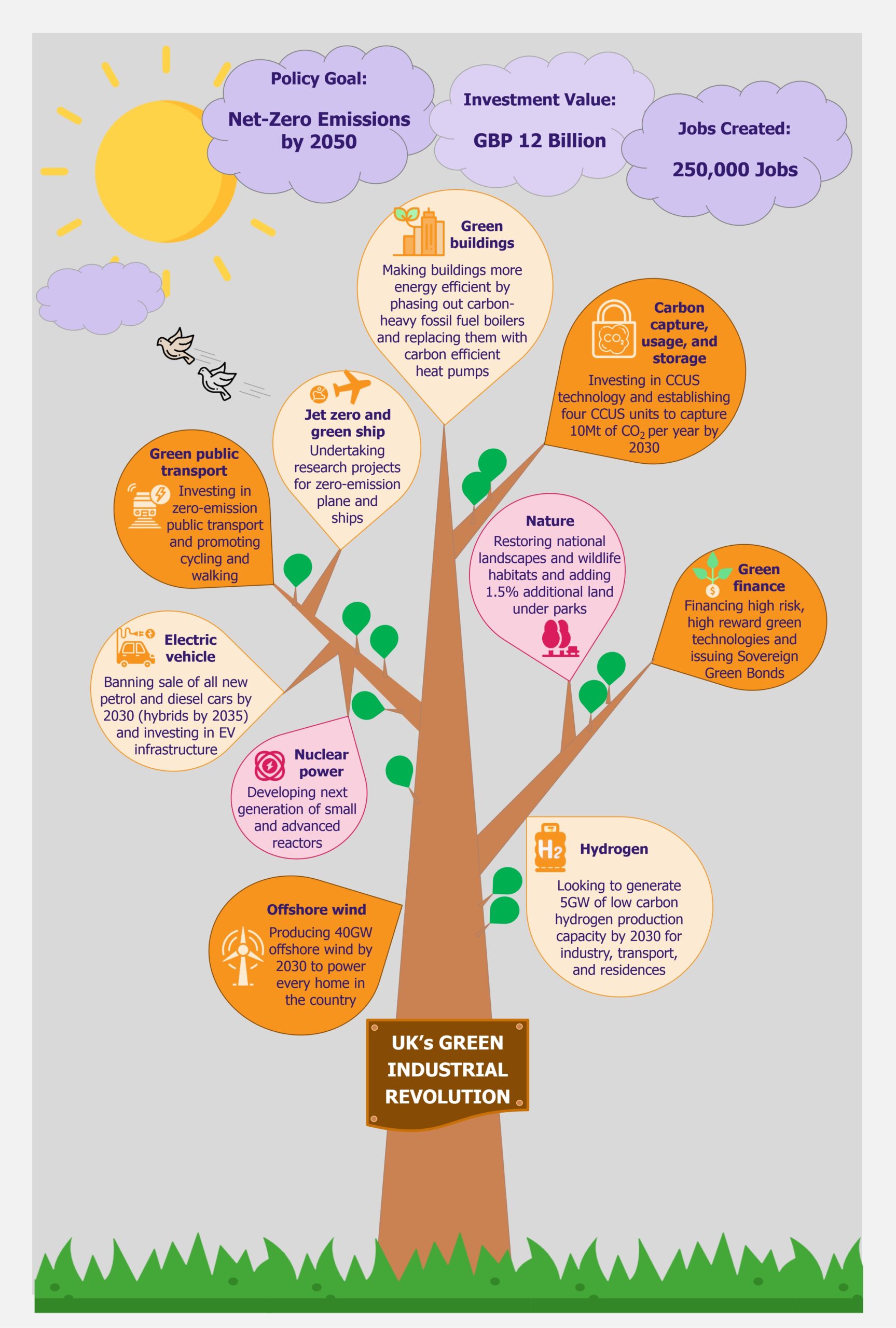
The UK is working to create a policy for building a more sustainable future for itself through the New Green Industrial Revolution, aiming to attain net-zero emissions in the UK by 2050. As the country separated itself from the EU through Brexit, it is also setting its own environmental goals and in that, its own version of the EU’s 2019 Green Deal (we wrote about it in The EU Green Deal – Good on Paper but Is That Enough? in March 2020). With highly ambitious targets, the proposed investments are worth GBP12 billion, creating 250,000 jobs in the process. While this seems like a promising funds allocation, the plan’s success will actually depend on significant investments in next-generation technologies, which have currently not been proven commercially. Moreover, a lot will depend on an equal involvement from the private sector that might be more cautious with investments than the public sector.
The UK is in a bid to position itself at the forefront of global markets for green energy and clean technologies. To achieve this, it proposed a 10-point Green Industrial Revolution in November 2020, which aims to mobilize GBP12 billion funds and create 250,000 jobs in the UK. Through this plan, the UK aims to achieve net zero carbon emissions by 2050. The key areas covered under the plan include offshore wind, hydrogen, nuclear, electric vehicles, public transport, jet zero and greener maritime, homes and public buildings, carbon capture, nature, and innovation and finance.
Offshore wind
The new Green Industrial Revolution outlines the UK government’s commitment to put offshore wind energy at the forefront of the country’s electricity needs. It has increased the offshore wind targets from previous 30GW to 40GW by 2030, aiming to produce enough energy to power all homes in the UK by 2030.
In addition to this, the government plans investments of about GBP160 million to upgrade ports and infrastructure in localities that will accommodate future offshore wind projects (e.g. Teesside, Humber, Scotland, and Wales).
This investment in developing offshore wind energy is expected to support about 60,000 direct and indirect jobs by 2030 in construction and maintenance of sites, ports, factories, etc.
While the government’s plan is great on paper, meeting the 40GW target will require 4GW of offshore wind projects to be commissioned every year between 2025 and 2030, which is extremely ambitious and challenging. Moreover, just developing offshore wind projects will not be enough until works are also done to update the electricity grid. Further, the target 40GW generation is calculated based on current electricity demand by households, which in reality is bound to increase as a shift towards electric vehicles is being encouraged.
Hydrogen
With the help of industry partners, the UK government plans to develop 5GW of low carbon hydrogen production capacity by 2030 for industries, transport, and residences. The government is expected to publish a dedicated Hydrogen Strategy in 2021, to position the UK as a front runner in production and use of clean hydrogen. It plans to develop 1GW (of the planned 5GW) hydrogen production capacity by 2025.
A central part of the UK’s Hydrogen Strategy is expected to have hydrogen potentially replace natural gas for the purpose of heating. The government is undertaking hydrogen heating trials, commencing with building a ‘Hydrogen Neighborhood’ and potentially developing a plan for the first town to be heated completely using hydrogen by 2030.
In addition to this, works with industry partners are under way to develop ‘hydrogen-ready’ appliances in 2021, such that new gas boilers can be readily converted to hydrogen if any future conversion of the gas network is commissioned. To facilitate this, the government is working with Health and Safety Executives to enable 20% hydrogen blending in the gas network by 2023. However, this is subject to successful trials.
In transportation, an investment of GBP20 million in 2021 is planned to test hydrogen and other zero emission freight truck technologies in order to support the industry in developing zero-emission trucks for long-haul road freight.
To achieve these targets, a GBP240 million Net Zero Hydrogen Fund is planned to be set up. It will provide capital co-investment along with the investment from private sector to develop various technologies. These will include carbon capture and storage infrastructure for the production of clean hydrogen that can be used in home, transport, and industrial requirements. The policy is expected to support 8,000 jobs by 2030 and push private investment worth GBP4 billion by 2030.
However, the government’s ambitious 2030 hydrogen policy requires significant investment and participation from the private sector. While several global companies such as ITM Power, Orsted, Phillips 66, etc., have come together to collaborate on the Gigastack project in the UK (which aims to produce clean hydrogen from offshore wind), such private participation will be required on most projects to make them feasible and meet the targets.
Nuclear power
In search of low-carbon electricity sources, UK plans to invest in nuclear energy. In addition to development of large-scale nuclear plants, the investments will also include small modular reactors and advanced modular reactors.
To this effect, the government has set up a GBP385 million Advanced Nuclear Fund. Of this, GBP215 million is to be used towards small modular reactors, i.e., to develop a domestic smaller-scale nuclear power plant technology that could be built in factories and assembled on site. Apart from this, GBP170 million is to be used towards research and development of advanced modular reactors. These are reactors that could operate at over 800˚C, and as a result, unlock efficient production of hydrogen and synthetic fuels. These are also expected to complement the government’s other investments and initiatives with regards to hydrogen and carbon capture.
While the government expects the design and development of small modular reactors to result in private sector investment of up to GBP300 million, these next generation small reactors are currently considered a long shot as no company has created them yet. While Rolls Royce has offered the government to design one, it is conditional on them receiving a subsequent order worth GBP32 billion for 16 such reactors as well as the government paying half of the GBP400 million design cost.
Moreover, nuclear power plants are expensive and long-term investments and are considered to be one of the most expensive sources for power. Thus it is very important to evaluate their economic feasibility. While the government is bullish on the role of nuclear power in decarbonizing electricity, it is very important for large-scale projects to be economical, while small-scale projects still remain at a conceptual stage.
Electric vehicles
It is estimated that cars, vans, and other road transport are the single largest contributor to the UK’s carbon emissions, making up nearly one-fifth of all emissions emitted. Thus the government is committed to reducing carbon emissions produced by automobiles. To achieve this, the country plans to ban the sale of all new petrol and diesel cars and vans by 2030 (10 years earlier than initially planned). However, hybrid cars will be allowed to be sold till 2035.
The government has planned a support package of GBP2.8 billion for the country’s car manufacturing sector, which in turn is expected to create about 40,000 employment opportunities up till 2030. Of this, GBP1 billion will be used towards the electrification of vehicles, including setting up factories to produce EV batteries at scale. In addition to this, GBP1.3 billion is planned to be spent to set up and enhance charging infrastructure in the country by installing a large number of charge points close to residential areas, office and commercial spaces, highways, etc., to make charging as convenient as refueling. The government plans to have a network of 2,500 high-power charging points by 2030 and about 6,000 charging points by 2035. Lastly, grants are planned to the tune of about GBP582 million up till 2023 to reduce the cost of EVs (cars, vans, taxis, and two-wheelers) for the consumer. In addition to the investment by the government, private investment of about GBP3 billion is anticipated to trickle into the sector by 2026.
While this is considered to be a very important step in the right direction, it is estimated that it will still leave about 21 million polluting passenger vehicles on the UK roads by 2030 (in comparison to 31 million in 2020). Moreover, the government continues to allow the sale of hybrid cars for another five years beyond 2030, which means that carbon emissions-producing vehicles will still be added to UK roads even after the target dates set in the New Green Industrial Revolution plan.
Green public transport
In addition to reducing carbon emissions from passenger cars, the government also wants to make public transport more approachable and efficient. It plans to spend about GBP5 billion on public transport buses, cycling- and walking-related initiatives and infrastructure.
In addition, funding of GBP4.2 billion is planned on improving and decarbonizing the cities’ public transport network. This will include electrifying more railway lines, integrating train and bus network through smart ticketing, and introducing bus lanes to speed up the journey. The plans also include investment in about 4,000 new zero-emission buses in 2021, as well as funding two all-electric bus towns (Coventry and Oxford) and a completely zero-emission city center. While York and Oxford have shown interest in becoming the UK’s first zero-emission city center, the government has not yet formally announced the city for the same.
Improvements in public transport networks in other cities are also planned to bring them on par with London’s system. A construction of about 1,000 miles of segregated cycle lanes is in plans to encourage people to take up this mode of transportation for shorter distances.
While it is expected these investments will encourage people to use public transport more, the current COVID pandemic has created apprehensions when considering such shared transportation. Although this is expected to be a short-term challenge, it may be a slight damper to the government’s plan for the next year or so.
Jet zero and green ships
Apart from road transport, the government also aims at decarbonizing air and sea travel. It plans to invest GBP15 million in FlyZero – a study by Aerospace Technology Institute (ATI) aimed at identifying and solving key technical and commercial issues in design and development of a zero-emission aircraft. Such an aircraft is expected to be developed by 2030. In addition to this, the government plans to run a GBP15 million competition for the development of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) in the UK. The plans also include investing in upgrading airport infrastructure so that it can service battery and hydrogen fueled aircrafts in the future.
In addition to aviation, the government is also investing GBP20 million in the Clean Maritime Demonstration Programme to develop clean maritime technology.
While the plans to develop greener fuel for aircraft and ships is a step in the right direction, it is still somewhat of a long shot as a lot more investment is required into this than proposed. Moreover, the shipping industry in particular has shown little interest in wanting to reform in the past and it is likely that both the sectors will continue to follow international standards (that are high in carbon emissions) to remain competitive globally.
Greener buildings
The UK has a considerable number of old and outdated buildings that the government wants to put in the center of its Green Industrial Plan, thus making existing and new buildings more energy efficient. The plan is to slowly phase out carbon-heavy fossil fuel boilers currently used for heating buildings and instead promote the use of more carbon efficient heat pumps. For new buildings, an energy efficiency standard is to be developed, known as the Future Home Standard. To achieve this, the domestic production of heat pumps needs to be ramped up, so that 600,000 heat pumps are installed annually by 2028. This is expected to support about 50,000 jobs by 2030. In addition to this, the government is providing GBP1 billion to extend the existing Green Home Grant (launched in September 2019) by another year, which is aimed at replacing fossil fuel-based heating in buildings with more energy efficient alternatives.
While the subsequent shift to heat pumps from gas boilers will definitely help reduce the buildings’ carbon footprint, heat pumps are currently much more expensive and more difficult to install. Thus, the government must provide ongoing financial incentives for consumers to make the switch.
Carbon capture, usage, and storage
Carbon capture, usage, and storage (CCUS) technology captures carbon dioxide from power generation, low carbon hydrogen production, and industrial processes, and stores it deep underground, such that it cannot enter the atmosphere. In the UK, it can be stored under the North Sea seabed. A the technology has a critical role to play in making the UK emission free, a GBP1 billion investment is planned to support the establishment of CCUS in 4 industrial clusters by 2030 to capture 10Mt of carbon dioxide per year by 2030. Developed alongside hydrogen, these CCUS will create ‘SuperPlaces’ in areas such as the North East, the Humber, North West, Scotland, and Wales. The development of the CCUS is expected to create 50,000 jobs by 2030.
CCUS is a very new technology, with no large-scale or commercially successful projects operational across the world. While the technology has been proved in pilot projects, its feasibility is yet to be seen. Also, a significant amount of private investment will be required to carry through the proposed project. While some private players, such as Tata Chemicals Europe have begun constructing the first industrial-scale CCU plant (expected to capture 40,000 tons of CO2 per year) in Northwich, the government needs several more private players to step up to meet its ambitious targets.
Nature
In addition to the above mentioned programs, the government plans to safeguard and secure national landscapes as well as restore several wildlife habitats to combat climate change. To achieve that, it plans to reestablish several of the nation’s landscapes under National Parks and Areas of Outstanding Beauty (AONB), as well as create new areas under these two heads. The National Parks and AONB program is expected to add 1.5% of natural land in the UK and will help the government in reaching the target of bringing 30% of the UK’s land under protected status by 2030.
In addition to this, the government plans to invest GBP40 million in nature conservation and restoration projects, which in turn is expected to create several employment opportunities across the country. Moreover, it plans to invest GBP5.2 billion over six years into flood defenses, which will help combat floods and damage to homes as well as natural environment. This is also expected to create about 20,000 jobs up till 2027.
Green finance and innovation
The last agenda on the 10-point Green Industrial Revolution entails developing new sources of financing for supporting innovative green technologies. To this effect, the government has committed an R&D investment of 2.4% of its GDP by 2027. This will extensively be used towards developing high risk, high reward green technologies, which will help the UK attain net zero emissions by 2030.
Additionally, the government launched a GBP1 billion Net Zero Innovation Portfolio that will focus on commercialization of low-carbon technologies mentioned in the 10-point agenda, including development of floating offshore wind, nuclear advanced modular reactors, energy storage, bioenergy, hydrogen, greener buildings, direct air capture and advanced CCUS, industrial fuel switching, and other disruptive technologies. In November 2020, the government launched the first phase of this investment, GBP100 million, towards greenhouse gas removal and in the coming year it plans to invest another GBP100 million towards energy storage. It also plans to invest GBP184 million for fusion energy technologies and developing new fusion facilities. Moreover, GBP20 million will be directed towards development and trials of zero emission heavy goods vehicles.
Apart from this the government plans to issue the UK’s first Sovereign Green Bonds in 2021. These bonds, which are likely to be first of many, are expected to finance sustainable and green projects and facilitate the creation of ‘green jobs’ in the country. Furthermore, similar to the EU Green Deal, the government plans to implement a green taxonomy, which helps define economic activities into two categories – the ones that help limit climate change and others that are detrimental to the environment – to help investors make better investment choices.
EOS Perspective
The UK’s Green Industrial Revolution seems to be a comprehensive policy with a multi-pronged approach to tackle climate change, promote green technology and investments, and achieve net zero emissions by 2050. With Brexit in action, it seems like a worthy counterpart to the EU’s Green Deal, which the UK was initially a part of. Moreover, it is an important framework for the UK to show its commitment towards controlling climate change, especially with the country hosting the upcoming 26th session of the Conference of the Parties (CoP 26) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change summit in Glasgow in 2021.
However, currently the UK’s Green Industrial Revolution is not a legally binding policy document but more of a proposal, which would need to go through several legislative procedures to become binding. Moreover, while the plan is ambitious, it depends heavily on next generation innovative technologies that require hefty investments to achieve the targets. Thus, its success depends on whether the government is seriously committed and prepared to spend heavily on commercializing these technologies along with managing to attract significant amount of private investment to complement own efforts. While few aspects of the 10-point approach have already received investment from the private sector and first phase of funding from the government, it is yet to be seen if the UK’s ambitious net zero emission goals are truly feasible.