Not many years ago, veganism or consumption of only plant-based foods, was considered an extreme form of lifestyle. Food options that were available for vegans were very limited and meat alternatives were based mainly on tofu, tempeh, and nuts. However, this is not the case anymore. Not only has the mindset regarding vegan food changed in the recent times, but also plant-based alternatives have become the fastest growing food category in the USA. This is also driven by a greater number of meat eaters experimenting with plant-based meat alternatives, whether due to health benefits, growing awareness regarding animal cruelty, or environmental reasons. Moreover, tremendous amount of investment and research in this space has resulted in wide range of food options, including vegan cheese and vegan meats that taste similar to animal-based proteins.
Vegan food has been around for quite some time now, but it was largely considered to be a niche market having a separate shelf in the supermarkets or being served in vegan-only restaurants and cafes. Moreover, it was considered an extreme lifestyle by many. However, over recent years, vegan meal options have found their way into the mainstream, with more and more people embracing veganism and meat-eaters adding plant-based food options in their diet. This is clearly evident from the steep growth witnessed by this food category, especially in the western world.
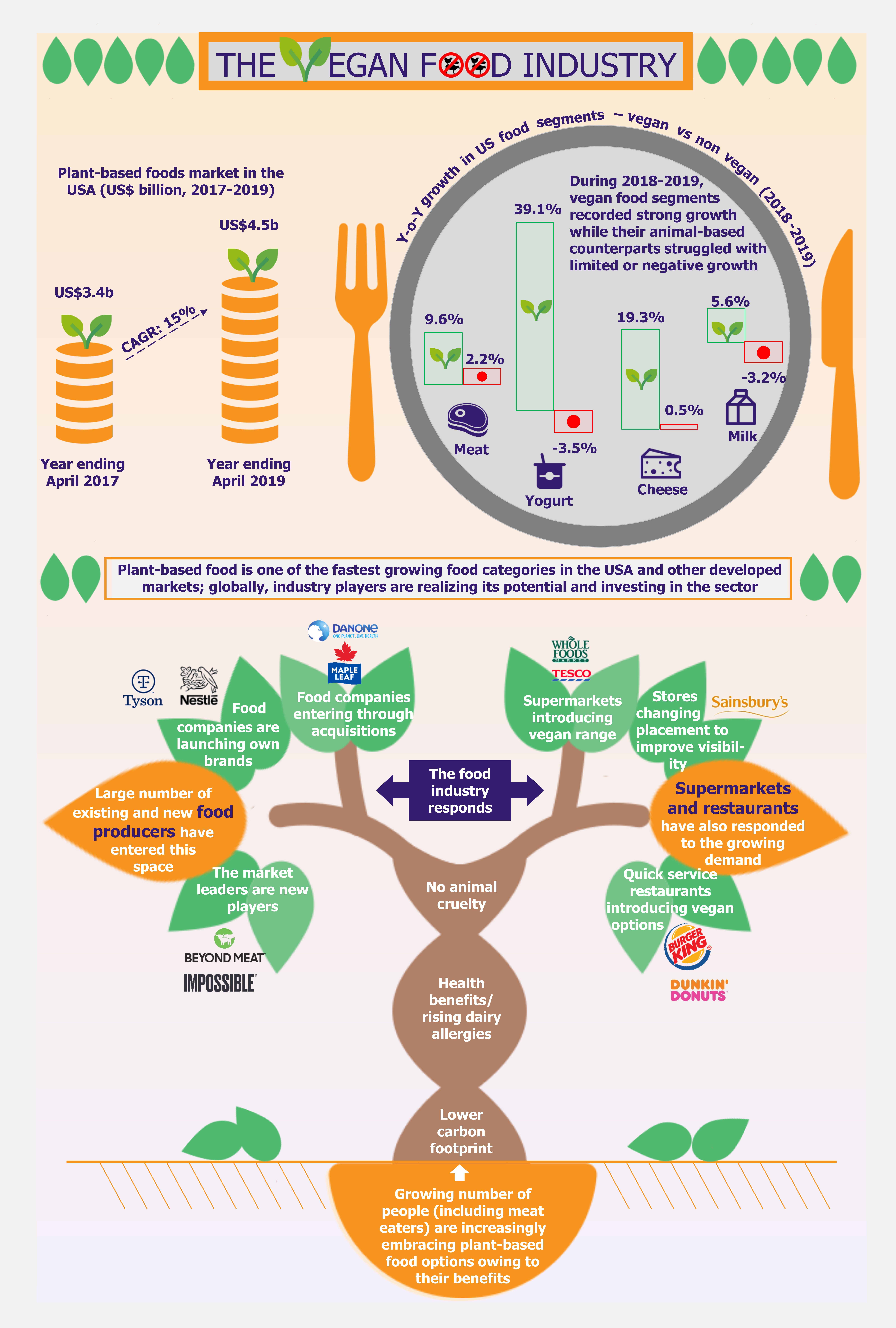
As per a study commissioned by the Good Food Institute (GFI) and the Plant Based Food Association in the USA, the retail market for plant-based foods was valued at about US$4.5 billion in April 2019, registering a year-on-year increase of about 11% and a growth of 31% in the two-year period from April 2017 through April 2019. The largest segment of vegan food market in the year ending April 2019 was the plant-based milk segment, which comprised about 40% of sales (US$1.9 billion). This category witnessed a y-o-y increase of about 6%. To put this in further perspective, animal-derived milk sales for the same period declined by 3%. While plant-based meat alternatives, cheeses, yogurts, eggs, and creamers are relatively new and smaller categories, they are driving growth in the vegan food segment too.
The growing sales across most vegan food segments indicate a momentous shift towards a vegan diet, which is not only propelled by an increasing number of people turning purely vegan but also a rise in meat eaters that prefer plant-based alternatives in some food categories, such as milk and milk-based products. This is due to growing lactose intolerance among consumers, with about 65% of the world’s population estimated to be lactose intolerant. The environmental benefits (i.e. lower carbon footprint) of maintaining a vegan diet and a growing uproar regarding animal cruelty have also driven conscious consumers to adopt a vegan lifestyle.
The environmental benefits (i.e. lower carbon footprint) of maintaining a vegan diet and a growing uproar regarding animal cruelty have also driven conscious consumers to adopt a vegan lifestyle.
The trend is further supported by the launch of vegan meat substitutes that resemble meat products in taste, look, and even texture. US-based players, Impossible Foods and Beyond Meat, are leading this space with the latter having received investments from the likes of Bill Gates, Leonardo DiCaprio, and Twitter co-founders Biz Stone and Evan Williams.
Industry players are diversifying into plant-based foods
Understanding that this trend is more than just a fad, several food companies (including large meat producers) have started entering this space, by either buying or investing in plant-based food start-ups.
Tyson Foods, USA’s leading meat producer, invested in Beyond Meat in 2016 and 2017, by acquiring a 6.52% stake in the company. However, in April 2019, Tyson Foods sold its stake in Beyond Meat with an intention to develop its in-house line of alternative (plant-based) protein products.
Nestle, which is one of the largest food companies globally, has also been expanding its portfolio with a keen focus on plant-based alternatives. In 2017, the company purchased Sweet Earth, a California-based producer of vegan meals and snacks, while in 2018, it purchased majority stake in Terrafertil, a plant-based organic food player that was founded in Ecuador and has presence across the USA, UK, and Latin America.
In January 2019, Nestle expressed its plans to launch its in-house vegan burger patty, called the Incredible Burger under its Garden Gourmet brand. The company is also looking to develop a portfolio of dairy-free beverages, such as purple milk (which is made with walnuts and blueberries) and blue latte containing spirulina algae. It is also adding vegan options to its existing brands, such as Haagen-Dazs (which launched a range of dairy-free ice creams in July 2017) and Nescafe (which introduced vegan protein-based coffee smoothies in December 2018).
Similarly, Marfig, Brazil-based leading meat processor, also entered the plant-based food alternatives market through a partnership with Archer Daniels Midland in August 2019. Under the partnership, Archer Daniels Midland will produce the raw material while Marfig will produce and sell the end product through foodservice and retail channels.
Canada-based Maple Leaf has also made significant investments in plant-based food players to expand its product portfolio and brand positioning. In February 2018, it acquired US-based plant protein manufacturer, Lightlife Foods, for US$140 million. Through this acquisition, it added Lightlife’s refrigerated plant-based products, such as hot dogs, breakfast foods, and burgers, to its portfolio and garnered a strong footprint in the US plant-based food market. To further strengthen its hold in this market, in December 2018, the company entered into an agreement to buy US-based Field Roast Grain Meat Co. for US$120 million. Field Roast Grain Meat supplies grain-based meat alternatives (including sausages, burgers, etc.) and vegan cheese products to the North American market.
Danone, a global food company with large number of dairy products is also bullish on the growing popularity of plant-based foods. In April 2017, it purchased WhiteWave Foods, a US-based leading player in plant-based food and beverage for US$10 billion. It rebranded the company to DanoneWave and in October 2017, further invested US$60 million into its plant-based milk operations. In 2019, the company expressed plans to triple its revenue (to about US$5.6 billion) from its plant-based food line by 2025.
In addition to these, many other large food processors and retailers have entered the plant-based food market either through acquisitions or the launch of in-house products and brands. These include Brazil-based JBS Foods, US-based Smithfield Foods, UK-based Hilton Food Group, Germany-based Wiesenhof, UK-based Heck Food, Canada-based Saputo, and US-based Dean Foods Company, among many others.
In addition to these leading food producers, many other large food processors and retailers have entered the plant-based food market either through acquisitions or the launch of in-house products and brands.
Fast food chains have also joined the vegan bandwagon. In April 2019, Burger King introduced a vegan version of its classic sandwich, called the Impossible Whopper. Similarly, Dunkin introduced a vegan breakfast sausage made by Beyond Meat, while KFC launched vegan fried chicken also made by Beyond Meat. In 2017, McDonald’s launched a vegan burger in Finland and Sweden and has plans to launch the same in Germany. In 2016, UK-based café, Pret a Manger opened a vegan pop-up store in central London and later made it permanent in 2017. Over the years, it opened three more stores (two in London and one in Manchester) under the name Veggie Pret. In April 2019, the company purchased rival food chain, Eat, and aims to convert about 90 of its stores into its vegan chain, Veggie Pret.
Just like the food producers and quick service restaurant chains, supermarkets have also been quick to respond to the vegan trend. In 2018, Tesco, a leading UK-based supermarket chain, launched its own range of vegan foods under the name Wicked Kitchen. Similarly, British department store chain, Marks & Spencer has also introduced a vegan food range in its food department. Vegan options have been introduced and are easily available across a wide range of US-based departmental stores such as Whole Foods, Target, and Kroger.
However, the key shift seen in departmental stores regarding plant-based meals is their placement. Traditionally, vegan food including plant-based meats and dairy were stocked together in a ‘vegetarian’ or ‘vegan’ isle or section. However, recently, these options have begun to be stored alongside their animal-based counterparts. For instance, plant-based dairy has now been moved to the beverage or dairy case. This exposes shoppers to a wider range of options for milk and increases the shopper’s chances of trying plant-based alternatives. This thereby opens the category to shoppers who otherwise would have not explored the separate vegan section in the store.
Similarly, plant-based meat options are also being increasingly stored along with traditional meat items, widening the choice for consumers who are flexitarians (i.e. consumers who are not completely vegan but do also consume vegan food from time to time). UK-based department chain, Sainsbury, was the first supermarket in the UK to place vegan products that are designed to look and taste like meat within the meat section.
Challenges ahead
While the number of vegan consumers is on the rise, it is still very low when compared with people consuming a meat-based diet. Moreover, while a great number of people are exploring vegan options, vegan meals are still largely perceived as offering limited nutritional value when compared with traditional meat-based meals, especially with regards to protein intake. While there is limited truth to this, companies offering vegan options have to invest substantially to educate consumers regarding the nutritional value of vegan meals.
In addition to this, vegan or plant-based meal options face another mindset block. Meat eating has long been associated with masculinity. This by contrary gives vegan meals a perception of being less ‘manly’ and thereby limiting the number of men who are open to embracing this meal option. To counter this, market leaders such as Impossible Foods and Beyond Meat have been avoiding terms such as vegan and vegetarian in their marketing strategy and have been promoting their burgers at male-centric locations such as sports events. Instead of pushing men to eat less meat, they are working towards expanding the definition of meat in the consumer’s mind to include plant-based options. They have also included ingredients (such as beet juice) in their burger to resemble a bleeding beef, making it clone the beef burger in terms of appearance, texture, and experience of consuming.
Other than mindset, price is also currently a considerable barrier for consumers. Plant-based meat substitutes are more expensive when compared with animal meat. While the Beyond Burger sells for about US$12 a pound at Whole Foods (a leading retail chain), its beef counterpart retails for about US$5. Similarly, Beyond Meat’s, Beyond Sausage retails for US$10.30 a pound, charging a premium of about 70% over a comparable pork sausage. Higher price points are off-putting for a big chunk of consumers, who may otherwise be willing to change eating habits owing to health or environmental reasons. While currently, the prices differ greatly, it is expected that the price difference will reduce in the long run (or be wiped off completely). Understanding price to be a big limiting factor, companies such as Beyond Meat are researching and investing into alternative plant protein sources that would lower the cost.
Price is also currently a considerable barrier for consumers. Plant-based meat substitutes are more expensive when compared with animal meat. While the Beyond Burger sells for about US$12 a pound at Whole Foods (a leading retail chain), its beef counterpart retails for about US$5.
However, one of the biggest roadblocks faced by the vegan food producers in making them mainstream is the backlash from the meat industry, which has in some cases resulted in labeling regulations that are damaging for the growth of the plant-based food sector.
In 2017, the EU banned the use of the term ‘milk’ and other dairy products, such as ‘cheese’, ‘yogurt’, etc., for plant-based alternatives (however, traditional versions such as almond or coconut milk and peanut butter are excluded from the ban).
In April 2018, France banned meat names for plant-based alternatives, such as vegetable ‘steak’, soy ‘sausage’, and ‘bacon-flavored strips’. Similarly, in May 2019, the European Parliament’s agriculture committee proposed a ban on the use of meat-related terminology on their labels and product description for vegetarian or vegan products. This includes terms such as ‘steak’, ‘sausage’, and ‘burger’. The proposal will be voted upon by the Members of the European Parliament in autumn 2019 and if passed, will be a big setback to the vegan industry as they would be required to remove the word burger from any product that does not contain meat.
In the USA, a Dairy Pride Act, which requires FDA to stop all plant-based dairy alternatives from being labeled as ‘milk’, was reintroduced in Congress in March 2019 (after being squashed earlier in 2017). While the chances of the bill being passed remain slim, if passed, it could seriously dampen growth in the vegan dairy market in the USA. Most of these legal actions are likely to have stemmed from strong meat and dairy lobbies that are directly impacted by the growth witnessed in the vegan market.
EOS Perspective
There is no doubt that the plant-based food market is growing exponentially and the food industry is taking notice. Meat producers and animal-based dairy companies are currently at a fork, where they may face some level of cannibalization of sales (especially in case of dairy) when they introduce vegan alternatives to their portfolio. The cases of Kodak and Apple are important examples when discussing the prospects of cannibalization of sales. While Kodak failed to innovate at the time of camera digitalization due to a fear of cannibalizing sales of its then popular camera films, Apple has made this one of its strength by innovating and launching new products that have (to an extent) cannibalized its own sales (IPhone for IPods and IPad for Mac).
While most players in the food industry have been quick to understand the potential of plant-based food market and have started to invest in this segment, several others still remain resistant to change. This may cost them dearly. Moreover, evaluating the future prospects of this industry, it may be prudent for meat producers to be focusing more on their plant-based food section than their long existing meat business. In a first of its kind case, in May 2019, Vivera Foodgroup, a leading European meat company sold off its meat business retailed under the brand name, Enkco, to Netherland-based Van Loon Group so that it could solely focus on its vegan food line.
However, while plant-based foods seem to be the future now, things may stir up again when clean meat (also known as lab-grown meat) goes mainstream. Currently, a lot of industry players (such as Tyson Foods) and business tycoons (such as Bill Gates) have begun investing in companies that are researching and developing lab-grown meat. It is expected to become a reality very soon, however, it may still take some years for lab-grown meat to match the prices and volume of farmed animal meat as well as obtain the required regulatory approval. While clean meat will definitely upset sales of farmed meat, it may also have a considerable impact on the plant-based food market as several consumers (who turned to vegan options due to animal cruelty and environmental reasons), may switch to clean meat instead of vegan alternatives. Thus vegan companies must stay ahead of the curve in terms of pricing as well flavors and product range to not only thrive but also survive in the coming times.