The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) into the healthcare industry has significantly transformed the delivery of medical services, enhanced patient experiences, and revolutionized medical practices. While the benefits of IoT are undeniable, there are challenges that come with its adoption. Issues such as device hacking and data breaches pose significant obstacles that must be addressed. Therefore, it is essential for device manufacturers to design medical devices with caution. By taking a proactive approach and investing in robust cybersecurity measures during the design and development phases, manufacturers can create devices that are more secure and less vulnerable to hacking.
IoT has revolutionized the healthcare industry by enabling medical devices to connect and communicate with each other, as well as with healthcare providers and patients. These devices utilize cloud computing and collect valuable data in real time, allowing for remote monitoring, timely interventions, and personalized care.
The average hospital room worldwide has an estimated 15 to 20 interconnected medical devices. This number is steadily increasing due to the rising adoption of internet-connected devices. The market for IoT medical devices is close to US$40 billion as of 2023. With exponential growth, it is likely to cross US$150 billion over the next five years. This upward trajectory is geared towards reducing healthcare systems’ costs, enhancing patient care, and streamlining clinician workflows.
Healthcare organizations are not immune to cybersecurity breaches
Amid this inevitable growth in adoption, it is crucial to prioritize the security of medical devices to protect patients’ lives, safety, and privacy. While these devices have the potential to streamline and improve treatment, they also pose significant risks due to their susceptibility to cyberattacks.
According to a 2019 report by Fierce Healthcare, 82% of healthcare organizations experienced cyberattacks targeting IoT devices. Moreover, about 53% of medical and IoT devices in hospitals had vulnerabilities. Cybercriminals have honed in on the healthcare industry as a prime target, capitalizing on its perceived lack of robust cybersecurity protocols.
Healthcare bleeds out money without a cybersecurity cure
According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach 2023 report, the average cost of a cyberattack in the healthcare industry is US$4.45 million per breach, marking a 2.3% increase from the previous year’s average cost of US$4.35 million.
This significant uptick in costs since 2020, when the average overall cost of a data breach was US$3.86 million, represents a substantial 15.3% increase over three years. This growth underscores the importance of prioritizing cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive patient data and ensure the safety and integrity of medical devices in healthcare settings.
Unaddressed IoT challenges in medical devices lead to unauthorized access
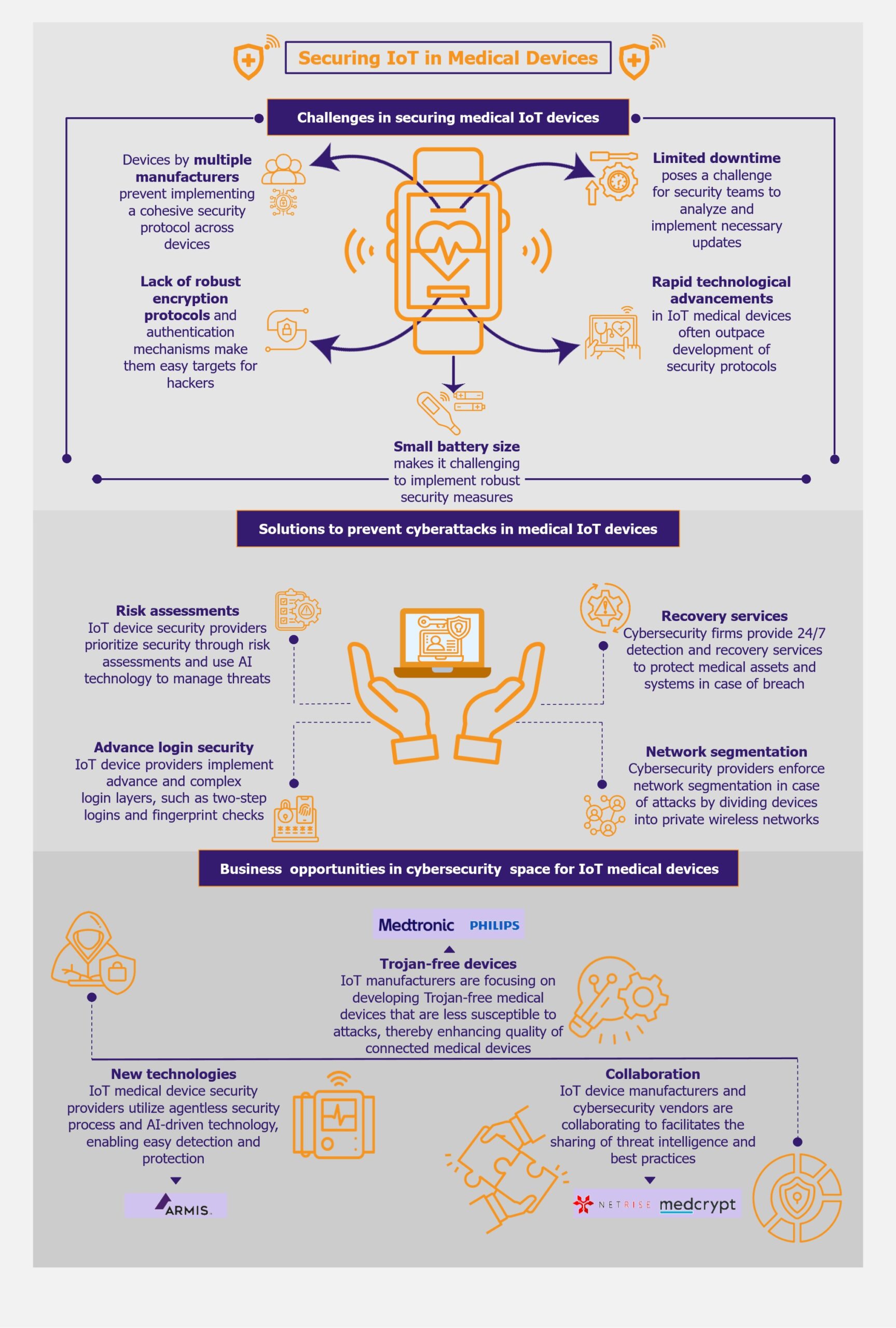
Despite the many potential benefits of IoT medical devices in healthcare, the lack of adequate security measures continues to be one of their main challenges. Many devices do not have robust encryption protocols or authentication mechanisms, making them easy targets for hackers.
These vulnerabilities could potentially be exploited to gain unauthorized access to patient information or manipulate the device to deliver harmful treatments. As these devices become more interconnected with other healthcare systems, the potential cyberattacks only increase, posing a serious threat to patient safety.
Prescribing Security Diagnosing and Treating the IoT Universe in Healthcare by EOS Intelligence
Hackers endanger patients’ health and lives
Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in IoT medical devices to gain access to sensitive patient information, alter treatment settings, or sabotage critical systems. This poses a grave threat to patient safety and privacy, as well as the overall integrity of healthcare infrastructure. Furthermore, since IoT devices are interconnected, a breach in one device could potentially compromise the entire network, leading to widespread disruptions and chaos in healthcare delivery.
One example of such a breach occurred in 2019 at a Springhill Medical Centre in the USA involving a ransomware attack. This attack disabled patient monitors for several days, leading to a substantial impact on patient care. A lawsuit has been filed, alleging that the disabled monitoring devices led to infant death during delivery at the center.
IoT medical devices need improved security to match technological advancements
The rapid pace of technological advancements in IoT medical devices often outpaces the development of security protocols. New features and functionalities are constantly added to these devices to improve patient care.
However, these updates may also introduce additional security vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit. Many healthcare providers struggle to keep up with these evolving threats and may not have the resources or expertise to effectively secure their IoT devices on an ongoing basis.
Diversity of IoT devices complicates securing healthcare environments
The healthcare environment is characterized by a diverse range of interconnected devices, often developed by various manufacturers with varying security protocols, making it difficult to implement a cohesive security strategy across all devices. This diversity complicates efforts to achieve comprehensive visibility and security, as each device may require distinct monitoring and protection strategies.
Additionally, the sheer number of devices in use within a healthcare facility can overwhelm IT teams responsible for monitoring and securing them, increasing the likelihood of overlooking potential security risks.
Limited downtime poses cybersecurity challenges
IoT medical devices are used continuously in real time, leaving little room for downtime. This lack of downtime poses a challenge for security teams, as they have limited time to analyze the devices and implement necessary patches to ensure their security.
The constant use of these devices in healthcare settings highlights the importance of finding a balance between security and functionality in order to safeguard sensitive patient data and uphold the integrity of the healthcare system.
Devices’ size and continuous connection result in insufficient battery support
Another challenge in the realm of IoT devices is related to their powering. Many of these devices use batteries and their compact size restricts the capacity for large, durable batteries. They need to be constantly connected to transmit data, which continually drains power.
These devices’ limited power and memory make it difficult to incorporate encryption, continuous software updates, and authentication protocols that can protect sensitive patient information from hackers.
Durability of IoT medical devices poses a security risk
Additionally, IoT medical devices are engineered to have a long lifespan. Their durability can pose a security risk. Once a vendor ceases production or stops releasing updates for these devices, hospitals may continue to rely on outdated technology, making them vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Hospitals must play a role in safeguarding their IoT device systems
Securing healthcare IoT devices can be a complex task, but it is essential to implement a variety of solutions to guarantee their security.
Part of this responsibility lies on the healthcare institutions themselves. Hospitals must ensure regular software updates, avoid default settings, and provide comprehensive training to staff members. Healthcare providers must implement unique and multilayered login structures for every device, such as two-step logins, hard-coded passwords, firewalls, and fingerprint checks to ensure that patient information is securely stored.
Leading players’ solutions increase devices’ resilience to breaches
Advanced and complex security solutions
Prominent vendors, such as Medigate, Medcrypt, and Cynerio, provide advanced platforms designed to assist healthcare organizations in safeguarding their networks and connected medical devices.
These security vendors offer complex security solutions, including real-time threat detection, device monitoring, network activity visibility to medical device manufacturers, and vulnerability management solutions to enable healthcare providers to effectively identify and mitigate potential risks associated with their connected medical devices.
Detection and recovery plan
Cybersecurity providers are generally vigilant in offering detection and recovery services to safeguard medical assets and systems around the clock. In the event of a security breach, they must be able to swiftly implement response and recovery plans to mitigate the impact. With a focus on healthcare, they must be able to identify issues efficiently without overwhelming users with excessive information. They need to aim at taking instant action to restore normalcy as quickly as possible.
Network segmentation
Another important solution players should provide is network segmentation, which involves dividing devices into separate, private wireless networks to protect data in the event of a cyberattack. Firewalls and multi-factor authentication can achieve this. By segmenting the network into distinct zones, healthcare providers can isolate medical devices from other parts of the network, reducing the risk of a cyberattack spreading across the entire network. This segmentation also allows for more granular control over medical devices, limiting the potential for unauthorized access or tampering.
Modern network segmentation for medical devices now relies on technologies such as virtual LANs and subnets to keep up with advanced cyber threats. For instance, Cisco Systems, a multinational technology conglomerate, offers medical device security solutions whose key aspect is network segmentation. Cisco also provides specialized monitoring and analytics tools to assist healthcare organizations in detecting and responding to security incidents in real time. These tools can identify abnormal behavior on the network, alerting security teams to potential threats before they can cause harm.
AI technology and machine learning
IoT device security providers, such as IBM Corporation, Cylera, CyberMDX, Sternum, ClearDATA, and Palo Alto Networks, place emphasis on conducting comprehensive risk assessments during software validation to guarantee devices’ security. In the event of new cyberattacks, these providers inform stakeholders and offer solutions, such as security updates. They have integrated programs that utilize AI technology and machine learning to proactively manage risks and stay ahead of cybersecurity threats.
Security vendors contribute to IoT device safety protocols transformation
The cybersecurity industry is currently experiencing a surge of new companies that are transforming security protocols. Armis, a leading US-based asset intelligence cybersecurity company and provider of agentless device security solutions, is spearheading this movement.
Notably, Medtronic and Zimmer Biomet have incorporated Armis’ security platform into their products, such as insulin pumps and orthopedic devices. Armis offers the Armis Centrix platform, powered by the Armis AI-driven Asset Intelligence Engine. The platform has the capability to detect breaches, run routine security scans or updates, maintain asset visibility, identify blind spots, optimize resource allocation, and perform essential maintenance. Armis’ solutions encompass advanced threat intelligence and machine learning features, enabling the system to adapt to new and emerging threats. This proactive cybersecurity approach is essential in the healthcare sector, where any disruption or compromising of medical devices could have severe repercussions.
Collaboration is key to effectively managing cyberattacks
Collaborations between medical device manufacturers and cybersecurity vendors to combat IoT medical device hacking have great potential. It also facilitates the sharing of threat intelligence and best practices, enabling vendors and manufacturers to proactively address emerging threats and vulnerabilities. Their collaborative efforts center on safeguarding critical devices from cyber risks by implementing protective measures for both the devices and the data they collect.
Philips partnered with CyberMDX to create a vendor-neutral cybersecurity service
In November 2020, Philips, a prominent player in healthcare technology, partnered with CyberMDX, a cybersecurity expert specializing in medical devices. This partnership focused on enhancing the security of connected medical devices and systems, essential for protecting patient data and for the smooth operation of healthcare facilities.
Drawing from Philips’ industry expertise and CyberMDX’s cybersecurity solutions, together they provide vendor-neutral options to protect IoT medical devices. They focus on managing connected devices in hospital settings, whether they are managed or unmanaged, by utilizing a combination of risk assessment, detection, threat intelligence, and prevention capabilities in the constantly evolving healthcare technology landscape.
Medcrypt collaborated with NetRise to address cybersecurity issues
In August 2023, Medcrypt, a US-based proactive cybersecurity provider, partnered with NetRise, another US-based cybersecurity company. By combining Medcrypt’s experience in identifying and managing vulnerabilities with NetRise’s ability to develop Mobile Device Management software featuring a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) for embedded devices and firmware, medical device manufacturers now have access to a comprehensive solution to protect their devices from potential cyber threats throughout their lifecycle.
Medcrypt integrated NetRise’s SBOM generation capabilities into the Helm tool, enabling continuous integration, analysis, and transparency of the ever-changing state of medical device software. This integration facilitates the proactive identification and mitigation of the most exploitable vulnerabilities, extending support for SBOMs across the entire lifecycle of medical devices. The resulting solution empowers medical device manufacturers to create, ingest, enhance, manage, and monitor SBOMs, providing invaluable insights into the vulnerabilities present in their embedded devices and firmware. This collaboration represents a significant advancement in bolstering cybersecurity measures within the healthcare industry.
The industry is moving towards Trojan-free devices to safeguard against cyberattacks
Among the various cybersecurity threats faced by IoT medical devices, hardware Trojans are emerging as a grave concern. Hardware Trojans involve the deliberate manipulation of an integrated circuit or electronic device to compromise its security features or functionality.
Hardware Trojans are typically small in size, consist of only a few gates, and alter the device chip’s functionality. Due to their small size, hardware Trojans are challenging to detect using traditional offline methods such as side-channel analysis or digital systems testing. As a result, the healthcare industry is increasingly prioritizing the development of Trojan-free medical devices to enhance the security of IoT medical devices.
Unlike other medical devices, Trojan-free devices are highly secure and challenging to breach. Attackers would need a high level of expertise to understand the device’s design blueprint through reverse engineering and then create a manipulation that can only be triggered under specific conditions.
Moreover, the development of Trojan-free medical devices presents a unique opportunity for manufacturers to drive innovation, improve patient care, advance cybersecurity solutions, and shape regulatory standards.
One example of a Trojan-free medical device is the Philips IntelliVue patient monitor, which tracks patients’ vital signs and provide real-time data. This device works with advanced network security measures, including firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection/prevention systems, to safeguard against unauthorized access and malware infiltration. Its cybersecurity features are specifically designed to protect against potential threats such as unauthorized access and data breaches.
Boston Scientific’s S-ICD implantable cardioverter-defibrillator is another Trojan-free medical device. It treats patients at risk of sudden cardiac arrest by delivering an electric shock to restore normal heart rhythm. This device employs encryption to secure communication between the device and the programmer and authentication protocols to ensure that only authorized healthcare professionals can access and control it.
EOS Perspective
IoT has transformed numerous industries, with healthcare being no exception. In the realm of healthcare, IoT medical devices utilized in virtual wards, such as remote monitoring devices and wearable sensors, are susceptible to cyberattacks. These attacks can result in unauthorized access, data tampering, and disruption of patient care. Detecting and responding to cyber threats targeting medical devices is crucial.
To combat these threats, security vendors employed prevention systems, anomaly detection algorithms, and advanced analytics to identify potential cyberattacks and abnormal device behavior. Implementing robust incident response plans, conducting simulated exercises, and utilizing strong device security measures is imperative to safeguard against device-level cyber risks.
The field of cybersecurity in healthcare is intricate and constantly evolving. Addressing cybersecurity risks necessitates a comprehensive approach that encompasses technology, policies, regulations, and education. Continuous collaboration, vigilance, and adaptation to emerging threats are essential to ensure the security and safety of medical devices in the future.
Moreover, healthcare facilities must prioritize the implementation of robust device security risk management practices. This involves establishing standard protocols, automating device isolation, utilizing asset intelligence to minimize security breaches, and ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks such as HIPAA, FDA, ISO 13485, and HITRUST when acquiring and managing connected medical devices.
In addition, healthcare facilities must provide comprehensive training to professionals who work with these devices on cybersecurity best practices and identifying potential security threats.
Collaboration between healthcare providers, device manufacturers, cybersecurity experts, and regulatory bodies is essential for enhancing the security of medical IoT devices. By sharing knowledge, resources, and best practices, stakeholders can collectively address vulnerabilities and safeguard healthcare systems.
Their collaborative efforts facilitate the adoption of SBOM formats, threat modeling processes, Secure Product Development Framework, encryption technologies, AI-based anomaly detection, regulatory frameworks, and secure hardware modules. This approach ensures a more secure environment for medical IoT devices and ultimately protects patient data and healthcare systems from potential cyber threats.
Innovations such as blockchain technology, biometric authentication, predictive analytics, regular patching or updates, and Trojan-free medical devices offer promising opportunities to enhance security measures in the healthcare sector. Trojan-free medical devices, in particular, show great potential in safeguarding patient data, ensuring device integrity, and maintaining the trustworthiness of healthcare technology. This not only improves device reliability but also reduces downtime, benefiting both patients and healthcare providers. This is likely the direction the industry will take in the long run.
By prioritizing proactive cybersecurity measures and compliance with regulations, healthcare security providers can offer potential solutions to enhance the security and integrity of medical devices and the data they handle.






