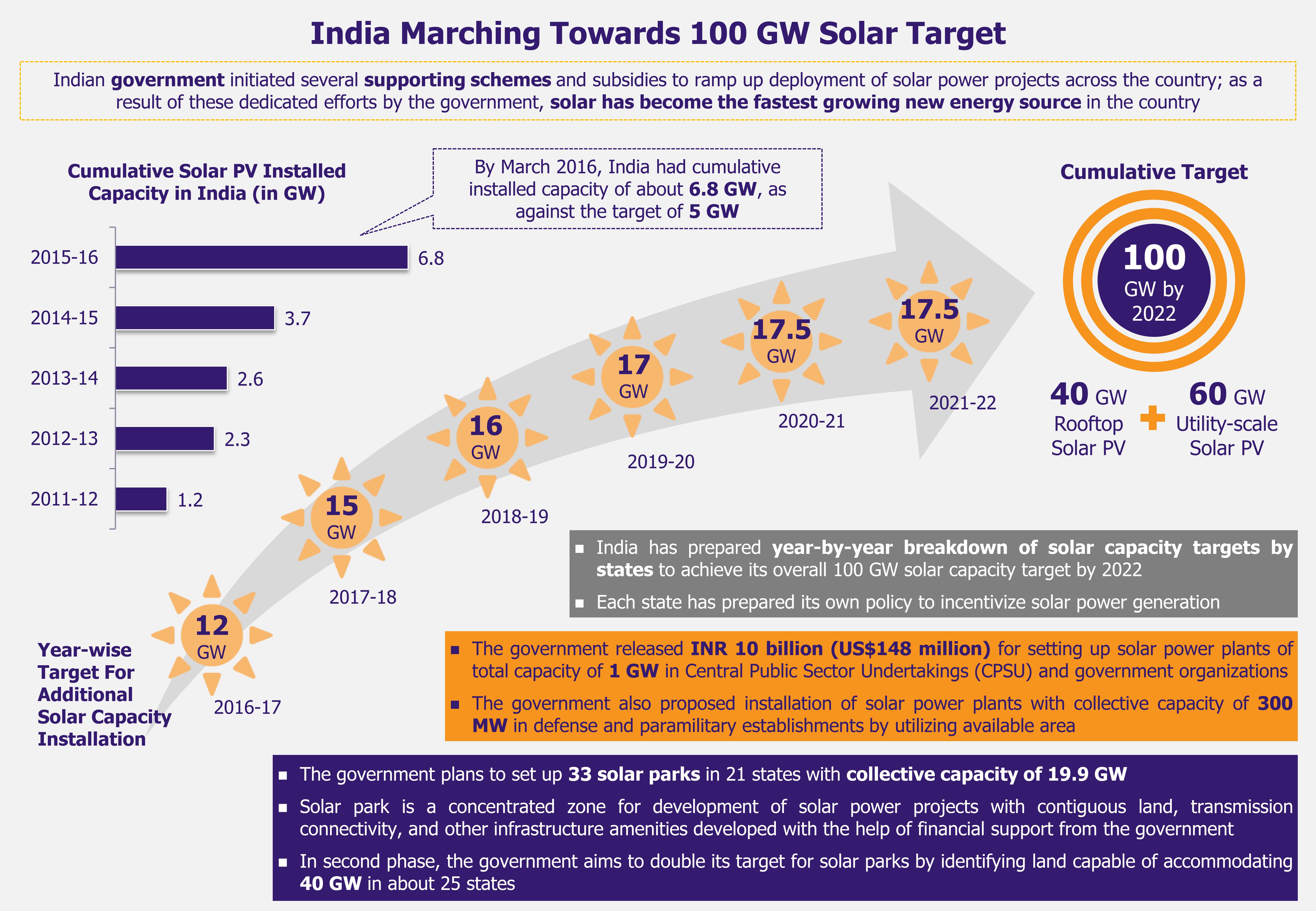
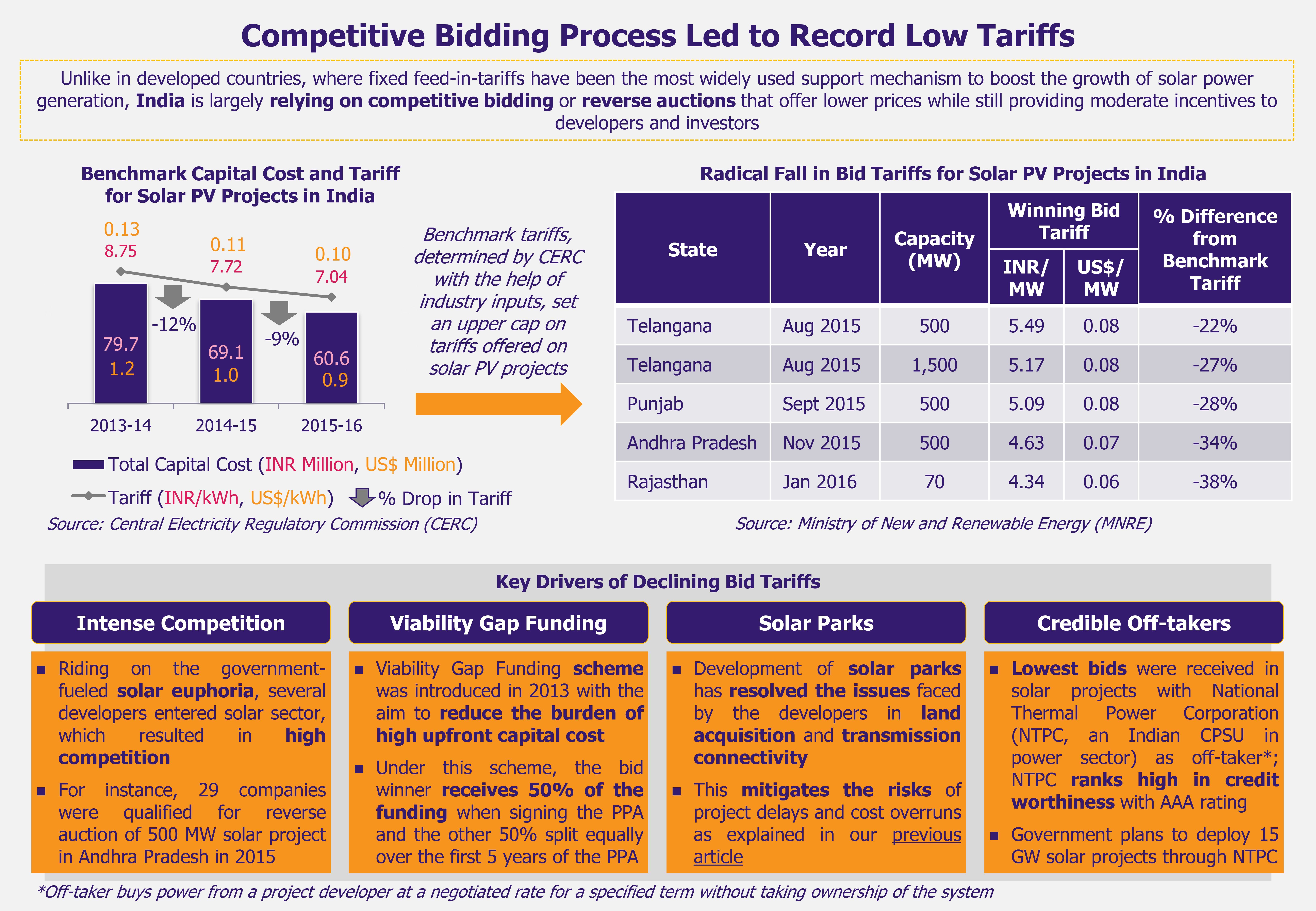
The new Indian government, elected in 2014, has created a wave of enthusiasm in Indian solar sector with its announcement of an ambitious target to install 100 GW of solar power capacity by 2022. But considering that India had an installed solar PV capacity of only 3.74 GW as of March 2015, achieving this target seems to be a herculean task.
This article is part of a series focusing on solar PV market across selected Asian countries: China, India, Thailand, and Malaysia.
The series closing article Solar Rises in the East examines challenges and opportunities in all four markets, with additional look into Indonesia and
The Philippines.
Market overview
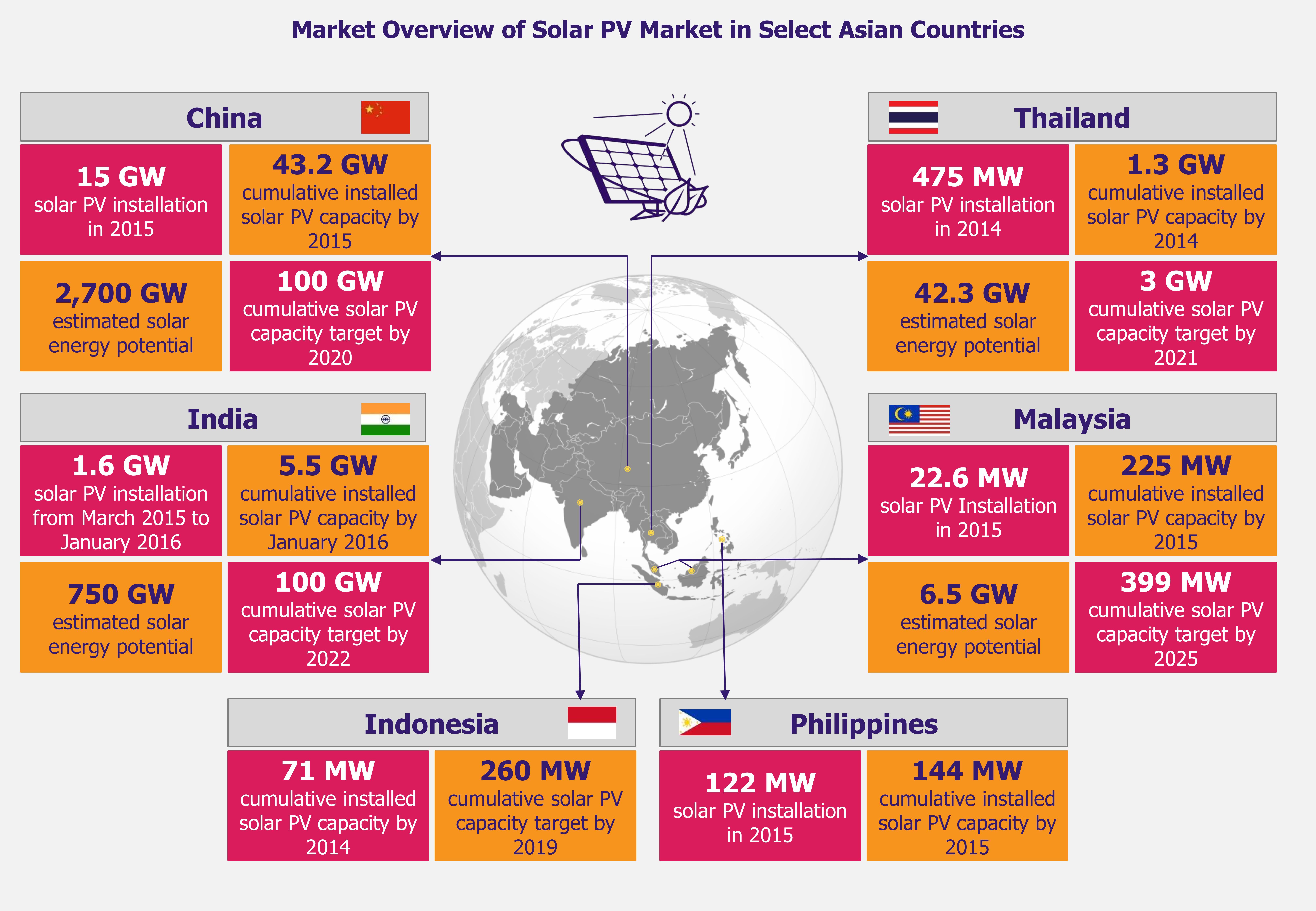
India’s still modest solar PV capacity indicates how ambitious the 2022 target is. The country expanded its cumulative solar PV installed capacity from a mere 35.15 MW in March 2011 to 3.74 GW in March 2015. According to Indian government calculations, the country would need to invest US$110 billion between 2015 and 2022 to achieve the target of 100 GW solar power capacity. While obtaining such funding seems like a challenging task, it seems India has it all sorted out. At RE-Invest 2015 (a renewable energy global investment promotion conference held in New Delhi in February 2015), Piyush Goyal, minister of state for coal, power, and renewable energy, managed to get commitments worth US$200 billion from Indian companies as well as foreign investors. Furthermore, government managed to get commitment to build 166 GW solar installations from several solar developers.
Government is in talks with leading multilateral funding and lending agencies, such as the Asian Development Bank, World Bank, Germany-based KfW, Japan International Cooperation Agency, and Japan Bank for International Cooperation, to raise US$3 billion for solar power projects. In 2014, India received a funding of US$1 billion from US Exim Bank for solar power projects in the country. Announcement of 100 GW solar target has also caught attention of several private equity firms such as Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, IFC, and Standard Chartered. All of these efforts to secure funding for solar projects allow to hope that the 100 GW target by 2022 is achievable.
As India is blessed with virtually limitless solar energy, such inflow of 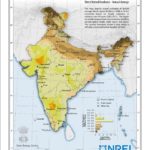 large-scale investment can aid rapid development of solar market in the country. With more than 300 days of sunshine, India ranks among the highest irradiation-receiving countries in the world. Most parts of the country receives solar irradiation between 4-7 kWh/m2 per day (as seen in India Solar Resource Map, sourced from National Renewable Energy Laboratory).
large-scale investment can aid rapid development of solar market in the country. With more than 300 days of sunshine, India ranks among the highest irradiation-receiving countries in the world. Most parts of the country receives solar irradiation between 4-7 kWh/m2 per day (as seen in India Solar Resource Map, sourced from National Renewable Energy Laboratory).
A report, released in November 2014, by Indian Ministry of New and Renewable Energy estimated the country’s solar power potential at about 750 GW indicating that India has the prospects to become one of the largest solar power markets in the world. As per the report’s estimates, regions of Rajasthan (142 GW) and Jammu & Kashmir (111 GW) have the highest solar power potential in the country. More than 60 GW of solar power potential is estimated for Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra, which are among the largest of the Indian states with large wasteland resources.
Key growth drivers
Rising Energy Gap

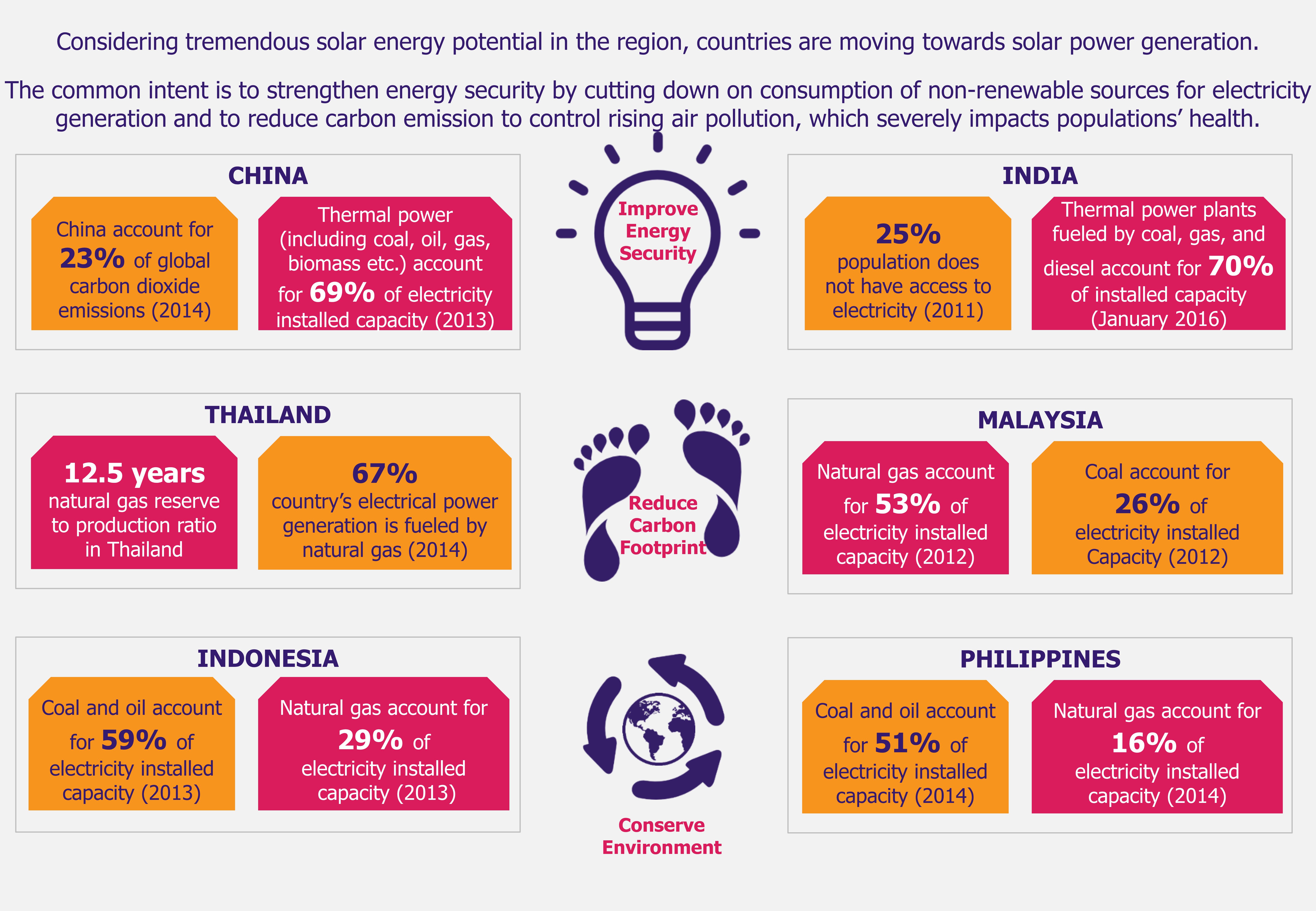
India is experiencing unprecedented energy demand from its increasing population (1.27 billion as of 2014) and rapidly developing economy (India’s economic growth rate for fiscal year 2014-15 is estimated at 7.4%). The country consumed 869,000 GW of electricity in 2012, representing 130% increase as compared to electricity consumption in 2000.
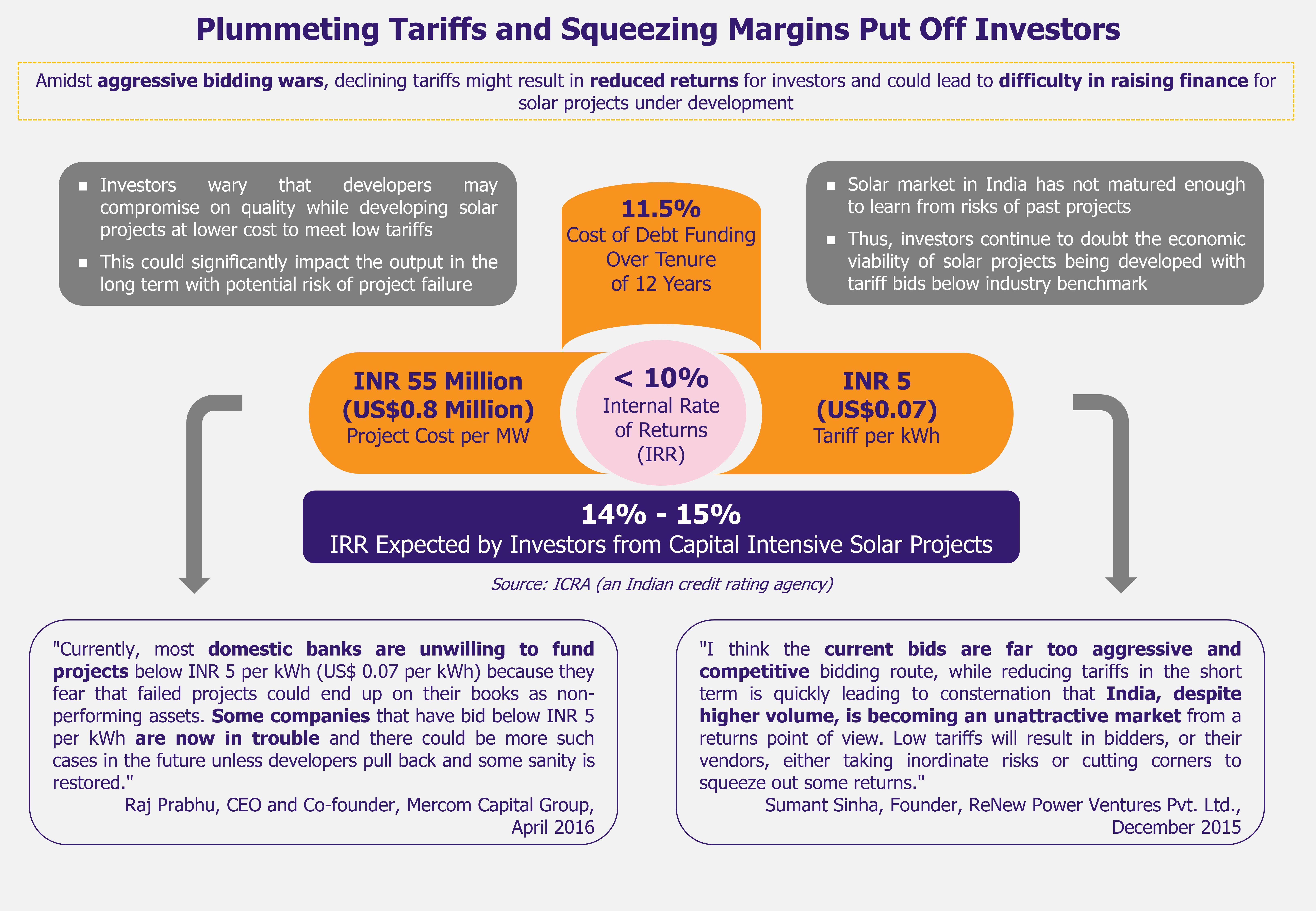
India remains a power-deficit country, with 25% of its population not having access to electricity, according to Census 2011. The country suffers from severe shortages of electricity, particularly during peak hours of demand. Moreover, significant dependence on oil imports to meet energy needs poses threat to country’s energy mix. Considering country’s tremendous solar potential, solar power generation can potentially fill in the mounting energy gap of the power-hungry nation.
Declining cost of solar power generation
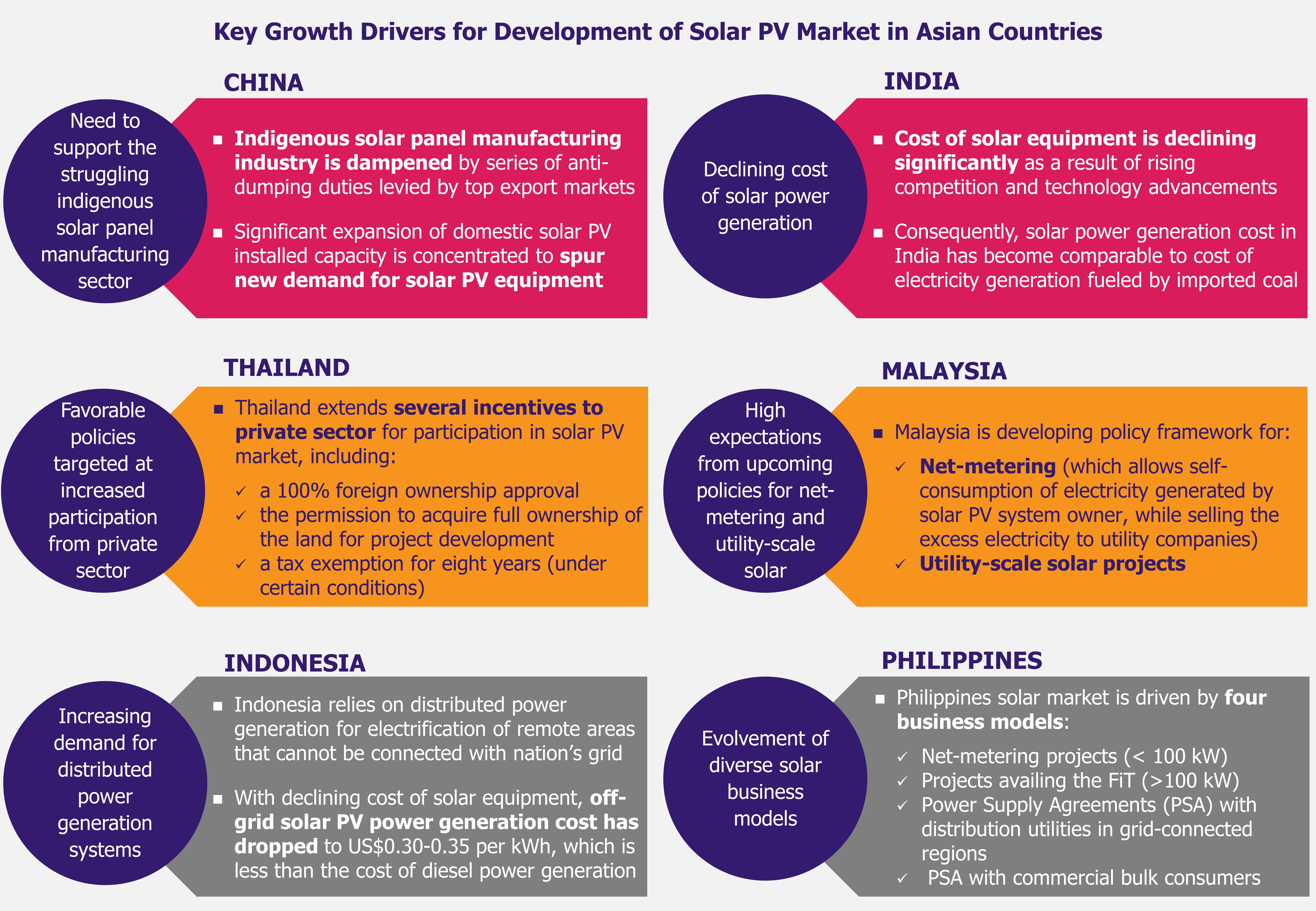
Solar power is becoming increasingly affordable, with cost of solar equipment declining significantly over the last few years as a result of rising competition and technology advancements and innovation.
We are already close to grid parity as the cost of modules has come down and the generation cost of thermal and gas plants has gone up due to increase in fuel cost.
– Rajya Wardhan Ghei, CEO, Hindustan Cleanenergy, 2014
In case of utility-scale solar PV projects, solar power generation costs in India have come down from about INR 18 (US$0.28) per kilowatt-hour (kWh) in 2010-2011 to INR 5.25 (US$0.08) in 2014, which is comparable to cost of electricity generation by power plants using imported coal (coal accounted for 59% of total installed electricity capacity in India in 2014, and about 23% of the demand for thermal coal, which is used primarily in power generation, was met by imports in 2014). Institute of Energy Economics and Financial Analysis concluded in 2014 that newly built imported coal-fired power plant would require power purchase agreement of INR 5.4-5.7/kWh (US$0.85-0.9/kWh).
Solar is going to become one of the lowest-cost forms of generating electricity, even cheaper than fossil fuel.
– Pashupathy Gopalan, Head of Indian operations and President-Asia Pacific, SunEdison, 2014
An A.T.Kearney publication in 2013 suggested that solar power would achieve grid parity (grid parity occurs when an alternative energy source can generate power at a cost lower than or equal to the price of purchasing power from the electricity grid) with conventional power between 2016 and 2018. Similarly, in 2014, Bridge to India, a solar consultancy firm, suggested that the grid parity would be achieved by 2018.
In case of roof-top solar PV projects, experts believe that grid parity is nearly achieved. An article published in The Hindu in March 2015 suggested cost of electricity generation through roof-top solar PV was almost at par with cost of conventional power for commercial consumers (rate of electricity in India varies depending upon state of location, e.g. Gujarat, Rajasthan, Haryana, etc., and type of consumer i.e. domestic/residential, commercial, industrial, and agricultural consumers) in 40% of the Indian states.
As the economic viability of solar power generation continues to increase in India, solar power is expected to gain traction over conventional energy sources, which would further accelerate development of solar market in the country.
Government incentives for solar development
Indian government has taken several initiatives to support solar market growth. Central and state governments offer both tax and non-tax benefits to promote investment in solar power sector.
TABLE I: Tax and Regulatory Benefits (Source: RE-Invest 2015)
| Income Tax Holiday |
- 100% for 10 consecutive years – 20% Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT) to apply (if a company’s income tax in India is less than 18.5%, then it has to pay the MAT)
|
| Accelerated Depreciation |
- Accelerated depreciation – 80% on solar assets
- Additional depreciation – 20% on new plant/machinery in the first year
|
Deemed Export Benefits
(“Deemed Exports” refer to those transactions in which goods supplied do not leave country, and payment for such supplies is received either in Indian rupees or in free foreign exchange) |
- Advance authorization from Directorate General of Foreign Trade
- Deemed export drawbacks on the customs duty paid on the inputs/components
- Exemption/return of Terminal Excise Duty
|
| Service Tax |
- Services of transmission or distribution of renewable source-generated electricity by an electricity utility are exempted from service tax
|
| Customs And Excise Laws |
- Various duty concessions and exemptions to Renewable Energy (RE) Sector
|
| Reduced VAT |
- Certain states allow reduced value-added tax rates (around 5%) on RE projects
|
| Additional One-Time Allowance |
- 15% additional one-time allowance available in budget 2014 on new plant and machinery
|
| Tax-Free Grants |
- Grants received from the holding company engaged in generation, distribution, or transmission of RE power
|
TABLE II: Non-Tax Benefits (Source: RE-Invest 2015)
| Feed-in-Tariffs |
- Applicable when renewable generators sell to state utilities under the MoU route (MoU route means agreements entered into bilaterally without inviting bids)
|
| Rebates |
- Available on the manufacturing of solar and wind components
- Targeted at specific types of renewable energy technology
- Include subsidies and rebates on capital expenditures
|
| Government R&D Programs |
- Improve renewable energy technologies
- Lead to growing performance, importance, and reducing costs
|
Government-led measures to create a conducive business environment for solar sector in India are expected to lure new players – local as well as global – and eventually expand the market space to support country’s solar mission.
Key challenges
Inefficient transmission infrastructure
Inadequate transmission infrastructure to connect solar power to the grid is expected to be a major roadblock to country’s 100 GW solar ambition. Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry indicated in 2013 that the transmission and distribution losses due to poor grid structure were around 23% of the electricity generated. This clearly shows that a rapid up-gradation of transmission infrastructure would be essential to sustain the envisaged growth in solar power generation.
The solar target is very ambitious. There will be transmission and other infrastructure constraints to contend with.
– Bharat Bhushan Agrawal, Analyst, Bloomberg New Energy Finance, 2014
India has begun to work on developing high capacity transmission systems to accommodate the projected solar capacity as part of the US$6.96 billion ‘Green Energy Corridor’ project (announced in 2013), under which the government has planned to construct inter-state and intra-state transmission infrastructure across seven states of the country by 2017-2018. KfW, a German government-owned development bank, is expected to lend an initial US$285 million for this project. However, despite availability of funds, not much progress has been noted in the proposed ‘Green Energy Corridor’ project. By early 2015, just two sub-stations were constructed, one each in Tamil Nadu and Rajasthan, to feed renewable power to the main grid. Power Grid Corporation of India, which is to execute the project, argues that there is not enough renewable energy capacity addition and they are still on wait-and-watch mode. With this approach, the proposed green corridor project is likely not to be completed within the proposed time frame. So, it seems that despite concentrated efforts to improve the transmission infrastructure, the progress has been slow, which will hamper the proposed development plans of solar market in the country.
Difficulties in land acquisition
The challenges and menaces involved in sourcing land for large-scale solar projects is daunting many solar developers in India. Large-scale solar power plants require huge space – construction of a 100 MW solar plant typically require around 500 acres of land. The issue is that, in India, land is very fragmented (according to a media article by The Indian Express in March 2015, the average landholding size in India was three acres). And, as per the Land Acquisition Act (The Right to Fair Compensation and Transparency in Land Acquisition, Rehabilitation and Resettlement Act, 2013), in order to acquire a tract of land, private companies need to get consent of 80% of the land owners of the particular area, while public-private partnership projects need to get consent of 70% land owners. Thus, it becomes extremely difficult to individually negotiate with all the land owners in an area selected for construction of a solar plant, and convince them to sell their respective portion of land and make a large space available. Furthermore, in India, the records of landholding cannot be easily verified and authenticated and many land owners do not have clear title to the land they possess, which might lead to litigations and disputes over the land at a later stage.
Land titles are usually not very clear [and] even if a land deed is shown to be in one person’s name, another relative can come forward and stake his claim and the matter can be sub-judice for years, if not decades. – Jasmeet Khurana, Solar Analyst, Bridge to India, 2014
Many solar projects have been stalled in the country due to these challenges in land acquisition, which has eventually impacted the project budget and costs.
| Challenges faced by Essel Infraprojects in acquiring land for solar power plants
In June 2014, Essel Infraprojects, infrastructure arm of an Indian conglomerate – Essel Group, were nearing the completion of a 20 MW solar power plant in Maharashtra, and only last 10 km of transmission lines were to be set up to connect the INR 2 billion (US$31.5 million) plant to the state electricity grid. However, owners of the land on which the transmission towers were to be erected refused to allow their construction.
Negotiating terms with the land owners resulted in delay of project completion by six days. Though the delay was relatively short, unlike in other large-scale infrastructure projects where the litigations with land owners can go on for years, even the six day delay lead to a considerable loss of INR 500 million (US$7.87 million) in bank guarantees.
Learning from their experience in Maharashtra solar power plant project, for their next solar project (a 30 MW solar power plant in Punjab) Essel Infraprojects first acquired the land for transmission towers. In this case, the company struggled to acquire the land for plant itself. The company had started negotiating land deals at INR 800-900 thousand (US$12,598-14,173) per acre, but during the talks the price demanded by land owners increased, and the company had to settle paying INR 2.5 million (US$,39,370) per acre. |
Land acquisition for solar projects has proved to be challenging not only for private companies, but also for state-owned enterprises. In 2014, Mahagenco, Maharashtra state-run power utility company, reported delay in construction of solar projects of 125 MW capacity (100 MW in Osmanabad and 25 MW in Parbhani) due to difficulties in acquisition of land. The land holdings on the proposed construction sites are in small segments and Mahagenco is facing difficulty in convincing all the land owners in that area to sell their respective parcels of land to create a larger land area available for the solar plant. Because of the delay, the state missed its target of installing 313 MW of solar capacity for 2013-2014.
Difficulties in sourcing land for solar projects has resulted in delay of project execution and escalated costs. Government has proposed amendments in the Land Acquisition Act, including removal of ‘consent’ clause, to ease and expedite the process of securing land for reform-oriented projects. But this proposal has been stalled due to immense opposition from most political parties and social activists, who argue that the proposed amendments would weaken the rights of land owners. Unless the issues pertaining to land acquisition process are addressed, the country’s solar ambitions are likely not to be achieved in the desired time frame.
Opportunities for global solar companies
Global solar companies eye India as an emerging market opportunity
Indian government offers favorable policy framework for foreign investment in solar sector. 100% foreign direct investment is allowed under the automatic route, without any approval from the government of India. Further, no approval is required for up to 74% foreign equity participation in a joint venture. Additionally, 100% foreign investment as equity is permissible with the approval of Foreign Investment Promotion Board. Investors are also allowed to set up a liaison office in India.
Apart from this favorable framework, global companies are attracted to Indian market thanks to the promising returns on investments. Bridge to India concluded in 2015 that global utility companies could expect 13-15% return on equity invested in solar projects in India, while return for global solar developers could be expected to be in the range of 15-17%.
India is seen as an upcoming solar investment hotspot. Given the conducive business environment and attractive returns, many global solar firms have announced investment plans in Indian solar market. These include leading global solar developers and utilities such as Acme (joint venture between France-based EDF Energies Nouvelles, Luxembourg-based EREN, and India-based ACME Cleantech Solutions), US-based SunEdison, US-based First Solar, France-based Solairedirect, to name a few.
Insufficient domestic solar PV cells and modules production capacity offers opportunities for global suppliers
Minister Piyush Goyal stated in 2014 that domestic manufacturing capacity of photovoltaic cells (PVCs), which accounts for 60% of the cost of a solar module, is 700-800 MW, which is not sufficient to meet country’s solar ambitions. Indian PVCs manufacturers have also been unable to compete with cheaper Chinese and Taiwanese imports. In 2014, the Ministry of Commerce in India proposed anti-dumping duties of between US$0.11-0.81 on PVCs/modules imported from China, USA, Malaysia, and Taiwan (accounting for about 80% of modules used in Indian solar projects).
Indian government rejected the proposal to impose anti-dumping duties on import of solar PVCs and modules, explaining that as the domestic solar PVCs and modules production capacity was inadequate to meet the demands of country’s envisaged solar plans, the proposed anti-dumping duties would result in higher costs for solar projects and eventually hinder the growth of solar market in the country. With no protective measures in place to support the indigenous PVC manufacturing industry, India’s dependence on imports of solar PVCs and modules is likely to increase with expansion of solar PV market, creating manifold opportunities for global solar PVCs and module suppliers.
EOS Perspective
Abundance of solar irradiation along with continuously falling solar PV prices have created a distinctive opportunity for electricity-deprived India to bank on solar power generation. Realizing this, Indian government is marching towards the goal of installing 100 GW solar PV capacity by 2022. Favorable policy environment and government incentives would be pivotal for the growth of solar market in India. Government’s dedicated efforts to raise institutional funding and develop other financing avenues to support country’s solar power ambitions have received impressive response from investors across the globe.
However, experts caution that most of the announcements in solar sector are made based on just preliminary commitments or MoUs. It is yet to be seen to what extent these plans materialize over the coming years. Despite challenges, Indian solar market is poised to grow rapidly in the near future owing to the euphoria created by recent announcement of government’s ambitious solar vision followed by private sector’s surge of enthusiasm in the solar market. However, whether the country will be able to sustain the growth stride, remains a question.