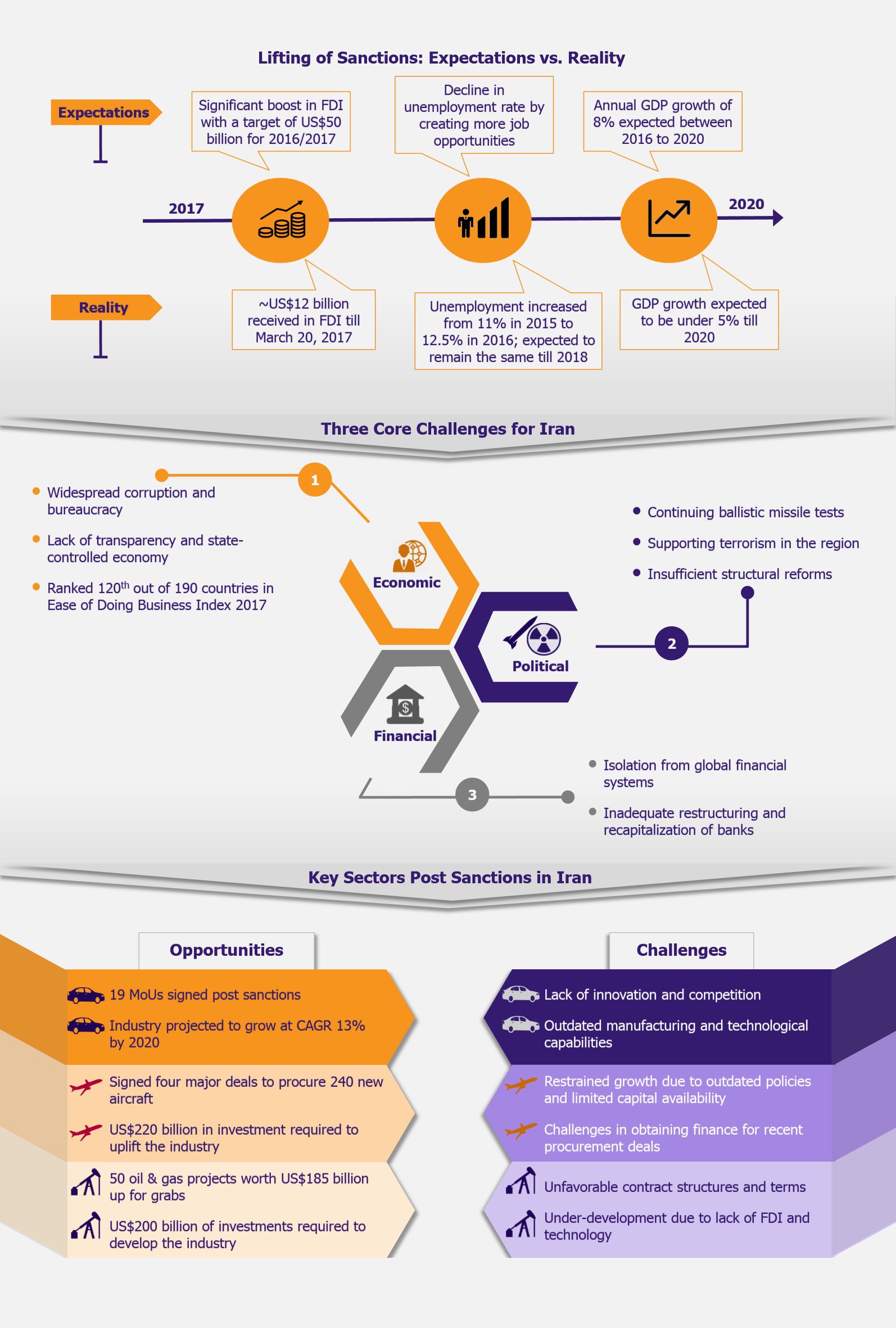
Iran’s emergence from economic isolation in 2016 was considered by many industry experts as the largest market opportunity since the fall of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), paving way for plethora of new business opportunities. They expected massive influx of foreign direct investments (FDI) and a rapid economic growth in the country. As a result, many business delegations traveled from all over the world to Iran, hoping to tap its lucrative industry opportunities. Over a year later, we take a close look at Iran’s progress so far and whether it has truly leveraged its growth potential.
At first glance, multinationals saw the lifting of sanctions as the opening up of paths for foreign investments and international trade in crucial sectors such as oil and gas, automotive, aviation, mining, tourism, and financial services. In addition, Iranian president Rouhani’s long-term political vision with its focus on various domestic structural reforms and the stance on improving relations with the West were viewed by the international business communities as promising signs. Iran achieved 6.6% GDP growth during 2016-2017 as well as a drastic decline in annual inflation to 8.9% from nearly 40% during 2013.
Despite the economic growth achieved, a closer look at the ground realities in the country depicts a different picture, especially when comparing the expectations and the country’s actual achievements so far. The growth achieved in 2016 was largely due to the oil sector’s rebound in both production and exports. Growth in non-oil sectors was mere 0.9% during the first half of 2016. In the same year, unemployment rate also increased to 12.8% from 11% in 2015. There are still serious questions about the country’s ability to sustain its economic stability in the long run. To add fuel to the fire, Iran’s ballistic missile testing and accusations of sponsoring terrorism in the region have brought the nuclear deal again in jeopardy, eroding newly-regained investor confidence.
Although the FDI saw a massive 600% increase in 2016, it is still nowhere near the government’s projections. While several MoUs were signed, not many have converted into actual deals till date. It was realized soon by many that Iran still remains a challenging place for multinationals to conduct business due to high levels of state interruption, bureaucratic bottlenecks, lack of transparency, and outdated business and financial systems. Iran still continues to be isolated from the global financial systems. Majority of international banks are reluctant to re-engage in Iranian transactions mainly due to potential links with terrorism they might be implicated in and massive financial repercussions such transactions could entail. Therefore, investors are holding their horses amid current ambiguity over local and global political developments (Trump’s final stance on nuclear deal as well as President Rouhani’s reforms post elections).
Automotive
The automotive sector is Iran’s second largest industry after oil and gas, contributing around 10% of the GDP. Iran Khodro Company (IKCO) and SAIPA, the two major companies (state funded), have long benefitted from monopoly and protectionist policies, and therefore are reluctant to innovate. Currently, Iranian cars are considered to be of inferior quality mainly due to lack of technological innovation and outdated production platforms. The industry also suffers from price controls, unfavorable import tariffs, and other state interventions.
Since the lifting of sanctions, many expected car prices to decline and FDI to increase, both of which have not materialized quite yet due to the overall financial and political hurdles the country currently faces. Despite 19 MoUs already signed by global automakers, only few have progressed so far. With the new reforms pertaining to local content and export requirements, and the government’s ambitious plan to boost domestic production from 1.6 million cars at present to 3 million cars by 2025, the automotive industry presents a lucrative opportunity for foreign investors. Vehicle sales are projected to grow at a CAGR of 13% by 2020. Joint ventures with foreign automakers and deregulation are the top priorities for the government to unleash the industry potential.
Aviation
Due to the years of economic isolation, Iran’s aviation industry has failed to stay abreast with the latest industry developments, which we discussed in detail in our article New Wings to Fly – Post-Sanction Scenario of Iran’s Aviation Industry in April 2016. The sanctions restricted Iran to procure new planes as well as any maintenance or repair services for its existing fleet. As a result, the nation remains inherited with an outdated fleet that requires immediate modernization. Iran requires nearly US$220 billion in investment to uplift its aviation industry. Besides investments, Iran will have to make significant changes to the existing business and financial policies that have become outdated and unprofitable. The current pricing and finance management strategies have resulted in many local airline companies running with severe losses.
In the post sanctions era, Iran has signed four major procurement deals for over 240 new passenger aircrafts. However, industry experts believe that it will be challenging for Iran to finance these deals. The delivery of third Airbus A330 was postponed recently (March 2017) and banking restrictions were cited as the main reason. Considering the heavy investments required in this sector as well as the current ambiguity of political developments and financing bottlenecks, Iran’s aviation industry will still take a few good years to start its journey towards growth trajectory.
Oil & Gas
Iran’s underdeveloped oil and gas industry has attracted the eyes of many. This was evident from the visit of Chinese president Xi Jinping to the country just weeks after the sanctions were lifted. Oil production has increased rapidly from 3.2 million barrels per day (BPD) in 2015 to 3.7 million BPD in 2016. The total output is expected to reach 4.2 million BPD in 2017. Similarly, exports in the post-sanctions period have also witnessed a rapid surge as many countries resumed purchasing Iranian oil. Experts suggest that Iran also has the potential to supply Europe with around 35 billion cubic meters of gas each year by 2030.
While many multinationals have recognized the country’s potential, various legal, political, and financial hurdles are holding them back from acting on their interest. As a result, despite the high number of initial MoUs signed throughout 2016, only the joint deal between Total, Petropars, and China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC) has materialized so far. With the current government’s strong focus to develop and boost the petrochemicals industry as well as to improve contract politics and terms to attract more investments, there are signs of growth in the medium to long term. The need of the hour for Iran’s oil industry is to attract FDI and technology to improve the current infrastructure in order to meet its long-term goals.
Implications for an Average Iranian
The nuclear deal and its expected socio-economic rewards are yet to yield significant benefits for an average Iranian. Before the recent elections, sentiments were mixed as many Iranians felt that their living standards have not improved as expected. In a recent 2016 survey by University of Maryland, only 46% of Iranians believed the country’s economic situation was good, compared to 54% expressing the same opinion in 2015. It is important to note that structural reforms at a national level and FDI deals require longer timeframes to be implemented and show their true impact on the economy as well as society. For example, it will take years for Airbus and Boeing to complete their deliveries and for Total to start pumping oil, and even longer for the financial benefits of these and other deals to trickle down to general population. Attaining economic prosperity as a result of investment deals is a time-consuming process and not something that happens overnight, hence, it is too early to judge the success or failure of the nuclear deal as of yet. Keeping in mind Iran’s current volatile environment, it will take at least few more years for Iranians to slowly start reaping the rewards.
EOS Perspective
The lifting of sanctions has helped Iran to boost its GDP, oil production, and trade, while at the same time, the country’s continuation of testing nuclear weapons and supporting terrorism has dampened investor confidence and business opportunities. The political and financial risk of doing business with Iran has forced many multinationals to refrain from pursuing new opportunities. In the current context, Rouhani’s recent victory echoes public acceptance towards his overall political propaganda including economic liberalization. The election results are expected to have a positive impact on Iran’s prospects in the next four years, as the government will continue to work towards reviving the economy by improving foreign relations and business policies.
In order to sustain the current economic recovery and to rekindle investor confidence, the government will have to implement major reforms with regards to its state-owned enterprises, financial systems, and business policies. In its second term, the government will have to push for investment promotion, upgrade its outdated policies, promote competitiveness, and business-friendly environment to encourage FDI. Further, with the current level of unemployment and present economic framework, it is clear that the pace of job creation is inadequate. There is a pressing need to diversify the economy and develop private sector free of current bureaucratic challenges. In the long run, the key question is whether Iran can leverage its natural resources to diversify its economic structure and ramp up its economic modernization.
Looking at the promising developments that Iran’s automotive, aviation, and oil and gas sectors have shown so far, there is no doubt about their growth potential in the long term. Over the next year or so, Iran should attempt to re-integrate itself into the global trade and finance systems. This would boost trade and open up more business opportunities, fueling growth in key industry verticals. In the short-term however one can only expect moderate growth.