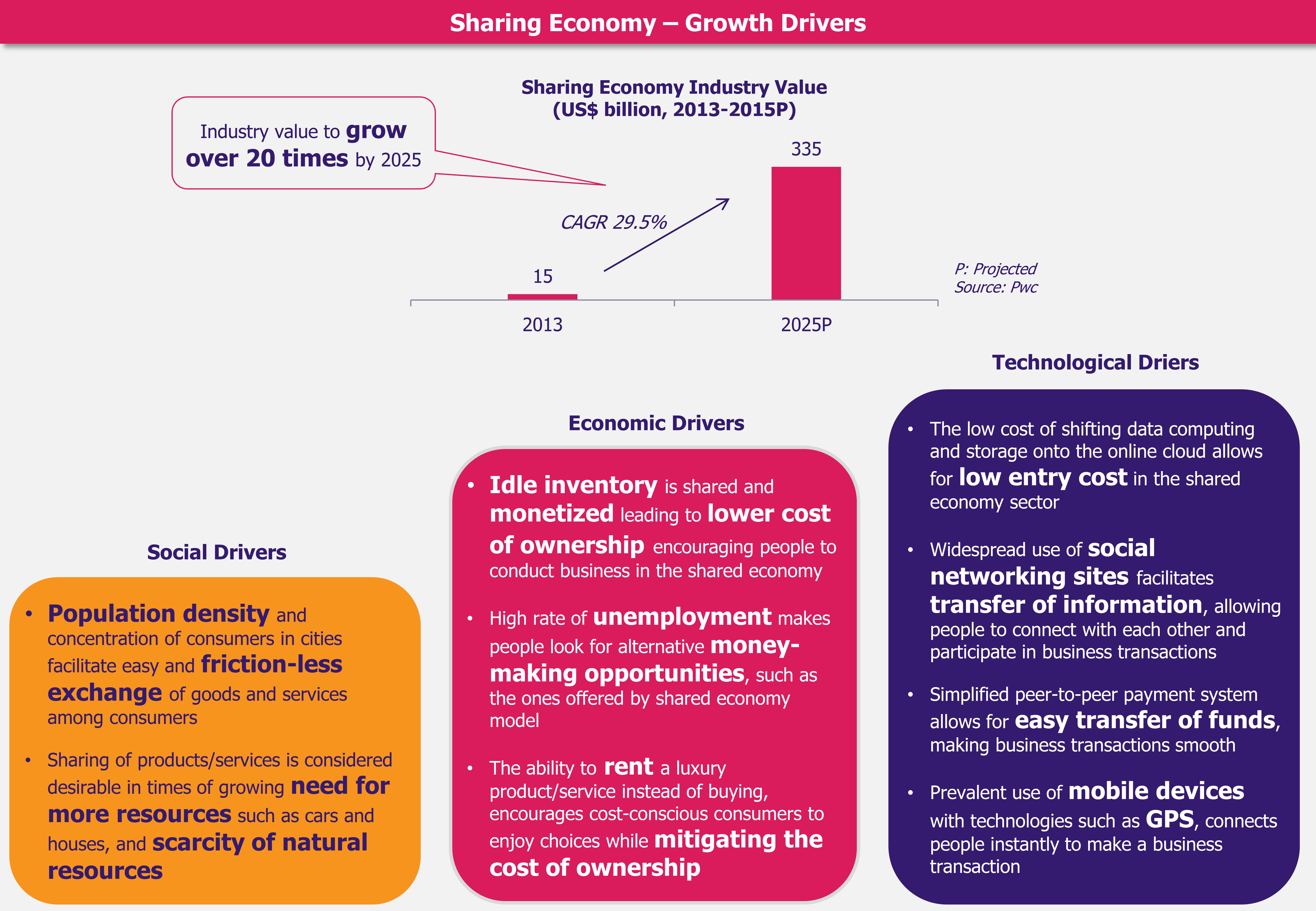
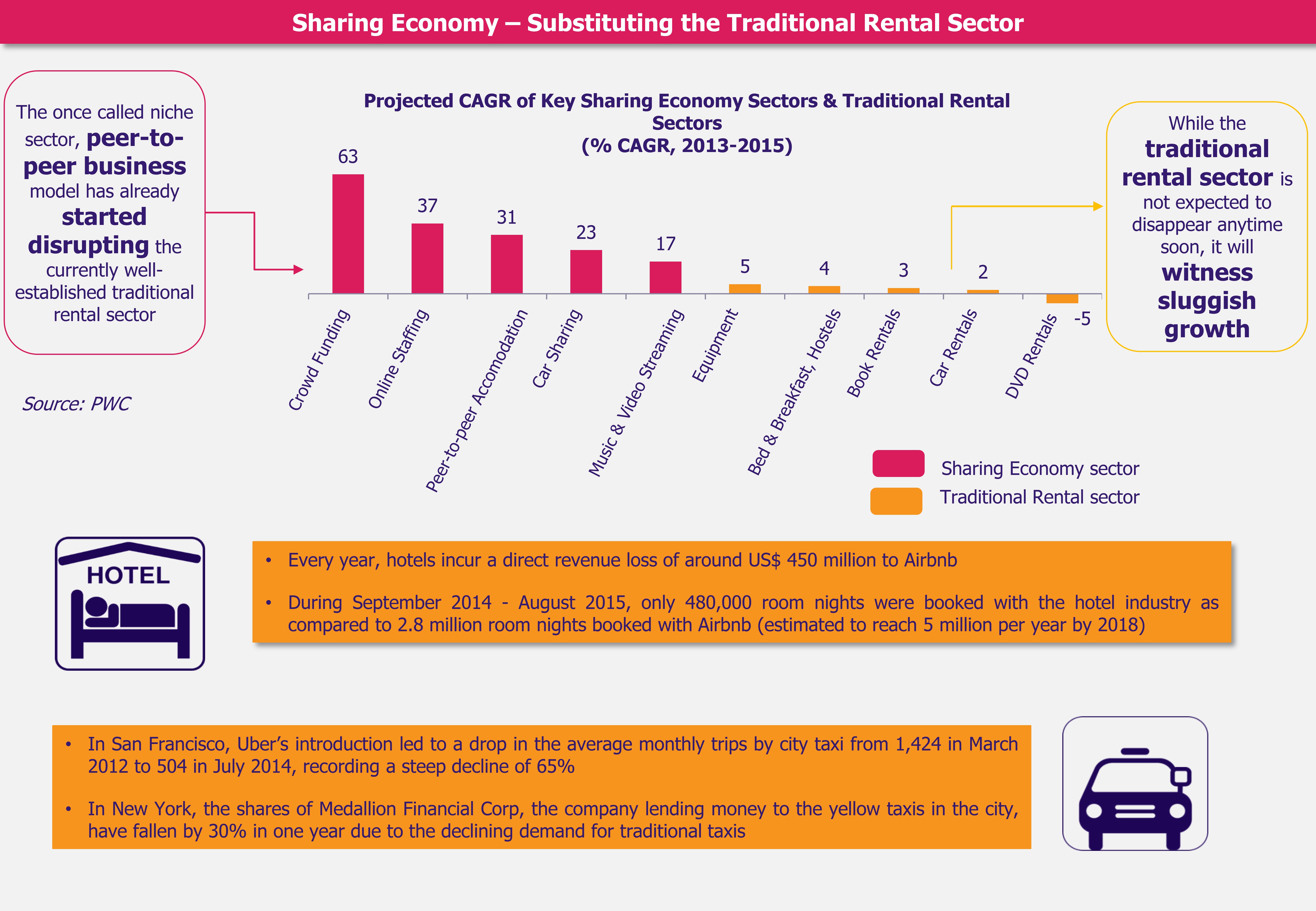
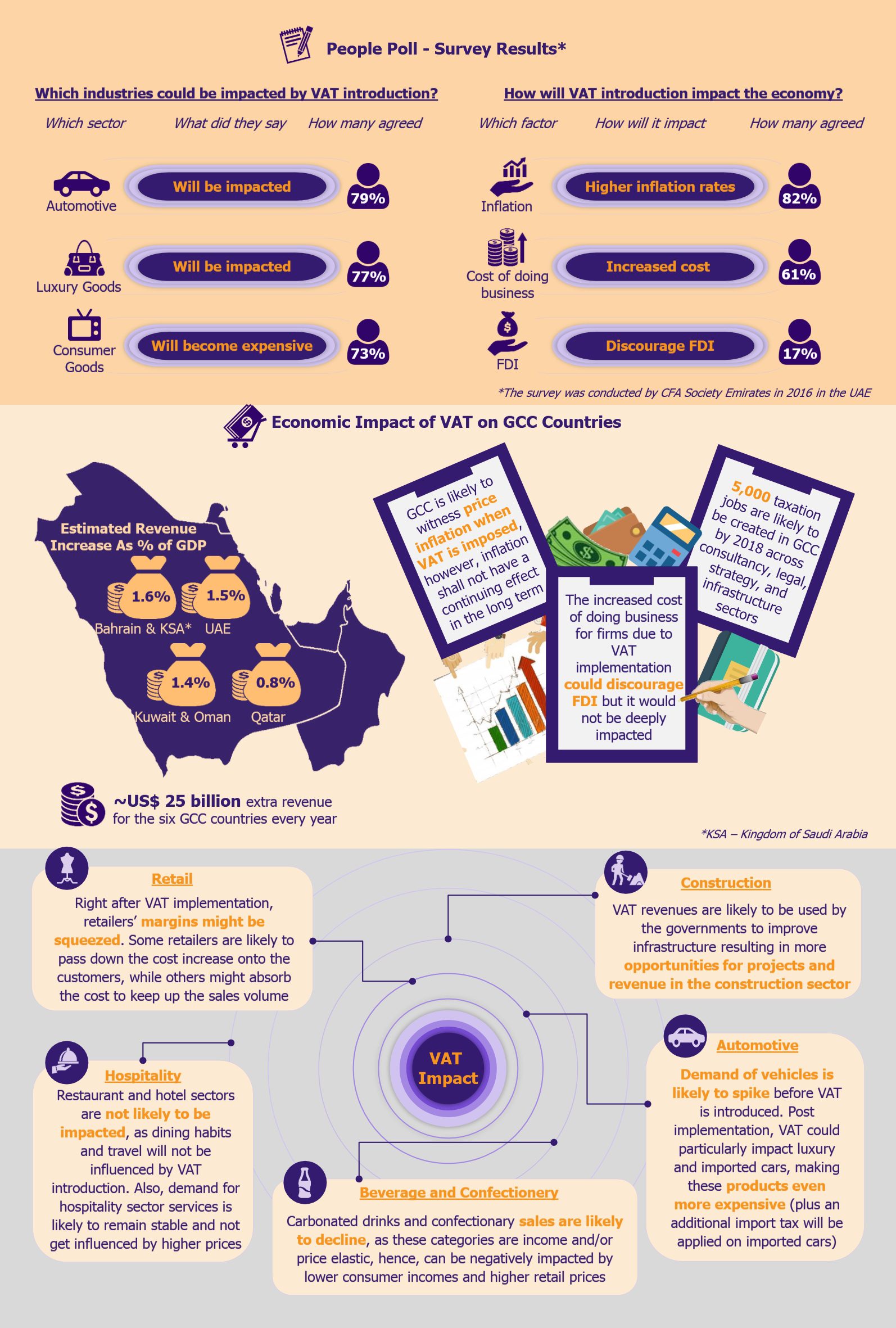
The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries are gearing towards rolling out a 5% Value Added Tax (VAT) starting January 1, 2018. Economies of GCC countries are highly dependent on the oil and gas sector revenues, which account for about 80% of the GCC governments’ budgets. The recent volatility in oil prices have battered GCC nations’ revenues, which motivated the governments to initiate a reform in the form of indirect taxation with a goal to diversify income sources. VAT is a measure that will impart more stability and robustness to the governments’ income considering the outlook for crude oil still remains volatile, while diversified revenue sources will cushion the GCC economies in times of financial crisis.
A standard rate of 5% will be applied on most products, except specified food items, domestic public transportation, and healthcare, education, and financial services. The proposed VAT rate is much lower in comparison with rates in most European countries, China, and Australia. Nonetheless, the GCC countries still stand to gain in income with the tax implementation – for instance, the UAE is forecast to generate US$3.27 billion revenue during the first year of VAT introduction.
Industries such as construction and automotive are likely to benefit from VAT implementation, while retailers might feel a pinch due to dwindling margins. The sentiment among the citizens is wary to say the least – for instance, according to a survey conducted by CFA Society Emirates, citizens of the UAE did not seem quite optimistic towards the economic impact of VAT across certain parameters such as price inflation, cost of doing business, and inflow of foreign direct investments (FDI).

EOS Perspective
Introduction of VAT could empower the GCC economies by bolstering revenue generation, aiding infrastructure development, and improving productivity levels. While some may believe that VAT implementation could tarnish GCC countries’, particularly the UAE’s, competitiveness and tax-free haven status, it is important to consider that GCC markets’ attractiveness goes way beyond only the tax benefits. GCC’s appeal also lies in developed infrastructure, competitive labor costs, lower trade barriers, and proximity to the developing Asian and African markets – implementation of a new tax reform will not change this favorable business environment.
There have been some discussions regarding the negative implications of VAT, considering residents and businesses have grown accustomed to high incomes and low deductibles for a long time. Post VAT implementation, businesses are expected to incur certain additional costs related to administrative expenses, upgrading IT systems, and training staff members, among others.
Also, highly competitive industry sectors, or those operating with thin margins are likely to witness cash flow burden, as they will be required to meet the VAT costs on purchases before they can be reclaimed from the government – in certain scenarios, when the businesses end up paying more as VAT to suppliers as compared to the VAT collected from customers, the difference can be reclaimed from public funds. The way businesses operate is likely to fundamentally transform once VAT is applied, however, with adequate preparation businesses should be able to introduce systems and processes to avoid unnecessary cost implications as well as smoothly align themselves with the new tax system.
The way businesses operate is likely to fundamentally transform once VAT is applied, however, with adequate preparation businesses should be able to introduce systems and processes to avoid unnecessary cost implications as well as smoothly align themselves with the new tax system.
VAT is not expected to have much impact on a common man, as vital household expenditure items will be exempted from it – this includes about 100 varieties of staple food items and essential services such as healthcare and education. However, for a section of the population with an appetite for luxury goods, services, and lifestyles, as well as for tourists (along with VAT, they will have to pay duty tax again on some goods in their country of origin) the brunt of new taxation is likely to be felt.
Nonetheless, a modest tax rate of 5% will ensure that certain social-economic distortions often associated with VAT are minimized. Also, the decision to exempt a few vital sectors (basic food items, and healthcare, financial, and education services) will ascertain that they are not affected by the tax reform.
VAT imposition is expected to become an essential part of GCC regions’ economic reforms and the taxation policy will immensely aid in diversification of revenue sources. Further, the pre-implementation period should be used by the GCC countries to develop a modern tax administration system that ensures compliance, so that once VAT is implemented, businesses and residents are able to smoothly adapt themselves to the new taxation policy.