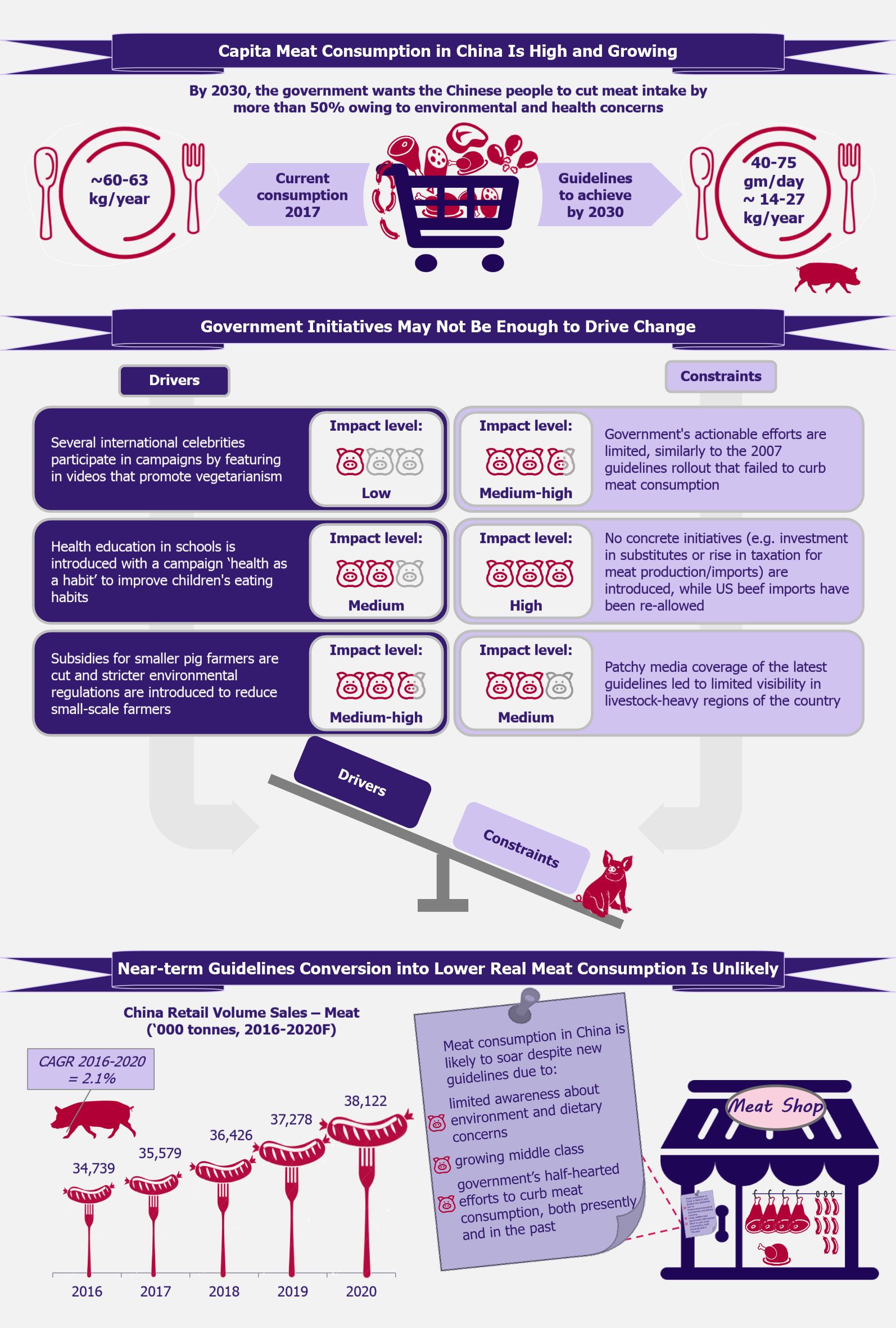
Sustainable food packaging has recently received an increased attention within the food & beverage sector. Most players try to make sure not to miss any chance of communicating their concern over plastic waste to the general public, showcasing their initiatives taken to curb the waste. Are such initiatives taken out of actual concern or are they just a move to position the brands right in the ‘environmentally-concerned’ market?
It is assumed that packaging is considered sustainable, if it meets three criteria of sustainability. First, it should be economically viable for the consumers as well as the manufacturers. Second, it should be socially acceptable in terms of ease of use, transporting, sorting, and storing. Most importantly, third, the packaging must be eco-friendly through the use of materials that are responsibly-sourced and reusable/recyclable, to reduce the environmental impact of the packaging.
Change fueled by multiple triggers
Food and beverage (F&B) and related packaging industry players have been under a growing pressure to be more transparent and to introduce changes to the way food products are packaged. Considering that a significant share of non-sustainable, non-biodegradable waste, especially plastic, comes from food industry, improving the packaging and transitioning to more eco-friendly solutions is becoming imperative, rather than optional, for increasing number of F&B companies.
At the same time, the pressure to reduce waste and protect the environment from non-biodegradable substances is creating new opportunities for the packaging materials producers and for F&B companies with regards to more relevant brand positioning in this highly competitive industry.
While a lot has been changing in the packaging sphere under the heat from environmentalists and legal requirements introduced by regulators, the role of an aware consumer exerting pressure through product scrutiny and shopping choices should not be underestimated in this process.
According to a report published in April 2019 by Globalwebindex, a market research company, there has been a rise in the number of consumers globally who are willing to pay more for eco-friendly/sustainable products (including their packaging), from 49% in 2011 to 57% in 2018. Consumer awareness is growing fast thanks to governments’ initiatives, educational media, and activists’ social media efforts, all of which have triggered an increased sense of responsibility amongst many consumers, who start to understand the importance of switching to eco-friendly and sustainable packaging.
Increasingly, consumer awareness is going beyond just passive understanding and translates into actions which have a real power to change F&B sector’s approach to food packaging. Consumers vote with their spending dollars and exert pressure by switching their loyalty to other brands, both of which approaches appear to be quite effective. According to the same survey by Globalwebindex, 61% of consumers are likely to switch from their currently-used brands to more environmentally-friendly ones if the latter score better on the environmental friendliness front. This shows that F&B companies really do need to re-think their product and packaging choices and start putting money and effort in sustainable solutions, if not from real concern over the environment, then for retaining consumer trust and maintaining brand values.
Big F&B brands appear to show initiative
The increased scrutiny over F&B companies’ packaging choices has already started bringing some results. Several major players are looking to invest in transforming their packaging materials to sustainable ones. Despite the challenges in bringing innovations into packaging materials and designs, and altering their supply chain, several F&B players are claiming to strive for their sustainability goals. Some claims may surely be genuine but some could possibly be a strategy to get the ‘sustainable company’ tag to stand out from the competition in the F&B industry.
Understandably, players are very vocal about their initiatives targeted at improving their eco-friendly standing to appeal to the environmentally-concerned consumers. F&B brands such as Coca-Cola, PepsiCo, Unilever, Nestle, to name a few, have already announced time-bound plans to revolutionize their packaging models.
For example, in January 2018, the beverage giant Coca-Cola announced a goal to collect and recycle the equivalent of every bottle it sells globally by 2030. The company with its bottling partners started an initiative with a plan called “World Without Waste” that is focused on entire packaging cycle from designing and manufacturing of bottles to their recycling. For the execution of this plan, the company plans to educate the public on what, how, and where to recycle, teaming up with local communities, NGOs, industry peers, and consumers. Furthermore, under the plan of “World Without Waste”, the company aspires to create packaging from at least 50% recycled materials by 2030 and continue pursuing the goal to make all consumer packaging 100% recyclable by 2025.
In addition to this, in October 2019, Coca-Cola European Partners (CCEP), the largest independent Coca-Cola bottler, announced it would switch the carriers on its multipacks from shrink wrap to paperboard to reduce packaging waste. The company claims that with this switch it will remove about 4,000 metric tons of single-use plastic per year from its current supply chain. The paperboard packaging is planned to be certified from either the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) or the Program for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC). Similarly, in January 2019, Coca-Cola packaging partner, Coca-Cola Amatil Australia, announced to cease the distribution of single-use plastic straws and stirrers, and distribute biodegradable Forest Stewardship Council accredited recyclable paper straws.
According to a report by Packaging Gateway, Coca-Cola claims to have made 88% of the consumer packaging recyclable, while its packaging used 30% of recycled material by the end of 2018. Also, about 58% of the equivalent of bottles and cans introduced by the company into the developed markets were refilled, collected, or recycled during 2018. Overall, the company’s recover and recycle rate was said to be 56% in 2018 as compared to 59% during 2017 or 61% in 2014. This proves that with growing sales, Coca-Cola’s efforts might not make as much impact as the company would want the public to think.
Nevertheless, the company is undertaking further initiatives to improve its environmental score. It committed to invest US$15 million in Circulate Capital, an investment management firm dedicated to incubating and financing companies and infrastructure that work upon curbing the plastic waste thrown into the oceans. Further plans of the company include increasing the use of recycled plastic in Australia by 2020.
In another example, PepsiCo also talks about becoming an environment-friendly company, announcing to use 25% of recycled content in its plastic packaging by 2025. In order to meet its target, in September 2018, the company announced its participation in the World Economic Forum’s Global Plastic Action Partnership (GPAP). The partnership focuses on stakeholders located in coastal economies, such as those in Southeast Asia, and its purpose is to help businesses, communities, and local governments redesign waste management to create circular models that include collecting waste and recycling or composting it to reduce waste streams to the oceans or landfills.
PepsiCo also announced other targets for improved sustainability to be achieved by 2025. These include to re-design all of its packaging to be recyclable, compostable, or biodegradable, to reduce virgin plastic content by 35% across its beverage portfolio, and to amp up investment to increase recycling rates in key markets.
Apart from individual targets, another initiative was also launched in October 2019 jointly by a few beverage players. As reported by a publishing firm, William Reed, three beverage companies, Coca-Cola, PepsiCo, and Keurig Dr Pepper, announced their partnership with World Wildlife Fund, The Recycling Partnership, and Closed Loop Partners under the “Every Bottle Back” initiative. This initiative, starting in late 2020, will include investment of US$100 million and will focus on sorting, processing, and collecting discarded plastic bottles in four US regions. The initiative also targets to educate consumers that PET bottles are 100% recyclable, easily remade into new plastic, bottles, shirts, shoes, coats, park benches, and playground equipment, by introducing pack label messaging.
Smaller players are emerging with packaging innovations
The pressure to embrace sustainable packaging is even greater for smaller and mid-size F&B companies, if they want to stay relevant to the customers, grasp their attention, and grow own market share. Smaller players in the industry seem to understand this and have proven to be more agile in introducing new products that focus on organic ingredients with sustainable packaging, while challenging big brands’ prices.
For example, in March 2016, Alter Eco Foods, a San Francisco-based chocolate-centric, healthy indulgence, and sustainability-oriented food brand, launched the first stand-up pouch made from renewable plant-based materials, designed for storing quinoa grain. This innovative pouch named “Gone 4 Good”, is not meant to be recycled but to be thrown in a composting bin where it will disintegrate within three to six months. Made from eucalyptus and breech trees for the exterior and compostable resin called “Matter-Bi” for the interior, the pouch has several green certifications. Apart from this, in early 2019, the company also transitioned its chocolate truffles packaging from non-recyclable plastic pouch to a recyclable paper box and claims to be looking for solutions to replace its current plastic Coconut Cluster pouch, since it is yet not recyclable or compostable. The company is determined to make all its products packed in 100% recyclable or compostable packaging by December 2020.
Another player, B.O.S.S. Food, a Texas-based nutrition bar company, started selling its premium nutrition bars in compostable wrappers made by TIPA (an Israel-based compostable packaging company) in 2017, focusing on ensuring the products’ packaging is environmentally safe. TIPA’s packaging is a bio-based blend with all the properties of normal plastic but is certified for both home and industrial composting through OK Compost mark by the TUV institute. The packaging also complies with food contact regulations in Europe and the USA.
Similarly, a UK-based beverage company named Earlybirds launched a 100% plant-based packaging for its breakfast drinks – bottles and lids made from sustainable sugarcane, over the span of two months of September and October 2019. The launch made the packaging 100% compostable as per EU biodegradability standards. The company’s advertisements claim that, under the right conditions, the bottle will breakdown in twelve weeks and it can be thrown in food waste bin and then composted at an industrial composter, reducing it back to soil. The company is the first in the UK to launch sustainable packaging for beverages.
These are just a few of several smaller F&B companies, which are focusing on bringing new packaging solutions to improve their rating as environment-friendly companies in the eyes of consumers. The initiatives are worth the effort, even though players face quite a few challenges in embracing sustainable packaging over traditional packaging.
Such challenges include higher costs, choosing the right material for packaging that must comply with the standards of environmental safety, as well sustaining the quality of the food product. It is estimated that the companies are required to spend nearly 25% more on the sustainable packaging than on the traditional packaging. This higher cost is attributed to major shifts in supply chain, including (but not limited to) procuring the raw material for packaging to collecting the used packaging for recycling. Another major factor contributing to higher costs of sustainable packaging is the R&D expenses that must be borne by the companies. The solutions still require a lot of research, as there are still very few commonly-used technologies and packaging products, thus a lot of players need to invent them. The companies need to invest considerable sums in developing an environment-friendly packaging material that is viable for their food product to sustain throughout the supply chain as well as shelf life, and (equally importantly) has the aesthetic appeal to grab the consumer’s attention.
But despite being smaller in size and having to deal with challenges, companies such as Alter Eco, B.O.S.S. Food, or Earlybirds have been investing extensively in R&D, a fact that resulted in several of them coming out with better and innovative packaging solutions. In fact, at times, smaller scale of operations works to these players’ advantage, as they do not have the constraint of having to convert the existing large-scale traditional packaging lines to ones suited to deliver new format or feature of packaging. Therefore, many efforts undertaken by smaller players seem to be converted into tangible solutions and launched more quickly and easily, also giving the companies a great marketing advantage over large F&B brands.
EOS Perspective
With the rise in awareness about plastic waste and environment safety among consumers, along with regulations formulated by governments across many countries to curb plastic waste, it has become paramount for F&B companies to enter the path of sustainability. At the same time, sustainability is becoming an important element of many companies’ marketing strategy to get ahead of the competition (or, increasingly, not to stay behind other players). The latter reason alone makes it no longer a matter of choice for F&B companies whether to keep assuring the public about efforts undertaken towards improving own sustainability rating across the supply chain.
Certainly, it is doubtful whether all these F&B companies are capable of actually achieving the claimed sustainability. On the one hand, there is a doubt if the scale of their efforts is relevant enough to bring about an actual change and not remain just a PR tool. On the other hand, the doubts seem to be really justified considering the challenges associated with achieving true sustainability goals.
The challenges range across many aspects. These include the complexity of the required changes in the supply chain, which involve both radical and incremental change, from manufacturers to users, owing to alterations in packaging materials and designs.
Another major challenge is the higher cost associated with changing the packaging materials from plastics to renewable or compostable materials. This starts with the development of the right product’s packaging material to ensure stable and long shelf life, and safe transportation with minimal waste, all of which is particularly challenging when dealing with food products. The costs and complexity of the task is further increased by the responsibility of creating an infrastructure for recycling of the packaging materials and taking the onus of collecting and recycling the packaging of own products, if not directly then through well-planned network of third-party entities.
Considering the complexity of these challenges and the high cost of going up the sustainability ladder, many F&B companies are likely to not be able (or to not want to) work towards full sustainability across their supply chain. In the midst of the growing pressure to meet the sustainability criterion, it is possible that some of the players might quietly opt for less sustainable solutions or stick to only those changes that are most visible to the consumer’s eye.