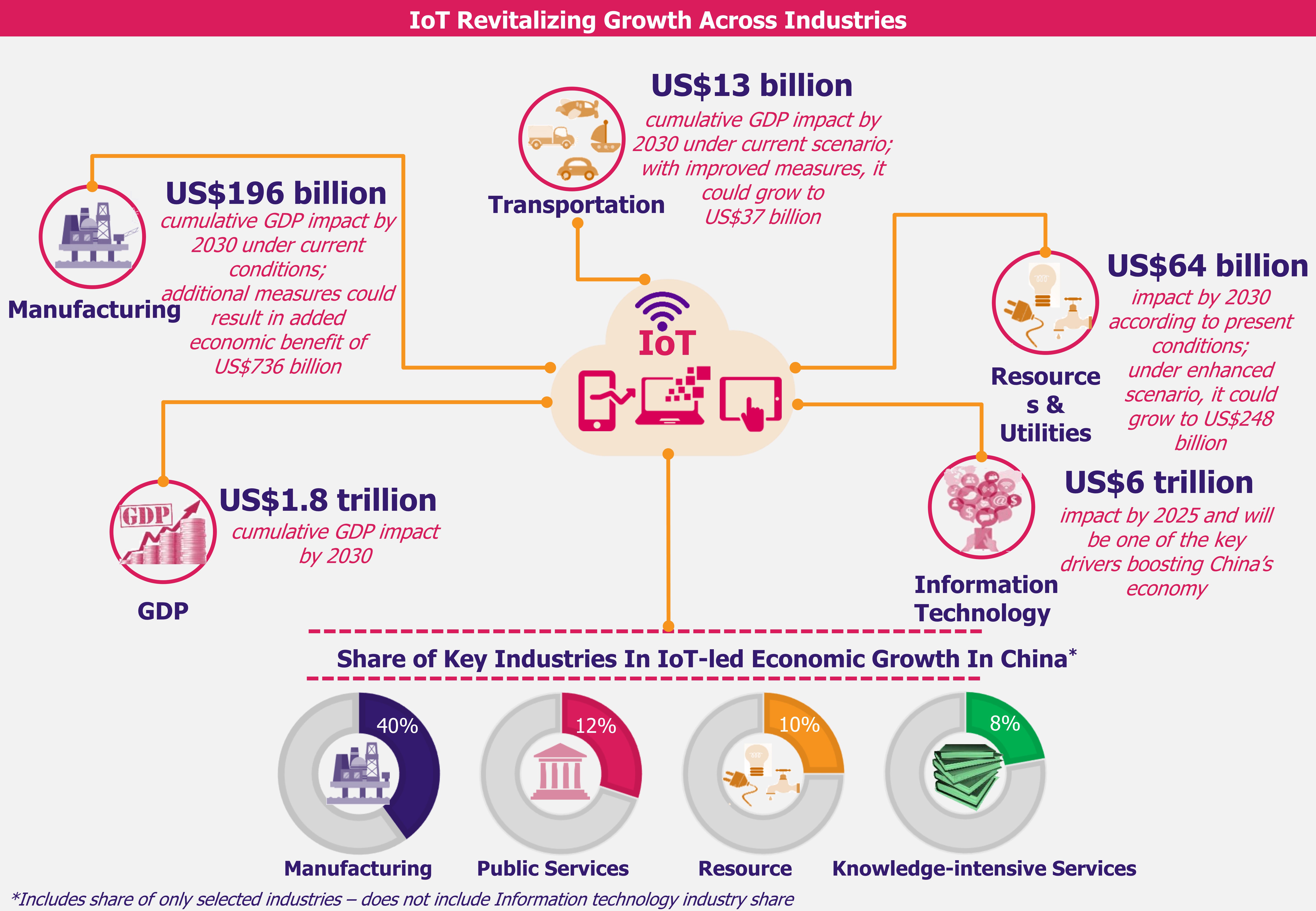
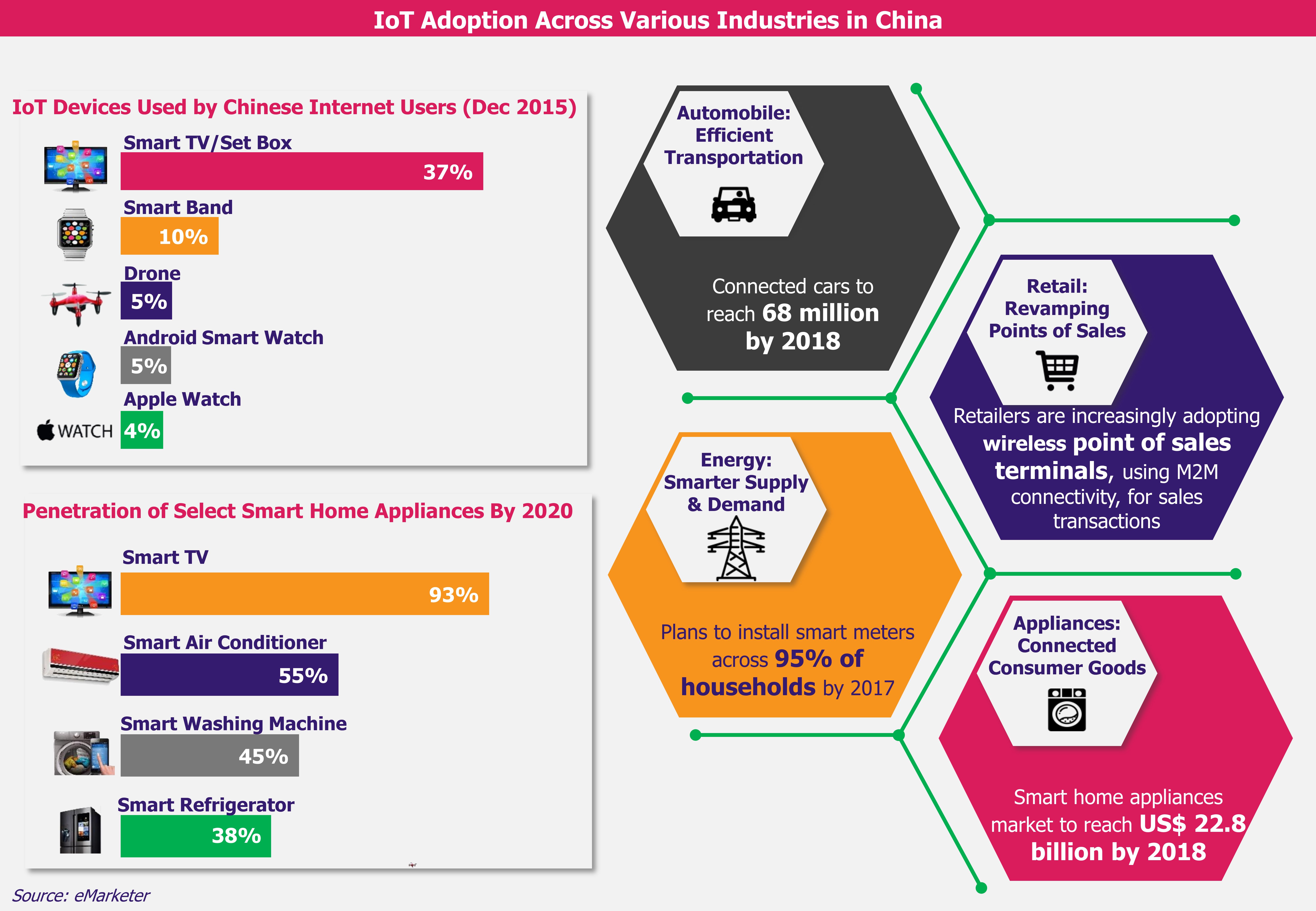
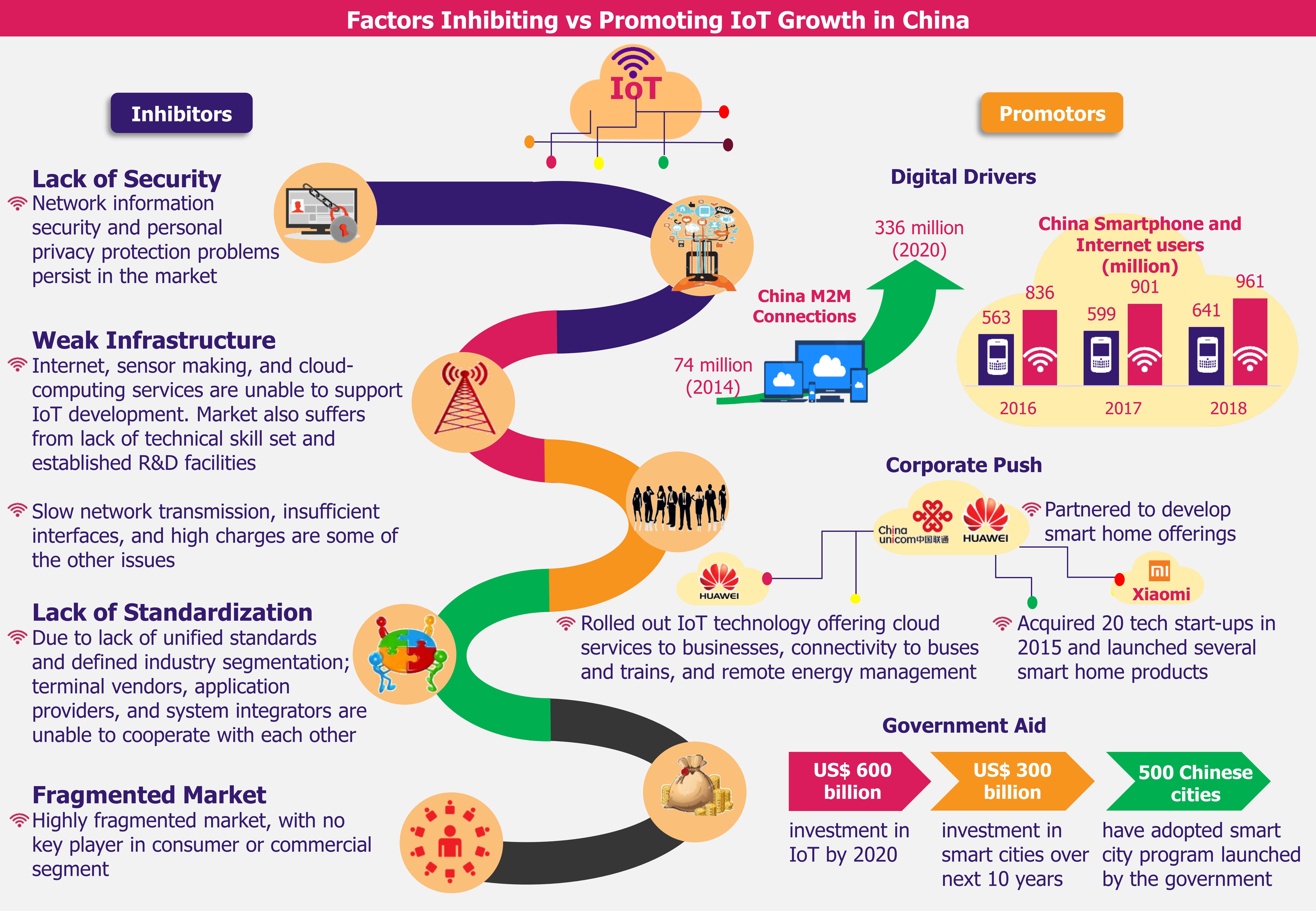
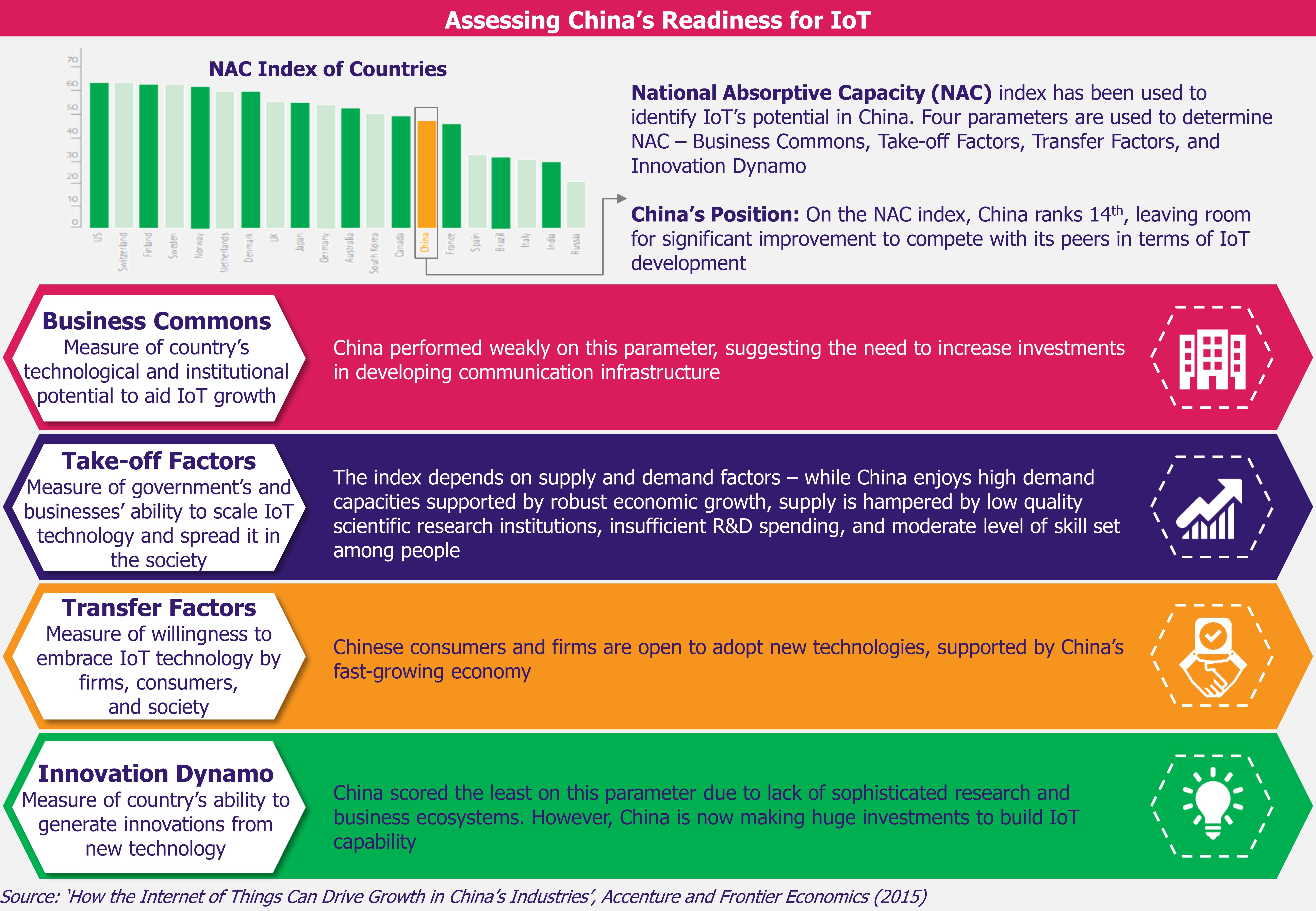
The USA perceives Huawei, world’s largest telecom network equipment supplier and second largest smartphone manufacturer, as a potential threat capable of using its telecom products for hacking and cyber attacks. The US government suspects that China could exploit Huawei for cyber espionage against the USA and other countries. Amidst national security concerns, the US government has called for global boycott of Huawei, including of its 5G product range. The USA’s efforts to clamp down Huawei have rippling effect across the 5G ecosystem.
The USA and China have been trading rivals since 2012, particularly on the technology grounds. This resulted in a ban on China-based telecom equipment provider Huawei preventing it from trading with the US firms, over the accusation of espionage of critical information to the Chinese government. As a result, Huawei was barred from selling any type of equipment to be used in the US communication networks. This ban pertained to the 5G network equipment as well, and thus, Huawei’s 5G network equipment was ruled out from deployment in all parts of the USA. Few other countries, which agreed with the USA’s accusations on Huawei, also imposed a ban on the company’s 5G network equipment. The move severely affected Huawei’s exposure to some of the potential 5G markets, but it came as sigh of relief for its global competitors wary of Huawei’s growing dominance in 5G space.
Further, on May 16, 2019, the US government decided to put Huawei on the Security Entity List which restricted the company from buying any US-based technology (key hardware and software) for their 5G network equipment without approval and license from the US government, thus aggravating the 5G war. This not only brought new set of challenges for Huawei, but also created a rough path for the USA’s own technology firms involved in supplying components to Huawei. Considering impact on the US technology firms having Huawei as a key customer, on June 29, 2019, the US government announced relaxation on the Huawei ban, thereby allowing these US firms to continue their supply to Huawei for a 90-day period which got over in mid-August. The relaxation period was further extended till November 18, 2019, giving temporary relief to Huawei and its US-based business partners.
Huawei bears the brunt of USA-China 5G clash
The USA has initiated a global campaign to block Huawei from next-generation wireless communication technology over security concerns and it is pressuring other countries to keep out Huawei from 5G rollout. This invited quite a few repercussions for the company. One of the major and obvious consequences involved a major loss of potential market opportunity in the US territory as well as in other countries which are under strong influence of the USA.
After prolonged persuasion by the US government, in July 2018, Australia banned Huawei from 5G rollout in its territory. Japan also joined the league in December 2018 by imposing a ban on Huawei’s network equipment for 5G deployment, amid the security concerns to avoid hacks and intelligence leaks. Further, New Zealand and Taiwan also followed the suit in shutting out Huawei from 5G deployment.
In June 2019, the founder and CEO of Huawei, Ren Zhengfei, indicated that the company is likely to experience a drop in its revenue by US$30 billion over the next two years, which can be seen as a knock-on effect of growing US sanctions on Huawei. Also, Huawei expects its smartphone shipments to decline by 40% to 60% by the end of 2019 as compared to the total shipments in the previous year.
Despite repeated warnings from the USA, some countries have come out in support of Huawei by rejecting the USA’s claims. The regulatory bodies of countries such as Russia, Germany, Brazil, South Korea, Finland, and Switzerland have taken their decisions in favor of Huawei and allowed the company to deploy its 5G network equipment in their territories, affirming that they do not see any technical grounds to ban the company from their telecom networks.
Moreover, the US government has been persistently urging many European countries, especially the UK, to join its decision of barring 5G trade with Huawei. In March 2019, the EU recommended its member countries not to impose outright ban on Huawei, but instead assess and evaluate the risks involved in using the company’s 5G network equipment. Already earlier, in February 2019, the UK government concluded that any risks from the use of Huawei equipment in its 5G network can be mitigated through certain improvements and checks which the company will be asked to make and hence the decision of completely banning the company’s equipment from UK’s 5G network was not taken.
Among Asian countries, India, the second-largest telecom market in the region, has not decided whether to allow Huawei to sell its 5G network equipment in the country. China has warned the Indian government that the repercussions of banning Huawei equipment would include challenges in catering to the demand for low-priced 5G devices, thus causing a hindrance in rapid development of India’s telecom sector. In June 2019, the Department of Technology of India indicated that, since the matter of Huawei concerns the security of the country, they will scrutinize the company’s 5G equipment for presence of any spyware components. India will see how other countries are dealing with the potential security risks before giving a green light to the company.
The USA’s allegations against Huawei have made all the countries cautious over dealing with the company. Despite having proven technological supremacy in 5G network equipment market, Huawei has come under strong scrutiny for its 5G network equipment across the globe.
Huawei ban: Boon for some, bane for others
Huawei’s troubles are turning into major opportunity for its competitors in the 5G network equipment and smartphones market space. However, suppliers to Huawei, particularly US-based companies providing hardware and software for 5G devices and network equipment, took a hard hit as they lost one of their key customers because of the trade ban.
Huawei ban presents increased opportunities for its global competitors in 5G network equipment market
Major competitors of Huawei in 5G network equipment manufacturing business – Samsung (South Korea), Nokia (Finland), and Ericsson (Sweden) – are positioned to get the inadvertent benefit of expanded market opportunities with one competitor less. With Huawei losing potential market in countries where it is facing backlash, its competitors managed to grab a few contracts.
For instance, in March 2019, Denmark’s leading telecom operator TDC, which had worked with Huawei since 2013, chose Ericsson for the 5G rollout. Further, in May 2019, Softbank Group Corp’s Japanese telecom unit, which had partnered with Huawei for 4G networks deployment in the past, replaced Huawei with Nokia for its end-to-end 5G solutions including 5G RAN (i.e. radio access network equipment including base stations and antennas which establish connection between individual smart devices and other parts of the network). In the USA, Samsung is gaining significant traction as it has started supplying 5G network equipment to some of the leading US telecom operators including AT&T, Verizon, and Sprint.
A report released in May 2019 by Dell’Oro (a market research firm specializing in telecom) indicated that Samsung surpassed Huawei for the first time by acquiring 37% of the share of total 5G RAN revenue in the first quarter of 2019. In the same period, Huawei stood second with 28% share, followed by Ericsson and Nokia with 27% and 8% share, respectively. Earlier, Huawei led the 5G RAN market in 2018, accounting for 31% share of total 5G RAN revenue that year. Huawei was followed by Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE (China), and Samsung with 29.2%, 23.3%, 7.4%, and 6.6% share, respectively. Due to widespread skepticism about Huawei over espionage accusations, a shift in 5G network equipment market can be expected by the end of 2019, since competitors are likely to gain more growth momentum over Huawei.
Demand for Samsung smartphones gets a boost as Google blocks Android support to Huawei
In the smartphones sector, Samsung, which is the world’s largest smartphones manufacturer, may turn out to be the winner in the Huawei ban situation. Huawei, through its low-priced Android smartphones with features similar to Samsung’s smartphones, is emerging as the largest rival of Samsung in the smartphone market.
As per IDC data, Samsung’s market share (by total smartphone shipments volume) declined from 21.7% in 2017 to 20.8% in 2018, whereas Huawei recorded 33.6% year-on-year growth as market share increased from 10.5% in 2017 to 14.7% in 2018. But since Huawei was placed on US trade blacklist, Samsung is likely to benefit from the situation because of the broken deal between Google and Huawei which led Huawei to lose access to Google’s Android operating system (OS) for its next-generation 5G smartphones.
While Google managed to get a temporary license to continue to provide update and support for existing Huawei smartphones, it prevented Google from providing Android support for Huawei’s new products including soon to be released 5G smartphones. Huawei indicated that its latest 5G smartphones Mate 30 series, which will be launched on September 19, 2019, will run on open-source version of Android 10 and it will not have any of the flagship Google apps such as Google Maps, Google Drive, Google Assistant, etc.
Huawei unveiled its own operating system named HarmonyOS on August 9, 2019, but it still seeks support of Google’s Android OS for its upcoming 5G smartphones along with access to widely popular apps such as Facebook and WhatsApp which all belong to American firms. Android OS, controlling over three-fourths of the mobile OS market as of August 2019, is widely adopted by both the app developers as well as the users. As of second quarter of 2019, Android allowed its users to choose from 2.46 million apps. Encouraging app developers to rewrite their apps as per platform-specific requirements of a new OS with low user base is challenging. Conversely, consumers prefer OS which allows them to use all the apps they like. If HarmanyOS needs to be used as Android replacement, Huawei will need considerable time and financial resources to work with app developers to add similar apps to Huawei’s HarmonyOS.
Explore our other Perspectives on 5G
The future scenario for global 5G smartphones market will depend on the pending decision of the US government over allowing US technology firms to trade with Huawei. If the US government allows the trade, Huawei will have high chances of leading in the 5G smartphones sector owing to its competitive pricing and innovative solutions. On the other hand, if the ban still persists in future, the market of Huawei’s global competitors, Samsung in particular, is likely to swell, owing to their trusted brand name and reliability along with the support of Android OS.
US-based hardware suppliers for telecom devices face revenue loss as they lose their key customer, Huawei
The US government’s executive order issued in May 2019 blocking US exports to Huawei led to adverse effect on the revenue of the US-based companies that used to supply key hardware to Huawei for its 5G network equipment and devices.
For example, Qualcomm which was one of the largest sellers of modem chips, mobile processors, and licenses for 3G, 4G, as well as 5G technology in the Chinese market, has experienced a decline in revenue by 13% year-on-year in the third quarter of 2019 along with decline of approximately 36% in shipments of chipsets and processors. Similarly, Broadcom, which supplies switching chips used in network equipment, is also facing challenges with loss of its highest revenue-generating customer, Huawei, accounting for US$900 million of company’s revenue in 2018. Considering the Huawei blacklisting’s impact on financial results in the first two quarters of 2019, Broadcom has even cut its revenue outlook of the fiscal year 2019 from US$24.5 billion to US$22.5 billion.
In view of financial implications of Huawei blacklisting on the businesses of US-based technology firms, the US government, in June 2019, reprieved the trade ban on Huawei till November 18, 2019. Post the relaxation period, the US government may again ban Huawei from doing business with US technology firms. In case the US government puts the ban in effect owing to the security concerns, the repercussions are likely to deepen further for the US firms over losing considerable revenue coming from China’s telecom hardware industry.
Ban on Huawei means telecom operators will have to pay a higher price for 5G network equipment
Huawei ban is also seen to be impacting the US telecom operators as they face a particular challenge of increasing outlay to build the 5G networks. This is because the 5G network equipment provided by Nokia and Ericsson is more expensive than Huawei’s. In March 2019, Huawei claimed that allowing the company to compete in the telecom market in North America would reduce the total cost of wireless communication infrastructure development in the region by 15%-40% and provide an opportunity for telecom operators to save US$20 billion over the next four years.
The cost factor has also made some European countries sway their decision in favor of Huawei. In June 2019, GSMA, an industry association with over 750 telecom operators as members, indicated that shunning Chinese equipment from 5G network deployment in Europe would add EUR 55 billion (~US$61 billion) to the costs of telecom operators and will also cause the delay of about 18 months in 5G network deployment. In fact, to avoid such repercussions, many European countries have already decided to continue buying telecom equipment (including 5G network equipment) from Huawei and other Chinese firms, Greece being the latest one to join the group of countries including Switzerland, Finland, Sweden, and few more.
India, which is a huge market for low-priced smartphones and telecom network equipment, still remains undecided on the proposed ban on Huawei. The 5G network equipment supplied by Nokia and Ericsson in India is expected to be 10%-15% more expensive as compared to Huawei’s. Also, Huawei claims that imposing a ban on the company will push back 5G deployment in India by two to three years. Moreover, the prolonged decision-taking has also affected the 5G network deployment timeline of the country and thus slowing down the overall development of its telecom industry. Dilemma whether to work with Huawei is seen to have wide-reaching implications on overall development of 5G technology in some countries.
EOS Perspective
The USA-China 5G war has taken many unpredictable turns over the last year, resulting in adverse implications for Huawei and its US-based business partners. The current status of the 5G war indicates a relaxation over the Huawei ban till November 18, 2019. This allows the US companies to continue supply of their technology products including key software and hardware required by Huawei for 5G equipment manufacturing. However, the relaxation of the ban is not intended to remove Huawei from the US Department of Commerce’s Entity List and the US companies still have to apply for temporary license for exporting products to Huawei.
The USA has been targeting Huawei since 2012, and there seems to be no stopping. Considering the implications of the US sanctions, Huawei has been making notable efforts to end the ongoing discord with the US government. Huawei has always denied all the accusations and maintained that the company is willing to work with the US government to alleviate their concerns over cybersecurity. In May 2019, Huawei proposed implementation of risk mitigation programs to address potential security threats. To further appease the US government, on September 10, 2019, Huawei proposed selling its 5G technology (including licenses, codes, technical blueprints, patents, as well as production know-how) to an American firm. This is seen as one of the boldest peace-offering deals by Huawei to win back the trust of the US government. Huawei claimed that the buyer will be allowed to alter the software code and thereby eliminate any potential security threats.
Currently, there is no US company manufacturing 5G network equipment. Acceptance of Huawei’s proposal would enable the USA to gain footing in the 5G network equipment market and mitigate the fears over rising dominance of Huawei in global 5G space. While the move risks to create a competitor for Huawei in the 5G network equipment market, the company could also use this as an opportunity to evolve from core manufacturing business to providing technical expertise to other companies for manufacturing 5G equipment. The proposal is still subject to approval from the USA and Chinese governments.
While Huawei is ramping up its efforts to break the deadlock with the US government, at the same time, the company is also devising a parallel strategy presuming the worst possible outcome of USA-China trade tensions over 5G, i.e. the USA eventually cutting off ties with Huawei. The company is working towards a contingency plan with an ambition to take control of its supply chain and reduce its dependency on the US technologies and supplies.
One of the major actions of its plan B includes developing its own operating system HarmonyOS as a substitute to Google’s Android OS. While Huawei wants to continue with Android OS for its future 5G smartphones, in case the US government blocks Huawei’s access to Google’s services, Huawei will have to switch to own HarmonyOS.
China, Huawei’s home market, is more receptive to the company’s products, and switching to own operating system is expected to work in favor of the company. In July 2019, Canalys, a Singapore-based technology market research firm, estimated that China would account for over one-third of 5G smartphones globally by 2023. Huawei could use this opportunity to develop its proprietary OS based on the learnings in China before expanding globally to compete with more established and mature OS such as Android OS and iOS (which respectively controlled 76.23% and 22.17% of the smartphone OS market as of August 2019).
On the other hand, in anticipation of loss of partnerships with key suppliers such as Qualcomm and Broadcom, Huawei had stockpiled critical components between May 2018 and May 2019, according to a research report by Canalys. This move was aimed at ensuring the continuity of production of 5G products that rely on core technology from US-based firms for three to twelve months.
Further, Huawei has been developing proprietary chipsets for its 5G smartphones and networking products, which are being considered as alternatives for products offered by Qualcomm and Broadcom. On September 6, 2019, Huawei launched Kirin 990, a new 5G processor for smart devices, which will power Huawei’s upcoming 5G smartphone including Mate 30 series. Further, in January 2019, Huawei launched a 5G multi-mode chipset, Balong 5000 that supports a broad range of 5G products including smartphones, home broadband devices, vehicle-mounted devices, and 5G modules. The company claims this chipset to be the first to perform to industry benchmark for peak 5G download speeds.
Seeing such developments at the Huawei’s end, it is clear that the company is striving hard to remain on the top of 5G network equipment and device manufacturing sector. The USA’s efforts to derail Huawei from its path to dominance in 5G are certainly going to impact the overall growth of the company in short term, but, with its plan B, things are expected to smooth out for Huawei in future. Even if Huawei is not be able to retain its current global leading position in 5G network equipment and device manufacturing, it will certainly remain one of the strong contenders. The US sanctions are further encouraging Huawei to evolve as an all-round player in the 5G ecosystem.
On the contrary, the USA’s aggression against Huawei is expected to hit its own technology industry in the long term. For instance, the blacklisting of Huawei will not only cost the US technology firms to lose one of its largest customers, but will also result in intensified competition as Huawei ramps up its in-house capabilities to fulfill the demand of the entire 5G ecosystem. An example of this could be Huawei’s announcement in April 2019 that the company was open to selling the 5G chips to rival smartphone companies, including Apple. Moreover, if Huawei’s HarmonyOS is able to succeed in gaining significant user base, it would challenge the dominance of Android and iOS. Hence, it would be in best interest of the USA and its technology industry, if the country could take a different approach and try to control and minimize security risks related to Huawei’s engagements, rather than placing an outright ban on the company. Similar to what Germany did in December 2018, the USA could encourage telecom operators to establish verification centers and hire third-party experts to identify and resolve vulnerabilities in Huawei’s 5G network equipment and devices.