Healthcare sector in India is witnessing a churn as a result of the government’s attempt to make healthcare more affordable and to promote domestic healthcare industry. Recent medical devices-related notification is also part of the government’s vision for a better managed healthcare market, though it has ignited a debate about the future of medical device industry. There is hope as well as an apprehension among the stakeholders, as they wait for the notification to become fully effective in next three years.
The Notification
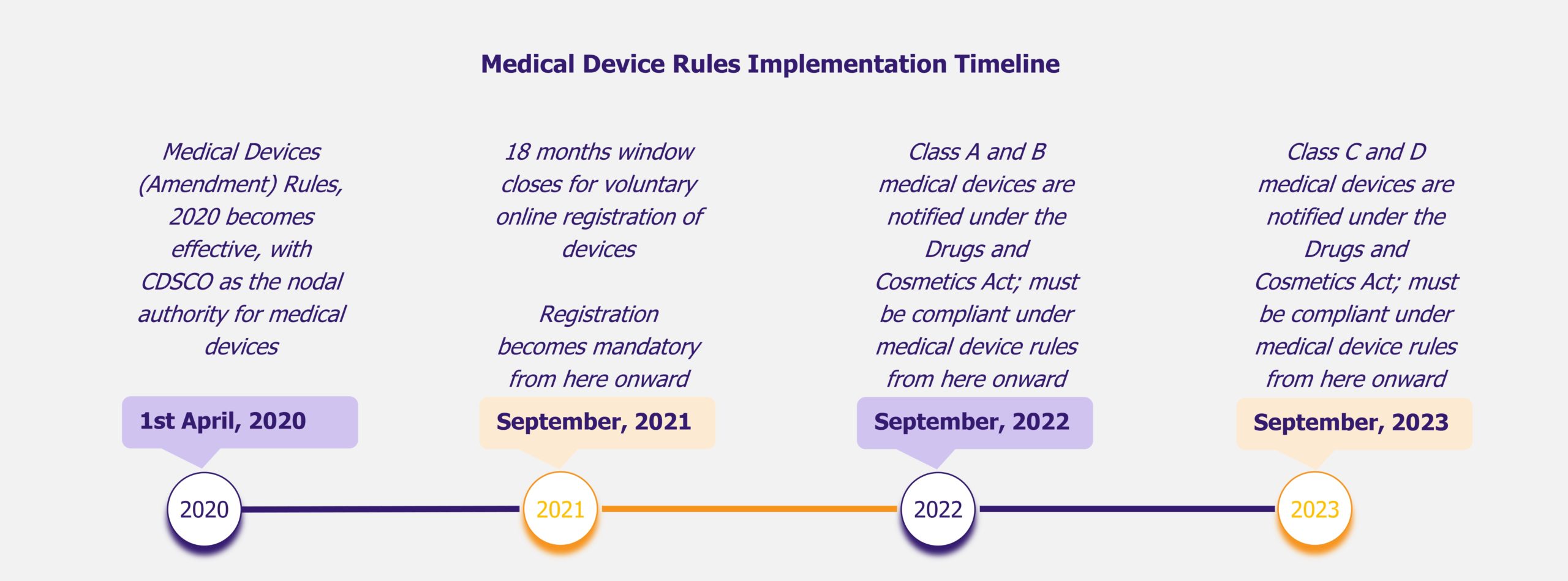
In the second week of February 2020, India’s Ministry of Health & Family Welfare announced that all medical devices sold in the country would be treated as drugs from April 1, 2020 onward and would be regulated under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act of 1940. To understand the context of this announcement, we will have to turn the clock back by about three years.
In 2017, Indian government announced Medical Device Rules-2017 (MDR-17) – a set of rules, which included:
- Classification of medical devices into four classes (A, B, C, and D), based on the associated risks, i.e. low, low moderate, moderate high, and high risk devices
- Procedures, including the required documents, for registration and regulatory approval of devices
- Details regarding manufacturing, quality audit, import/export, and labelling-related requirements
There was no risk-based classification of medical devices prior to 2017 and it was also difficult to introduce new products, as the approval procedures were undefined. In case of imports, only the products approved by Conformité Européene (CE) and the US Food and Drug Administration were allowed. MDR-17 were expected to unlock the potential of Indian medical device market by introducing a well-defined regulatory regime, while assuring quality products to consumers.
Under the rules, a medical device had to be notified as ‘drug’ under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act to be regulated by Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO):
- Initially, 15 categories of medical devices (syringes, stents, catheters, orthopedic implants, valves, etc.) were notified as drugs
- In 2019, the government notified (effective April 2020) another eight categories – MRI equipment, PET, bone marrow separators, dialysis machines, CT scan and defibrillators, etc., thereby placing a total of 23 categories of medical devices under drugs
The February 2020 notification, called Medical Devices (Amendment) Rules, 2020, has made the entire range of medical devices available in India (about 5,000 different types) under the ambit of drugs, as opposed to 23 categories before the announcement. The compliance requirements are to be enforced in a phased manner, with 30 months given to low and low moderate risk devices and 42 months for moderate high risk and high risk devices.
The Concerns
The February notification has drawn reactions, most of them positive, regarding the future from those associated with the industry. There are some concerns as well, such as:
- What if the device rules accord unrestrained power to drug inspectors due to medical devices being regulated under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act?
- Would the cost of quality compliance be substantial for device manufacturers?
- Would the government resort to price control of medical devices, as it does in case of drugs?
Though the concerns are valid, they are unlikely to cause immediate disruption, as there would be at least 30 months (time given for enforcement of compliance for class A and B devices) after the notification date for the rules to start impacting the industry. An increased cost of compliance is a possibility, however, it would be found across the industry and should not impact only specific companies or a specific product segment.
At present, for price control purpose, four medical devices – cardiac stents, drug-eluting stents, condoms, and intrauterine devices – are in the national list of essential medicines that can be further expanded. However, the expansion cannot be directly linked with the medical device rules, which were primarily framed to ensure a better operating environment for industry players. For instance, from the initial list of 15 categories (i.e. about 350 devices) under MDR-17, only cardiac stents and knee implants were brought under price control (condoms and intrauterine devices were already under the price control regime when MDR-17 were introduced).
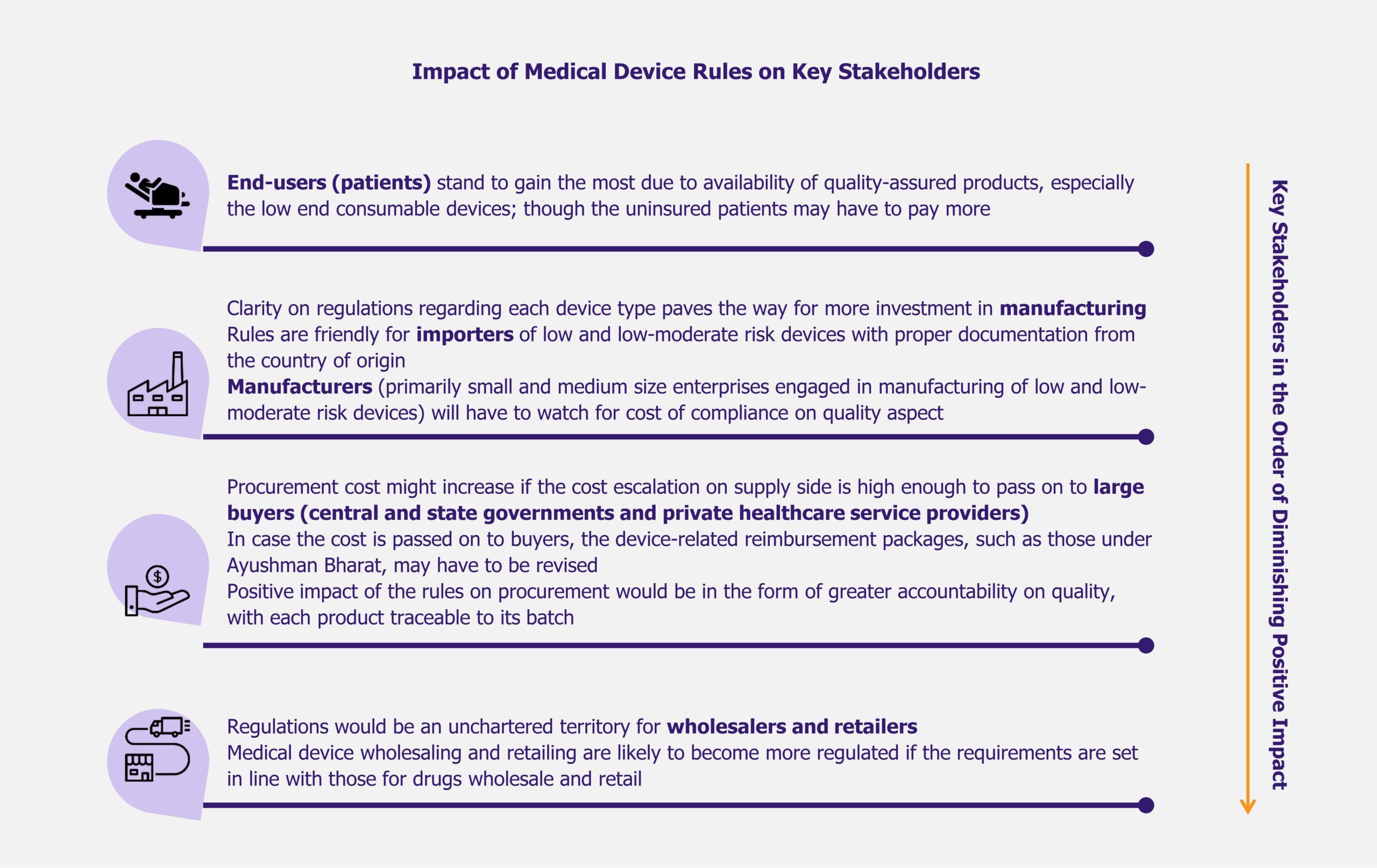
Impact on stakeholders
Indian medical device industry is expected to evolve under medical device rules (including the February 2020 notification). Even if the impact of the rules is speculative at present, it is interesting to take a look at their potential effect on key stakeholders in the coming years. While the patients appear to be the greatest beneficiaries due to improvement in quality of treatment, wholesalers and retailers of medical devices may have to prepare for a more demanding operating environment.
Read more on the implications for all stakeholders in the medical device industry in India in our article: Indian Medical Device Rules: Prospects among Ordeals for Manufacturers
EOS Perspective
Decision to notify all medical devices as drugs for regulatory purpose was a result of a long consultative process, which involved various stakeholders and experts, including Drugs Technical Advisory Board (DTAB). The industry was expecting such an announcement, as the government had previously shown its intent to do so. Hence, the February 2020 notification was only part of the process that was initiated in 2017 with the introduction of medical device rules. The notification is a show of intent by the government of India towards building a better regulated industry offering more quality products, thereby raising the standards of healthcare in the country. The phased implementation of rules is likely to provide enough time for the industry to adapt according to new regulatory requirement.
Any comment on the future of Indian medical device industry on account of probable price control measures would be purely speculative, as it is difficult to predict the outcome of such steps at present. The case in point is of stents, which were brought under price control regime in 2017. There were fears that the move might kill the sector; however, the stent-related procedures have not witnessed decline despite the multinational companies taking their high end products off the shelf, indicating that the domestic manufacturers have been able to cater to demand.
While the end-users can view the medical device rules as a means to provide better care to them, the device manufacturers can also look for positives, especially when the rules are seen along with the government’s other efforts, such as Make in India initiative, to boost domestic manufacturing. Device classification and the associated regulatory requirements have removed ambiguity for the manufacturers of medical devices in India. This clarity might also fast track investments in the sector, as the potential investors now know what to expect while operating in India. Under Make In India, up to 100% foreign direct investment is permitted in medical devices through automatic route.