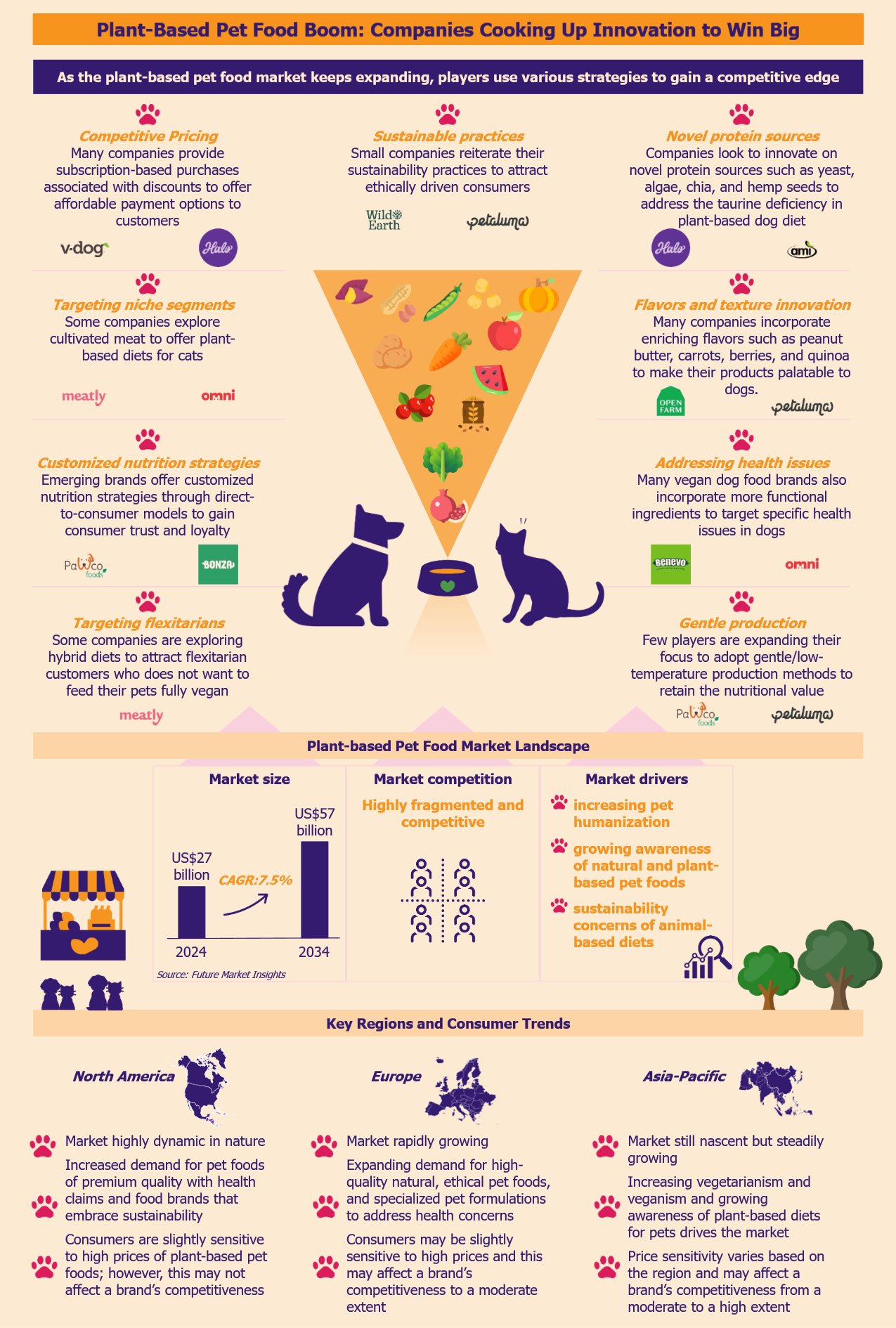
Over the past few years, the plant-based pet food market has been witnessing rapid growth due to pet humanization. As the market becomes increasingly competitive with many new brands and larger players, companies compete using innovative differentiation strategies to secure market share. By leveraging novel protein sources and innovative product formulations, brands look to enhance their product quality to gain an edge. Some brands focus on eco-friendly and sustainable practices to align their products with ethically-driven consumers. Others strive to optimize production processes to reduce costs and stay price-competitive.
According to Future Market Insights, the global plant-based pet food market was US$27 billion in 2024, with a growth forecast of a CAGR of 7.5% from 2024 to 2034. Vegan dog foods are some of the most common plant-based pet foods.
American and British companies overwhelmingly dominate the market. The leading players in this segment include Petaluma (USA), V-Dog (USA), Wild Earth (USA), PawCo Foods (USA), Omni (UK), The Pack (UK), and Benevo (UK). Other large players include Halo (USA), Nestlé Purina (USA), Mars Petcare (USA), and Hill’s Pet Nutrition (USA).
Plant-based dog food brands innovate with new protein sources
Creating products from protein-rich plants
One of the most critical components of a dog’s diet is protein. To compete with traditional animal-based dog foods, many vegan dog food brands focus on creating protein-rich formulas that match the nutritional profile of meat proteins. These products compete by combining and utilizing various plant proteins from sources such as peas, potatoes, lentils, and chickpeas.
Addressing the taurine deficiency in legume proteins
However, these plant proteins are often legume-based and deficient in taurine, an essential amino acid that dogs need in their diet. Some research studies claim that taurine deficiency increases the risk of dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), a heart disease in dogs.
As more companies enter the vegan dog food market, brands try to differentiate their offerings by introducing more non-legume protein sources to offer a complete amino acid profile and address DCM issues in dogs. More and more vegan dog food formulations use ingredients such as quinoa, chia seeds, yeast, algae, and hemp. For example, US-based Wild Earth uses yeast-based plant proteins in its products such as Wild Earth Maintenance Formula and Performance Formula to create a more balanced dog diet.
However, incorporating these specialized ingredients raises costs due to complex production processes, and this results in products’ high-end prices. For instance, an 18-pound (about 8.2kg) bag of Wild Earth’s performance formula food costs the consumer US$99, about US$5.50 per pound. On the other hand, a 20-pound (about 9.1 kg) bag of US-based Open Farm’s Kind Earth formula, which does not use a special protein source, costs only US$72.99, about US$3.65 per pound.
Innovation beyond protein sources also drives competition
Along with high-protein formulation, players compete through various advancements, including product formulation, ingredient sourcing, and catering to specific dietary needs.
Formulating nutritionally complete products
To ensure nutritionally complete offerings, companies are enhancing their plant-based dog foods with high-quality proteins, vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids. For example, the American company Natural Balance utilizes brown rice, oats, barley, peas, and potatoes as the primary sources of protein and carbohydrates in its Vegetarian Formula. The product is enriched with taurine and l-carnitine amino acids, along with antioxidants from spinach, cranberries, and dried kelp.
Innovating in more appealing flavors and textures
In an attempt to make their products stand out, many plant-based pet food companies incorporate enriching flavors such as peanut butter, carrots, berries, and quinoa to make their products appealing to dogs. For instance, Open Farm’s Kind Earth plant-based kibble includes ingredients such as barley and fava beans, aiming to provide a nutrient-dense and palatable meal.
Apart from diverse flavors, texture innovation is an important competitive factor. Companies attempt to develop products with a meaty and fibrous texture that carnivore pets prefer. For instance, US-based Petaluma introduced Sweet Potato Jerky treats, a plant-based alternative to traditional meat jerky, made from sweet potatoes.
Addressing specific health concerns
Many vegan dog food brands also incorporate more functional ingredients to target specific health issues in dogs. Some vegan dog food brands offer grain-free and gluten-free options for dogs with allergies or grain sensitivity. An example of this is the British Benevo Adult Dog Food brand that offers wheat-free products catering to dogs with grain sensitivity.
Some companies provide formulas rich in probiotics and fiber to support healthy digestion. For instance, American Halo Holistic enriches its plant-based dog foods with prebiotics, probiotics, and postbiotics for complete digestive health and immune function.
To address dogs’ health concerns and enhance the competitiveness of their products, some companies enrich their foods with targeted ingredients. A case in point is another British brand, Omni, which formulates its vegan dog food with glucosamine, curcumin, and turmeric – ingredients that support joint structure and mobility in dogs.
Some brands also try to add calming ingredients to address stress and anxiety issues in dogs. For instance, Petaluma uses chamomile and lavender to reduce agitation in dogs.
Brands that prioritize pet health distinguish themselves by aligning with owners’ unwavering focus: ensuring their pets’ lifelong well-being. This strategy delivers a measurable competitive edge — reducing long-term veterinary expenses, building durable trust through proactive care, and fostering customer loyalty. Collectively, these outcomes create a self-sustaining advantage, positioning brands as partners in pet care while raising barriers for competitors lacking similar commitment.
Developing hybrid diets for flexitarian consumers’ pets
Recognizing the flexitarian trend among pet owners, companies are exploring hybrid diets that combine plant-based and traditional meat-based foods. This approach caters to consumers seeking to reduce meat consumption without fully committing to a vegan diet for their pets. ProVeg International, a food awareness organization, recommends designing products suitable for flexitarian feeding practices, as a way to attract a broader customer base and increase sales by pet food companies.
Brands differentiate by focusing on fresh, instead of processed, foods
Kibble and canned food are the most prevalent forms of dog food. Currently, most vegan dog brands offer dry foods in the form of kibbles and treats. However, the process of producing kibble involves extruding ingredients at high temperatures, which might destroy essential nutrients in a dog’s diet. These foods can also contain excessive preservatives to extend shelf life and fillers to bulk up to the product, compromising their nutritional value and making them less suitable for a dog’s long-term health.
As awareness of this grows, players are strategically expanding their focus to adopt gentle production methods, offering minimally processed meals from fresh (and sometimes organic) ingredients. For instance, UK-based Bramble and US-based start-up PawCo Foods offer oven-baked fresh meals. The oven-baked slow-cooking process allows easy digestion with better nutrient availability for the dog’s optimal health. A few brands also use organic ingredients in their product formulations to attract consumers. For instance, Petaluma uses about 50% organic ingredients in its dog food.
Plant-based fresh meal options are still not common, thus providing these companies with a competitive advantage in this highly competitive industry.
However, fresh, unprocessed meals and organic ingredients can be considerably more expensive than conventional kibbles and other vegan pet foods. Furthermore, fresh vegan meals are less available in comparison to popular kibbles. Due to the high prices and limited distribution, many consumers may struggle to maintain these pet meals over the long term. Consequently, players pursuing this strategy may face strong competition from other vegan dog food brands that might offer better distribution and price their products more affordably.
Companies use sustainability to attract ethically driven consumers
Several vegan dog brands emphasize their environmental commitment to attract pet owners with ethical and sustainability values. These companies advertise practices such as eco-friendly packaging, ethical sourcing, advanced production processes, and lower carbon footprint.
For instance, Petaluma promotes itself as a green vegan dog food brand, catering to pet parents who prioritize sustainability. The company regularly publishes the products’ lab results and sustainability practices on its website. In addition, it offers its products in attractive compostable packaging with graphics that illustrate dogs and humans working together to achieve a better planet.
While emerging companies and smaller brands use the sustainability approach to gain customers’ attention, more prominent brands might struggle to justify their eco-friendly claims. These popular brands have a broader range of traditional (and cheaper) products that they produce using less sustainable processes. When these companies promote their plant-based pet food products, environmentally conscious pet owners might perceive them as capitalizing on the growing demand without genuine environmental commitment. Consequently, pet owners may view these larger brand products as examples of greenwashing and dismiss their sustainability claims.
Plant-based food brands use diverse strategies for price competitiveness
Plant-based pet foods are mostly pricey due to several factors. These products are still niche and produced primarily by smaller companies with limited sourcing and production capabilities, factors that increase costs.
Additionally, these foods use high-quality, complex plant ingredients, involving extensive research, development, and testing, to ensure nutritional completeness. The high prices may prevent customers from buying these products.
Offering subscription models to make products more affordable
Currently, many companies provide subscription-based purchases associated with discounts to offer more affordable options to customers. These options allow the companies to lock customers for a long time, creating recurring revenue streams.
Using direct-to-consumer models to build trust and loyalty
Vegan dog foods are not mainstream yet. Companies in this space, especially smaller firms, use e-commerce sites and online pet retail platforms to increase their brand visibility and reach. However, over recent years, they have increased the use of direct-to-consumer models where companies sell directly to customers through their websites.
Unlike online retail platforms, this model allows companies to gain more control over product pricing and achieve better profit margins without having any middlemen involved. Several companies offer customized vegan meal plans that they tailor to the dog’s age, health conditions, and dietary preferences. This model allows companies to foster a direct consumer relationship, thus building trust and loyalty.
Introducing process optimization to reduce production costs
There is also an increasing instance of smaller brands collaborating with larger companies to lower production and distribution costs. A few companies have started exploring innovative technologies to increase efficiency and lower production expenses. For instance, PawCo is leveraging AI to test its products’ palatability and to streamline simulation and production processes.
While smaller companies undertake various internal efforts to reduce product costs through process optimization, these companies might still struggle to compete with larger brands to provide affordable plant-based pet foods. Large companies offer vegan pet foods at affordable prices due to their strong brand presence, financial resources, and versatile distribution networks.
Read our related Perspective: Pet and Animal Health M&A: What’s the Scoop on the Industry’s Latest Shake-ups?
Plant-based food for cats poses greater challenges
While plant-based dog food is becoming more common, developing vegan cat foods is more challenging. Cats are obligate carnivores, meaning their nutrition relies primarily on animal-based meat. Cat owners have been skeptical about the nutritional profile of vegan diets. This makes them less willing to embrace such options for cats compared to dogs.
This creates an opportunity for players to innovate and compete in targeting cat owners. Some companies have been exploring solutions such as cultivated meat as an alternative to plant-based meat foods. For instance, Meatly, a UK-based start-up, has been exploring meat cultivation for cat food using cells from chicken eggs. While costly in R&D, this innovation could tap into a large market segment, offering cat owners more choices.
EOS Perspective
Health and sustainability will drive market growth in the West
While North America currently leads the market, Europe is not far behind and will likely experience significant growth in the coming years. Pet owners in the USA and Europe have been actively looking for plant-based pet foods that offer improved health benefits including oral, skin, joint, digestive and immune health.
Furthermore, there has been a growing demand for sustainable pet food products in these regions. Many pet owners are willing to pay high prices for vegan pet foods that promise minimal environmental impact and improved pet health.
Players in the Western plant-based pet food markets who are most likely to succeed will be those who effectively combine innovation, customization, sustainability, and consumer trust.
Asia-Pacific will be a rising frontier for players with localized strategies
Although the Asia-Pacific region lags behind North America and Europe in demand and availability of such products, it is poised for steady market growth. Key drivers mirroring Western trends, such as heightened pet health awareness, rising disposable incomes, and the growing appeal of veganism, are gaining traction across Asia.
The Asia-Pacific region’s diverse dietary and cultural preferences present both challenges and opportunities.
In recent years, some international plant-based pet food companies have entered Asia-Pacific, often forming partnerships with local retailers and pet food companies. For instance, in 2020, American V-dog launched its first plant-based pet food through Whole Foods, a major wholesale distributor in Japan. Such collaboration with Whole Foods, a reputable distributor, likely provided V-dog with strong market visibility and credibility. This entrance can serve as a strategic blueprint for other players aiming to expand into the region.
The region’s diverse diets and ingredients demand that companies tailor products to local preferences, such as incorporating sweet potatoes and seaweed in Japan. By aligning with these preferences, players can effectively navigate varied consumer demands. Those who can achieve that are better positioned to build relatability and trust with consumers, ensuring sustained long-term growth. A one-size-fits-all approach, or directly transplanting Western products into the regional markets, is unlikely to succeed.
The surge in online shopping across Asia-Pacific offers a significant opportunity to bypass traditional retail markups and reduce costs for consumers. Online platforms offer good growth avenues for brands that know how to strategically leverage e-commerce channels.
Asia’s price sensitivity will require careful threading
Price sensitivity will remain a critical factor and a barrier in this region, especially in developing economies such as India and China, where affordability often outweighs premium positioning. Here, players must adopt localized pricing strategies that cater to local economic conditions.
This can include offering smaller, budget-friendly packaging that can make plant-based pet food accessible for middle-income households. Hybrid products (combining plant-based and traditional ingredients) can serve as a cost-effective entry point for price-conscious consumers.
Subscription models, bulk discounts, and tiered pricing are good strategies for keeping product pricing accessible and relevant across diverse income levels. Tiered pricing, in particular, works well in markets with wide income disparities: simple formulations and no-frill products for budget-conscious consumers, enhanced formulations for middle-income buyers, and advanced formulations with premium ingredients for the high-income pet owners.
The regional markets also require investments in promotional campaigns, loyalty programs, and value-added offers that can further improve affordability and perceived value.
Brands that strike a balance between quality and affordability will likely appeal to a broader consumer base, ensuring deeper market penetration and success in the region.