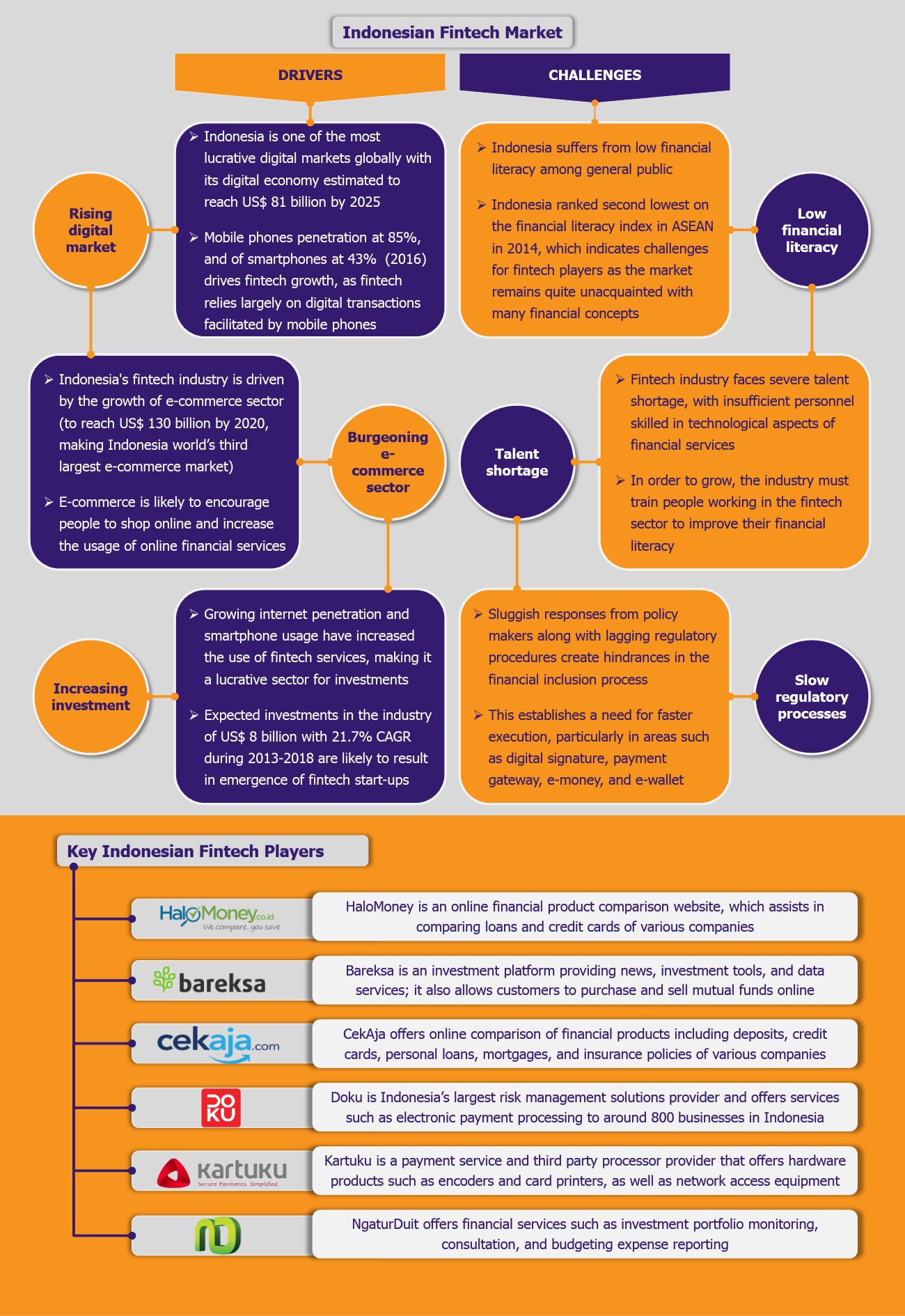
Over the past two decades, financial sector in Indonesia has witnessed a massive transformation with the introduction of fintech solutions, fuelled by growing digital market and increasing investments in the fintech market. The sector’s growth offers tremendous opportunities and has led to the emergence of various start-ups offering online financial services. Fintech promises technological solutions to various challenges within the financial sector and offers value-added services such as transaction analysis and customer engagement initiatives. However, challenges such as poor financial literacy among Indonesians and cumbersome regulatory processes continue to pose a threat to the market growth.
Fintech is increasingly gaining traction in Indonesia and changing the way financial companies do business. Gone are the days when banks were the only source of financial transactions in the country. Fintech has revolutionized the financial sector with the emergence of various technological start-ups in areas of mobile payment, loans, money transfers, asset management, etc.
Fintech sector’s growth in Indonesia is largely driven by the rapidly increasing internet penetration and rising smartphone usage, as well as solid and continuous investments – over 2013-2018, investments in the fintech industry are forecast to reach US$ 8 billion, growing at a CAGR of 21.7%. Despite these growth drivers, the sector faces several hurdles such as inexperienced financial personnel, lengthy regulatory processes, and poor financial knowledge among the Indonesian population.
Nevertheless, the country has been taking measures to tackle the challenges to create banks of the future. In November 2016, Bank Indonesia, central bank of the country, set up a fintech office in Jakarta to boost development of the industry. The office is aimed to optimize technological advancements across the fintech sector, assist players in understanding the regulations, and increase industry’s competitiveness by sharing its developments with international institutions. In addition, Indonesia’s Financial Services Authority is in the process of developing regulations to govern the industry, a significant step to enable both the fintech players as well as the regulators to function cohesively. Further, the industry is also receiving support from conventional financial institutions, which have started adopting digital innovations by initiating collaborations with fintech companies.
Indonesia’s high dependency on cash-based transactions along with low financial penetration rate serve as untapped opportunity areas for fintech players to explore. As of 2014, only 36% of the adult Indonesian population had bank accounts. Additionally, 89.7% of all transactions are still conducted in cash. Fintech players have gradually started leveraging these opportunity areas by expanding services with introduction of various start-ups offering a range of online financial products. As of 2016, the country hosted around 140 independent start-ups, an improvement from just a handful a few years ago, representing a steady growth of the industry. Some of the prominent players of the industry include HaloMoney, Cekaja, and Kartuku, among others.
EOS Perspective
Fintech is the answer to the need for a more secure, fast, and practical financial processing system. It has the potential to transform Indonesia’s financial industry by creating a paradigm shift in the way financial services sector operates. However, certain measures need to be taken to realize its full potential. In order to cultivate skilled personnel, the government should collaborate with universities across the country and promote fintech courses to develop the required skill set among people. Additionally, the government should encourage the association between conventional financial institutions and fintech companies to promote collaborative training and communication, which could help to improve financial education among players in the market. The association would also help both parties to improve their own areas of expertise.
Fintech industry has slowly started changing the way financial services are being accessed in Indonesia. Gradual yet steady on-going efforts to overcome hurdles are likely to result in a larger population enjoying benefits of digital financial services.



