The Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) region is believed to have bountiful energy resources, sufficient to meet the region’s energy requirements, however most of these resources are largely underdeveloped due to limited infrastructural and financial means. This has led to majority of the countries in the region to have restricted access to electricity, despite the presence of huge waterways, which could boost the hydropower sector’s growth, particularly the small hydropower (SHP) projects – plants with generation capacity between 1 and 20 MW. In recent years, SSA region’s focus has slowly shifted to SHP projects instead of depending on large-scale hydro plants, which are relatively expensive to construct and require longer time to build. However, question remains whether SHP has enough potential to improve electricity supply and reduce power outages across the SSA region.
African continent has approximately 12% of the global hydropower potential, most of which is centered in the Sub-Saharan region due to the presence of vast water bodies. Despite the underlying potential, the region faces massive electricity shortage partially due to under exploitation of hydropower.
Over the years, the SSA region has focused on the development of large-scale hydropower projects to increase its electricity generation capacity. However, recently, the emphasis has shifted to SHP because they are economically viable with almost negligible environmental effect and a short gestation period. Additionally, several small African economies utilize less than 500 MW of electricity annually, which negates the requirement to build a large dam, making SHP a viable option. Further, with comparatively lower overheads and maintenance costs, SHP could play a vital role in solving electrification problem in rural areas.
By 2024, the African SHP capacity is likely to reach 49,706.1 MW, growing at a CAGR of 19.2% since 2016, driven by the tremendous growth opportunities that the region offers. SHP projects are likely to proliferate in the region, owing to low capital investment requirement for installation, which makes SHP a more viable and affordable option than large-scale projects. SHP market still remains quite unexplored due to limited technological and infrastructural capabilities, and lack of sufficient promotion of SHP in national planning schemes.
Nevertheless, in the last couple of years, investments in the region’s SHP sector have increased, with various internationally-funded projects likely to commence installations. Geographically, countries such as Zambia, Uganda, and DRC (Democratic Republic of the Congo) are most suitable for SHP generation, due to the abundant presence of river basins and water resources. These countries depend predominately on hydropower for their energy requirements.
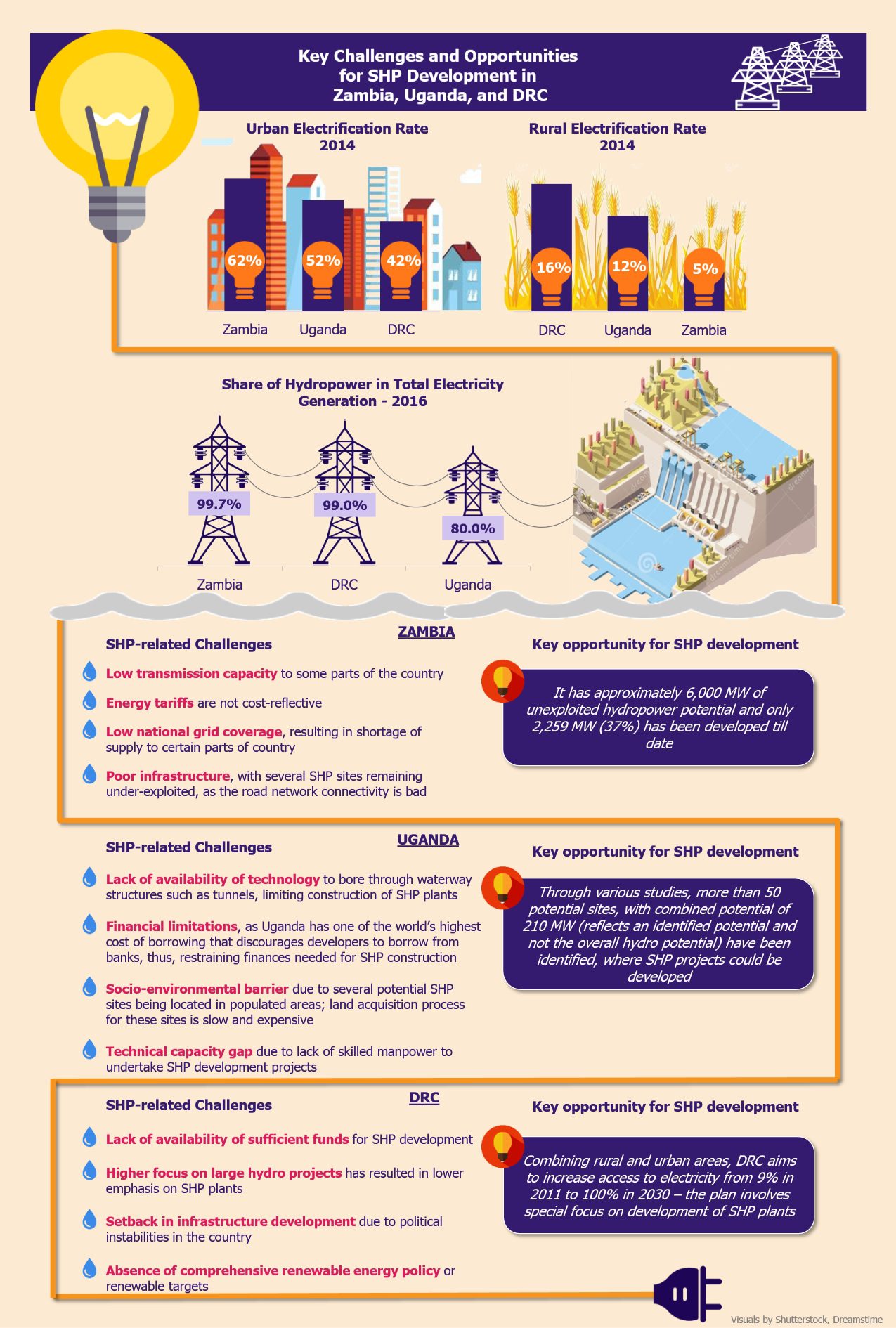
Hydropower is the primary source of power supply in Zambia, with a 99.7% dependency on hydropower to meet electricity needs. However, the country faces massive power outages due to fluctuating water levels, owing to persistent issue of scanty rainfall or droughts in the country, causing turbines to stop functioning to generate electricity. In 2015, the country witnessed a massive drought, which led to a huge decline in electricity generation. Nonetheless, since then, the country’s water level has improved, due to better rainfall pattern, resulting in higher level of power generation (as compared with 2015) through hydropower. The government has been making efforts to develop SHP stations to improve electricity supply – some of the SHP stations in the country include Lunzua, Mulungushi, Chishimba, and Shiwangandu hydropower stations.
Uganda’s power requirement is quite high due to extensive use of electricity in the industrial sector. The supply is always lower than the demand and the country faces frequent load shedding issue. Hydropower, accounting for 80% share in electricity generation, is the main source of power production in Uganda with a number of SHP plants in operation. Uganda’s government supports the hydropower market and has been making consistent efforts to promote SHP projects. For instance, in order to attract investors, the government provides incentives such as VAT exemption on hydropower projects.
DRC has the highest hydroelectricity potential in SSA due to the presence of particularly abundant water resources. Hydropower accounts for a share of 99% in DRC’s power generation. As of 2014, DRC’s total installed electricity generation capacity stood at 2,500 MW against its potential of 100,000 MW. In long term, DRC aims to become a key hydropower exporter in the region.
The SHP market across Zambia, DRC, and Uganda is still developing, with several potential SHP sites that could be harnessed to improve electricity supply. Each country faces its individual set of challenges in terms of SHP development, however, the hindrances seem trivial against the mammoth benefits that the countries could reap through SHP development.

EOS Perspective
Hydropower holds a key position in SSA’s energy generation mix and SHP projects have particularly witnessed steady growth in the recent years. However, whether SHP has the potential to alleviate the power crisis in SSA is still debatable.
Is high reliance on hydropower a reasonable approach to overcome energy crisis?
While hydropower plays a dominant role in energizing the SSA region, continued energy crisis across various countries reflects the dangers of over-dependence on one form of energy for power generation. The chronic power shortages, load shedding, and low levels of electricity penetration are a clear indication that the SSA countries are unable to keep pace with electricity demands by heavily relying on a single power source.
Pinning hopes solely on hydropower to alleviate the energy crisis has spelled catastrophe for certain key industries, heavily reliant on electricity for functioning, that are suffering due to the electricity shortage. For instance, in 2014, DRC’s mining sector was adversely hit by the electricity supply shortage and development of new mines had to be frozen. The limited electricity supply situation has not yet improved, as DRC announced plans (in 2017) to import electricity from South Africa to support the struggling mining sector.
A solution to the electricity crisis could be to avoid heavily investing in one source for energy generation as well as to focus on tackling the fundamental vulnerabilities of power sector. In the long term, addressing the energy crisis would demand better management of water resources, continuously growing capacity of existing power plants along with a well-planned diversification of energy generation.
Is SHP a holistic solution to SSA’s energy crisis?
While focusing only on hydropower as a solution to the entire energy crisis situation across SSA countries might not be the best approach, developing SHP for rural electrification could be ideal to eradicate energy poverty across rural communities. SHP alone cannot consistently satisfy the energy demands of SSA countries such as Zambia, Uganda or DRC, but it can surely become the best possible solution to electrify rural areas, as people residing in these communities typically live closer to a river than to a grid.
Rural communities are characterized by much lower electricity access rates as compared with urban areas because people residing in villages typically cannot afford grid connections and in most cases the electricity supply through national grid does not reach the remote areas. SHP could play a major role in off-grid electricity supply that can be used for domestic application in rural households.
Besides the requirement to develop SHP particularly for rural communities, it is also essential for various SSA countries to adopt a cost-reflective tariff, which would ease pressure on public finances and attract more private investments.
Further, focusing only on increasing electricity supply is not a comprehensive solution to the crisis, as certain SSA countries such as Uganda suffer due to high tariff rates, which also need to be monitored. Uganda has one of the world’s highest electricity tariff rates and consumption is partially affected by it due to low affordability. The high commercial and industrial tariffs adversely impact some major industries such as agro processing (agriculture is a core sector of Uganda’s economy). A lower tariff rate could help to boost production across industrial sectors (including agriculture) and improve affordability among households.
Nonetheless, development of SHP projects would certainly help to move closer to eradicating the energy crisis in SSA region but only to a certain extent. It is imperative to take other measures as well to completely tackle the issues of supply shortage and load shedding. Development of SHP projects across the SSA region is challenging, however, navigating through these obstacles would be well worth the efforts, particularly in countries such as Zambia, DRC, and Uganda, where SHP could play a major role in rural electrification.