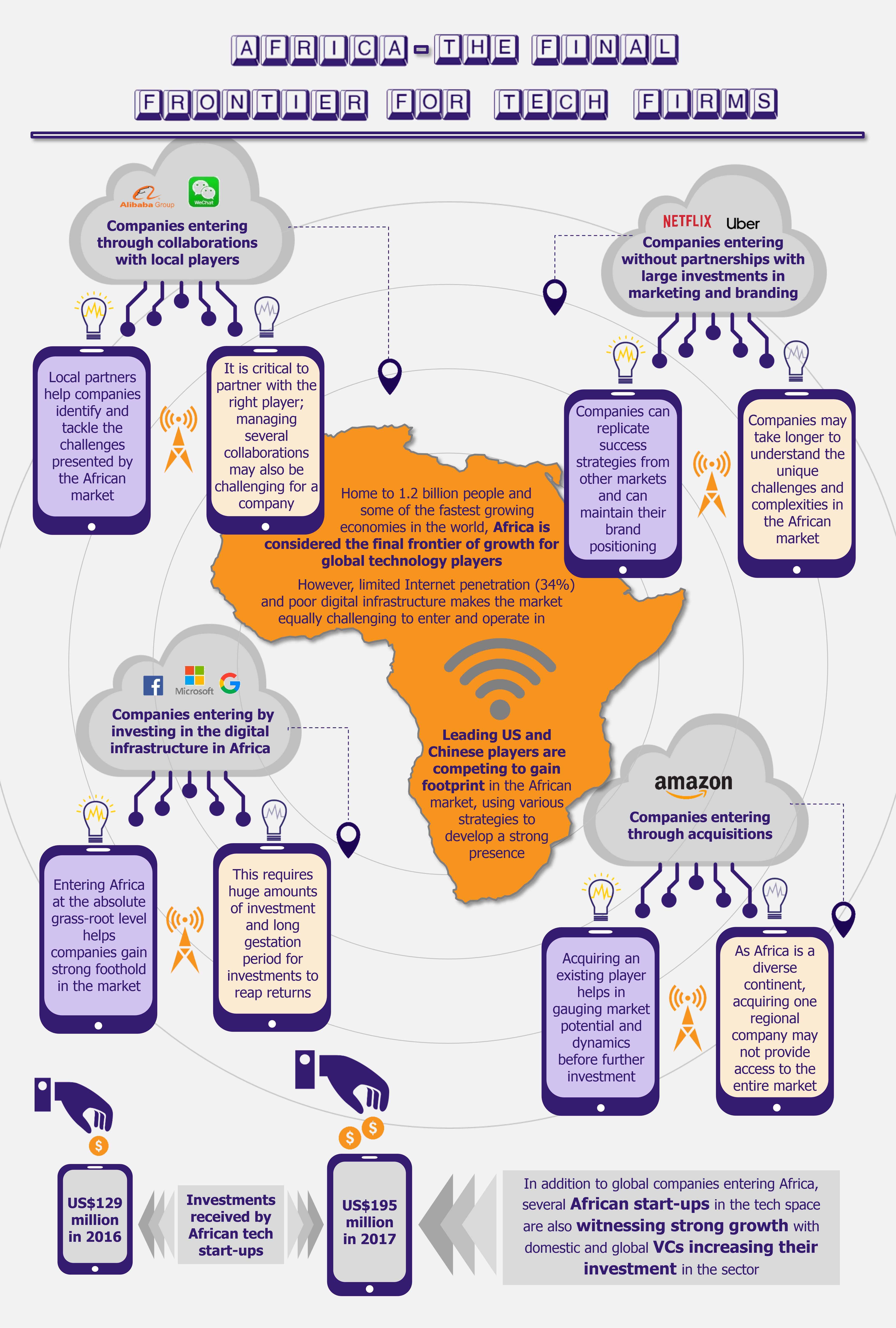
While in the past, most global tech companies have focused their attention on emerging Asian markets, such as India, Indonesia, Vietnam, etc., they have now understood the potential also offered by African markets. Africa currently stands at the brink of technical renaissance, with tech giants from the USA and China competing to establish here a strong foothold. That being said, Africa’s technological landscape is extremely complex owing to major connectivity and logistical issues, along with a limited Internet user base. Companies that wish to enter the African markets by replicating their entry and operating models from other regions cannot be assured of success. In addition to global tech firms building their ground in Africa, a host of African start-ups are increasingly finding funding from local as well as global VC and tech players.
Great potential challenged by insufficient connectivity
Boasting of a population exceeding 1.2 billion (spread across 50 countries) and being home to six of the world’s ten fastest-growing economies, Africa is increasingly seen as the final frontier by large global technology firms.
However, the African landscape presents its own set of challenges, which makes increasing tech penetration extremely complex in the market. To begin with, only about 35% of the continent’s population has access to the Internet, as compared with the global rate of 54%. Thus, Africa’s future in the technology space greatly depends on its ability to improve digital connectivity. This also stands in the way of large tech-based players that wish to gain foothold in the market.
Large players try to lay the necessary foundations
Due to this fundamental challenge, companies such as Google, Facebook, and IBM have initiated long-pronged strategies focusing on connectivity and building infrastructure across Africa. Facebook’s Free Basics program (which provides access to a few websites, including Facebook and Whatsapp, without the need to pay for mobile data) has been greatly focused on Africa, and is available in 27 African countries. With Facebook’s partnership with Airtel Africa, the company has started to strengthen its position in the continent.
Similarly, Google has launched Project Link, under which it rolled out a metro fiber network in Kampala, Uganda, with Ghana being in the pipeline. Through such efforts and investments, Google is aimed at bringing about faster and more reliable internet to the Africans.
Microsoft, which has been one of the first players to enter the African turf, is also undertaking projects to improve connectivity in Africa. The company has invested in white spaces technology, which uses unused radio spectrum to provide Wi-Fi connectivity at comparatively lower costs.
However, managing to get people online is only the first step in the long journey to develop a growing market. Companies need to understand the specific dynamics of the local markets and develop new business models that will fit well in the African market.
For instance, globally, the revenue model for several leading tech companies, such as Google and Facebook, largely depend on online advertising. However, the same model may not thrive in most African markets due to a limited digital footprint of the consumers as well as the fact that the business community in the continent continues to draw most transactions offline, using cash.
Players employ a range of strategies to penetrate the market
These tech giants must work closely with local businesses and achieve an in-depth understanding of the unique challenges and opportunities that the African continent presents. Therefore, these companies are increasingly focusing on looking for collaborations that will help in the development of successful and sustainable businesses in the continent.
Leading players, such as Google and Microsoft have been investing heavily in training local enterprises in digital skills to encourage businesses to go online, so that they will become potential customers for them in the future.
While this strategy has been used somewhat extensively by US-based and European companies, a few Chinese players have recently joined the bandwagon. For instance, Alibaba’s founder, Jack Ma announced a US$10 million African Young Entrepreneurs Fund on his first visit to Africa in July 2017. The scheme will help 200 budding entrepreneurs learn and develop their tech business with support from Alibaba.
The company has also been focusing on partnerships and collaborations to strengthen its position in the African market. Understanding the logistical challenges in the African continent, Alibaba has signed a wide-ranging agreement with French conglomerate, Bollore Group, which covers cloud services, digital transformation, clean energy, mobility, and logistics. The logistics part of the agreement will help Alibaba leverage on Bollore’s strong logistics network in Africa’s French-speaking nations.
Considering the importance of mobile wallets and m-payments in Africa, Alibaba has expanded its payment system, Alipay, to South Africa (through a partnership with Zapper, a South Africa-based mobile payment system) as well as Kenya (through a partnership with Equitel, a Kenya-based mobile virtual network operator). In many ways, it is applying its lessons learnt in the Chinese market with regards to payments and logistics, to better serve the African continent.
While Chinese players (such as Alibaba and Baidu) have been comparatively late in entering the African turf, they are expected to pose a tough competition to their Western counterparts as they have the advantage of coming from an emerging market themselves, with a somewhat better understanding of the challenges and complexities of a digitally backward market.
For instance, messaging app WeChat brought in by Tencent, China-based telecom player, has provided stiff competition to Whatsapp, which is owned by Facebook and is a leading player in this space. WeChat has used its experience in the Chinese market (where mobile banking is also popular just as it is across Africa) and has collaborated with Standard Chartered Bank to launch WeChat wallet. In addition, WeChat has collaborated with South Africa’s largest media company, Naspers, which has provided several value added services to its consumers (such as voting services to viewers of reality shows, which are very popular in Africa). Thus, by aligning the app to the needs and preferences of the African consumers, it has made the app into something more than just a messaging service.
While collaboration has been the go-to strategy for a majority of tech companies, a few players have preferred to enter the market by themselves. Uber, a leading peer-to-peer ridesharing company entered Africa without collaborations and is currently present in 16 countries.
While entering without forging partnerships with local entities helps a company maintain full control over its operations in the market, in some cases it may result in slower adoption of its services by the local population (as they may not be completely aligned with their preferences and needs). This can be seen in the case of Netflix, a leading player in the video streaming service, which extended its services to all 54 countries in Africa in January 2016 (the company has, however, largely focused on South Africa). Despite being a global leader, Netflix has witnessed conservative growth in the continent and expects only 500,000 subscribers across the continent by 2020.
On the other hand, Africa’s local players ShowMax and iROKO TV have gained more traction, due to better pricing, being more mobile friendly (downloading option) and having more relatable and local content, which made their offer more attractive to local populations.
Netflix, slowly understanding the complexities of the market, has now started developing local content for the South African market and working on offering Netflix in local currency. The company has also decided to collaborate with a few local and Middle-Eastern players to find a stronger foothold in the market. In November 2018, the company signed a partnership with Telkom, a South African telecommunication company, wherein Netflix will be available on Telkom’s LIT TV Box. Similarly, it partnered with Dubai-based pay-TV player, OSN, wherein OSN subscribers in North Africa and Middle East will gain access to Netflix’s content available across the region. However, while Netflix may manage to develop a broader subscriber base in South Africa and a few other more developed countries, there is a long road ahead for the company to capture the African continent as a whole, especially since its focus has been on TV-based partnerships rather than mobile (which is a more popular medium for the Internet in Africa).
On the other hand, Chinese pay-TV player, StarTimes has had a decade-long run in Africa and has more than 20 million subscribers across 30 African countries. While operating by itself, the company has strongly focused on local content and sports. It also deploys a significant marketing budget in the African market. For instance, it signed a 10-year broadcast and sponsorship deal with Uganda’s Football Association for US$7 million. To further its reach, the company also announced a project to provide 10,000 African villages with access to television.
US-based e-commerce leader, Amazon, is following a different strategy to penetrate the African markets. Following an inorganic approach, in 2017, Amazon acquired a Dubai-based e-retailer, Souq.com, which has presence in North Africa. However, the e-commerce giant is moving very slowly on the African front and is expected to invest heavily in building subsidiaries for providing logistics and warehousing as it has done in other markets, such as India. This approach to enter and operate in the African market is not widely popular, as it will require huge investment and a long gestation period.
Local tech start-ups are on the rise
While leading tech giants across the globe are spearheading the technology boom in Africa, developments are also fueled by local start-ups. As per the Disrupt Africa Tech Startups Funding Report 2017, 159 African tech start-ups received investments of about US$195 million in 2017, marking a more than 50% increase when compared to the investments received in 2016.
While South Africa, Nigeria, and Kenya remained the top three investment destinations, there is an increasing investor interest in less developed markets, such as Ghana, Egypt, and Uganda. Start-ups in the fintech space received maximum interest and investments. Moreover, international VC such as Amadeus and EchoVC as well as local African funds appear keen to invest in African start-ups. The African governments are also supporting start-up players in the tech space – a prime example being the Egyptian government launching its own fund dedicated to this objective.
African fintech start-ups, Branch and Cellulant, have been two of the most successful players in the field, raising US$70 million and US$47.5 million, respectively, in 2018. While Branch is an online micro-lending start-up, Cellulant is a digital payments solution provider. Both companies have significant presence across Africa.
EOS Perspective
Although US-based players were largely the first to enter and develop Africa’s technology market, Chinese players have also increasingly taken a deeper interest in the continent and have the advantage of coming from an emerging market themselves, therefore putting themselves in a better position to understand the challenges faced by tech players in the continent.
Most leading tech players are looking to build their presence in the African markets. Their success depends on how well they can mold their business models to tackle the local market complexities in addition to aligning their product/service offerings with the diverse needs of the local population. While partnering with a local player may enable companies to gain a better understanding of the market potential and limitations, it is equally imperative to identify and partner with the right player, who is in line with the company’s vision and has the required expertise in the field – a task challenging at times in the African markets.
While global tech companies are stirring up the African markets with the technologies and solutions they bring along, a lot is also happening in the local African tech-based start-ups scene, which is receiving an increasing amount of investment from VCs across the world. In the future, these start-ups may become potential acquisition targets for large global players or pose stiff competition to them, either across the continent or in smaller, regional markets.
It is clear that the technological wave has hit Africa, changing the continent’s face. Most African countries, being emerging economies in their formative period, offer a great potential of embracing the new technologies without the struggle of resisting to adopt the new solutions or the problem of fit with legacy systems. It is too early to announce Africa the upcoming leader in emerging technologies, considering the groundwork and investments the continent requires for that to happen, however, Africa has emerged as the next frontier for tech companies, which are causing a digital revolution in the continent as we speak.