India’s recent notification on regulating medical devices is another step on the government’s behalf to raise healthcare standards in the country. These regulations have implications for all stakeholders in the medical device industry, including medical device manufacturers and importers. The actual impact of these regulations will only be felt in next four to five years, once the regulatory regime comes into effect. However, based on some of the specific regulatory requirements, it is not difficult to ascertain what lies ahead for manufacturers and importers.
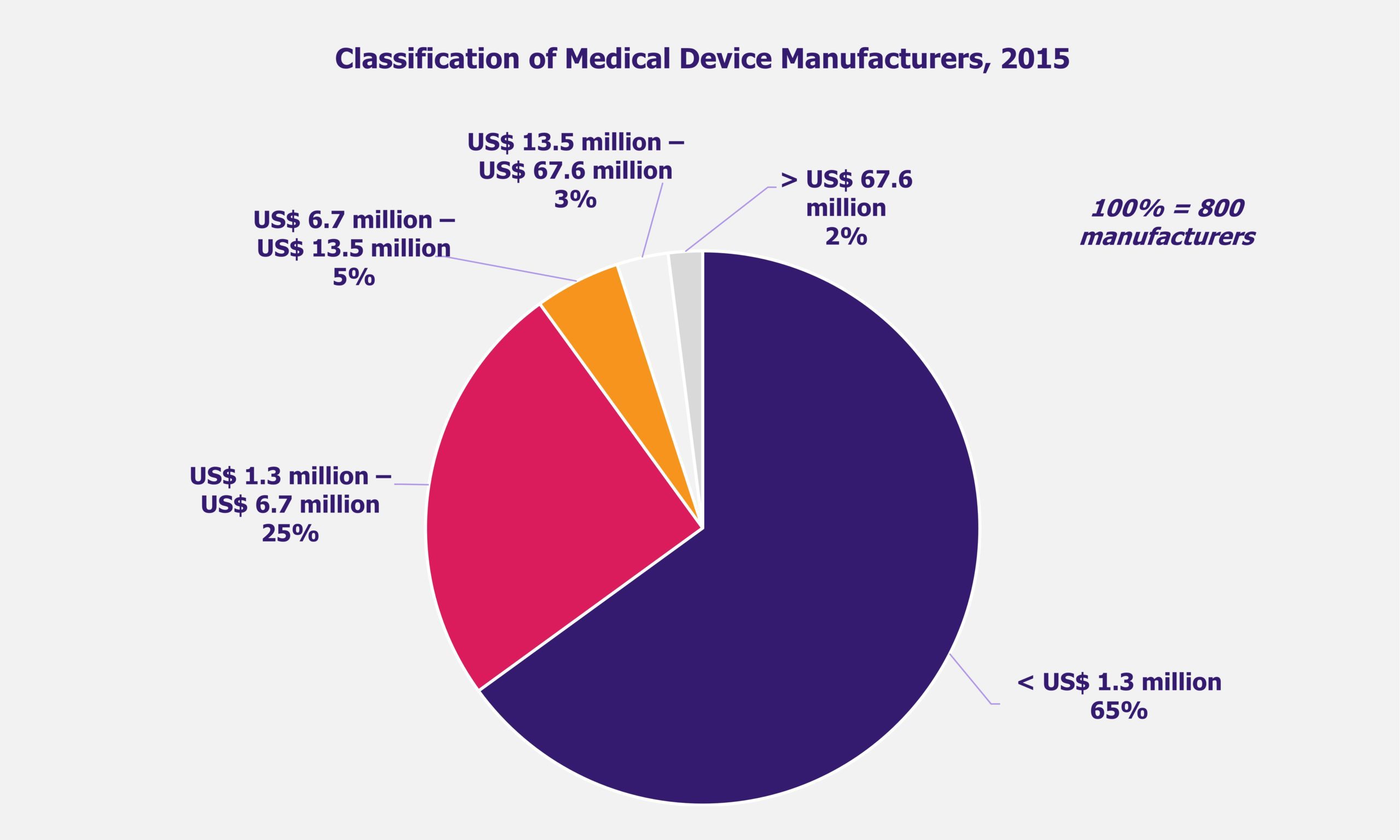
In 2019, Indian medical device industry was worth US$9 billion and is expected to reach US$14 billion by 2025. India imports nearly 70% of its medical devices, particularly high-end medical equipment including cancer diagnostics, medical imaging, ultrasonic scans, and PCR technologies, among others, the demand for which is met by multinational companies. The key medical devices that India imports include electronics and equipment – 53%, consumables – 14%, surgical instruments – 10%, IVD reagents – 9%, implants – 7%, and disposables – 7%. Domestic medical device market comprises mainly of small and medium medical device manufacturers with a large portion with turnover of less than US$ 1.3 million.
For many years, Indian medical device industry has dealt with a lot of challenges owing to lack of regulations. However, with the new medical device regulatory system, the scenario is expected to improve and reduce concerns among the device manufacturers around the lack of standardization and best practices. We discussed the new regulations of medical devices and their impact on various stakeholders in the healthcare sector in our article Indian Medical Device Rules: a Step towards a Better Future in February 2020.
Impact of new regulations on device manufacturers
Once the new regulations come into play, all manufacturers will have to maintain quality standards to avoid any punitive action by the regulator, as compromise on quality could result in suspension or cancellation of their license disabling them for doing business in the Indian market.
In order to assure quality, manufacturers will have to focus on quality management best practices to meet the quality objectives. This would mean creation of quality manual, documentation and execution of the quality-related procedures, and maintenance of quality-related records. Establishment of a quality assurance unit and installation of IT system to support quality-related processes will be the two key steps towards achieving quality objectives.
However, all this will not be easy to achieve from a financial viewpoint for manufacturers, considering majority of players are small and medium-sized. As an indicator, the average cost per year of having a five member quality assurance team in place can be anything between US$ 27,000 to US$ 34,000, which would account for about 2% of the annual turnover for a medical device company reporting US$ 1.3 million in sales (65% of the Indian medical device companies earn less than that). This would be a significantly high expense and, if incurred, is likely to be passed on to consumers.
The amount of expenditure on IT-related infrastructure for implementation on QA would depend primarily on two things. Firstly – the kind of medical device being manufactured (while some medical devices work on the principle of embedded software others do not require software-related quality checks, such as syringes, masks, head covers, etc.). Secondly – the extent to which a manufacturer wants to invest in IT (based on global standards, it would come to around 15-20% of annual IT budget).
Spending on IT infrastructure should be considered as a long-term investment, considering this would be required not only to ensure compliance on quality assurance but also to be done if the company wants to compete in export markets. In any case, the manufacturer would spend less than 1% of its annual revenue on IT for achieving quality objectives.
The government also wants all the device manufacturers to be compliant with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), laid down under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act of 1940, and currently introduced as a self-audit or self-assessment activity.
Getting a GMP certification (that confirms a firm uses quality assurance approach to ensure that products are consistently produced and controlled to the quality standards appropriate to their intended use and as required by the marketing authorization) for a single device is likely to cost less than US$ 135 for the manufacturer. Considering a manufacturer produces a range of devices, most of the small device manufacturing units do not follow the voluntary practice of attaining a GMP certificate citing certification costs (for the entire range of devices manufactured) and renewal fees (for each device after a certain number of years) to be adding to their overall expenses, but not significant enough to be passed on to customers. However, on the positive side, if companies were to get GMP certification, it would make their products compliant as per international standards making them more competent in the export market.
Road ahead for importers
Imports constitute a sizeable part of the medical device market in India. It is easier for importers now to place their products in the Indian market considering that there is a streamlined regulatory standard in place highlighting regulatory approval procedures to be followed in India, as against only the FDA (US Food and Drug Administration) or CE (Conformity Europé) approved products that were allowed to enter the market earlier. This will limit the importers’ cost required for approvals to market in India, rather than requiring marketing approval from international agencies.
Registration fees, license fees, and all duties levied for importing devices in India have been explained paving a clearer pathway for importers to operate in the market. Additionally, a list of forms specific for import purposes, required to apply for medical device approval has also been revealed.
All these practices and clarifications from the regulatory bodies have made it more convenient for manufacturers to import products. Clarity on import-related regulations is expected to make it easier for the importers to bring products to India thereby creating more challenges for the domestic players; however, it is too early to say how the market will evolve and which product segments will witness intensified competition in the next four to five years.
EOS Perspective
From the healthcare industry’s standpoint, governments’ step to ensure that medical devices available in the market meet quality standards in the future is positive and welcomed as it brings assurance of superior quality products for the people using them.
It is the small and medium sized enterprises that make up the low priced, high volume market segment of the medical device industry in India, that will need to make major operational changes and keep a close watch on the cost of compliance on quality aspect. The added cost aspect, if encountered, for developing high-quality products is most likely to hit them the hardest (especially the micro units and small-scale manufacturers) leaving them with no option but to pass on the increased cost onto the consumers. Larger players (5% manufacturers) are likely to remain practically unaffected. Nevertheless, it will be interesting to watch how these regulations shape the operations of device manufacturing companies functioning in India.