Brazil is likely to account for approximately half of US$64.4 billion retail e-commerce sales across Latin America in 2019. Being the region’s largest country with a whopping 200 million population, a tech-savvy and consumption-driven middle class, and one of the largest internet-connected populations of the world, Brazil is one of the most preferred Latin American countries where international retailers are looking to expand. However, e-commerce success in Brazil also comes with numerous challenges. Overcoming those challenges still remains a quagmire for e-commerce merchants.
This article is part of a series focusing on e-commerce in LATAM, which also includes a look into e-commerce market in Mexico
The good and the difficult
Despite the economic slowdown and political turbulence in the country, retail e-commerce market has continued to grow, recording 10% y-o-y growth in 2018. Brazilians are connected now more than ever, access to the internet and technologies is becoming affordable by the day, while consumers are particularly enthusiastic to purchase international products using online shopping websites, all of which is making Brazil Latin America’s e-commerce powerhouse. Another key reason for online retail growth is the fact that consumers have become cash-strapped amidst frail economic conditions, which has squeezed money out of the market, bringing a prominent change in buying behavior, where consumers are more price conscious and driven by promotions. In such a scenario, e-commerce has emerged as a clear winner by offering lower prices and good deals, as compared with offline channels.
Operating an e-commerce business in Brazil is a double-edged sword. On the one hand, the 140 million internet users represent an enormous e-commerce opportunity, while on the other hand, Brazil is plagued with operational challenges and struggles.
However, operating an e-commerce business in Brazil is a double-edged sword. On the one hand, the 140 million internet users represent an enormous e-commerce opportunity, while on the other hand, Brazil is plagued with operational challenges and struggles with complex logistics, high tax rates, and payment issues, among others.
An array of challenges
One of the key challenges for any international retailer operating in Brazil is the high tax rate of 6.4% applicable on all international payments, which is enough to disincentivize shoppers to make purchases from international retailers such as Amazon or Alibaba. Further, customers are required to pay 60% flat tax on all imported product purchases valued between US$50-500 (the range may vary across different states). The taxes almost double the price of products, which could deter digital sales. In addition to the taxes, Brazil’s customs procedures are slow and complex, and shipments take a long time to arrive, making the online shopping experience arduous for customers.
For international retailers to operate in Brazil, it is crucial that they familiarize themselves with various local payment methods such as Boleto Bancário (bank slips), payment options offered by regional players (MercadoLivre offers MercadoPago, which is equivalent to PayPal), among others. This is because only 20% of Brazilians have access to international credit cards and instead prefer paying through local payment channels. This could be an obstacle for e-commerce players, as most transactions on shopping websites rely on online card payments. Furthermore, credit cards provided by domestic banks can only issue payments that are made in Brazilian Real, hence, international retailers need to find a way to convert currency if they want to operate in Brazil.
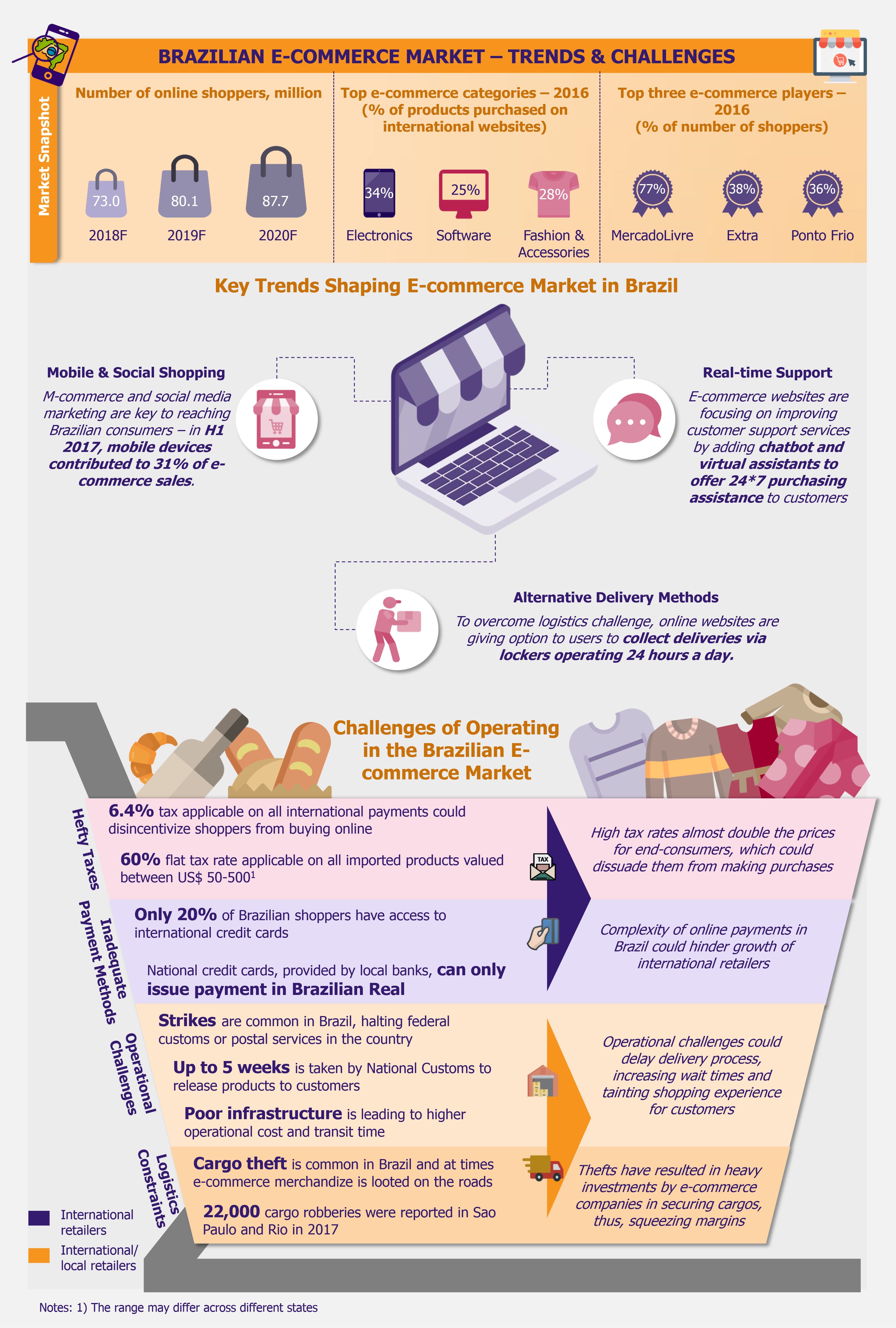
There are also several operational, logistics, and infrastructural challenges that are impairing e-commerce growth in the country. Strikes in Brazil are very common and happen quite often, consequently halting operations of federal customs or postal services. It usually takes some time to resume operations after the strike and the packages/deliveries could take even longer to reach the final destination. The recent truckers strike in spring of 2018 caused more than 3 million online deliveries to arrive with significant delays.
The country also lacks proper infrastructure to support e-commerce business – the distribution centers rarely function 24-hours a day due to security concerns and costly overtimes, which prevents shippers from collecting packages at night when the traffic is lower. Further, traffic situation in major Brazilian cities such Rio de Janeiro and Sao Paulo is so overwhelming that same day or next day shipping requirements are very difficult to fulfill. In addition, rampant cargo robberies are further disrupting e-commerce business in Brazil and are an acute problem in Rio. All major e-commerce players and logistics companies are investing heavily to protect goods, which increases security costs and is subsequently squeezing profit margins. Sao Paulo’s cargo transportation and logistics companies spend about 10-14% of revenue on ensuring cargo safety, while in Rio this ratio lies between 15% and 20% of revenue.
Sao Paulo’s cargo transportation and logistics companies spend about 10-14% of revenue on ensuring cargo safety, while in Rio this ratio lies between 15% and 20% of revenue.
Strong fundamentals promise opportunities
Nonetheless, challenges have not yet dissuaded customers from shopping online or prevented international and local players to expand operations in Brazil. Players are continuously making efforts to improve services to lure customers. One of the key trends that are reshaping customer support services is the increasing focus to provide chatbots on e-commerce websites for 24-hour shopping assistance. Brazilian e-commerce players are betting on chatbots to improve customer engagement and management, and to generate brand awareness.
With rising number of smartphone users in Brazil, mobile commerce is also growing and players are increasingly focusing on tapping this opportunity. In 2017, m-commerce users grew 42% y-o-y and mobile devices contributed to 31% of e-commerce sales in H1 2017. Furthermore, Brazil is a country with highly active social media users, a fact which serves as a key platform to expand business – as of March 2016, 60% of e-commerce sites used social media for sales and marketing. Numerous Brazilian companies use social media for marketing and it has become an integral part of e-commerce business, where social media is used as a tool for promotion and to reach out to customers.
EOS Perspective
While Brazil’s e-commerce market could be a cash cow for retailers, it also comes with various quirks and challenges. Localizing business in Brazil requires enormous amount of planning, calculation, and understanding the market before entering it. The high cost of doing business could be intimidating for several players along with online payment challenges, hefty taxes, and inferior infrastructure. However, forging local partnerships could solve some of the issues. For instance, cross-border e-commerce merchants could partner with Brazilian payment processing companies and invest in developing local payment methods to overcome the online payment challenge.
Alternative delivery channels are becoming popular, and these could help solve the logistics and shipping issues to a certain extent. InPost, a Polish company that operates a network of parcel lockers, introduced click and collect services in Brazil, which allows customers to place an order online and collect package from InPost’s lockers that are situated at most frequently visited places such as gas stations. Customers receive a QR code by email, which is used to operate the lockers. The lockers offer convenience for customers and reduce wait times, and greatly reduce logistics cost for retailers. While this is only one of potential novelties that could ease logistics problems, the arrival of established international retailers such as Amazon and Alibaba might be expected to bring in other innovations to reduce delivery, infrastructure, and payment barriers.
Despite the existing macro-economic and operational challenges, the country’s potential as a digital commerce market will continue to attract investments and is expected to keep growing.
Despite the existing macro-economic and operational challenges, the country’s potential as a digital commerce market will continue to attract investments and is expected to keep growing. With a large internet savvy consumer market eager to purchase international products and with westernization deeply influencing the young population, Brazil will continue to draw the attention of international retailers across the world. Amidst the country’s turbulent politics and economy, purchasing power grew 3% y-o-y in 2017, making Brazil even more attractive for online retailers. With new trends reshaping the industry and players forging ways to improve operations, the country is expected to remain the largest e-commerce market of Latin America ahead of Mexico and Argentina in the foreseeable future.