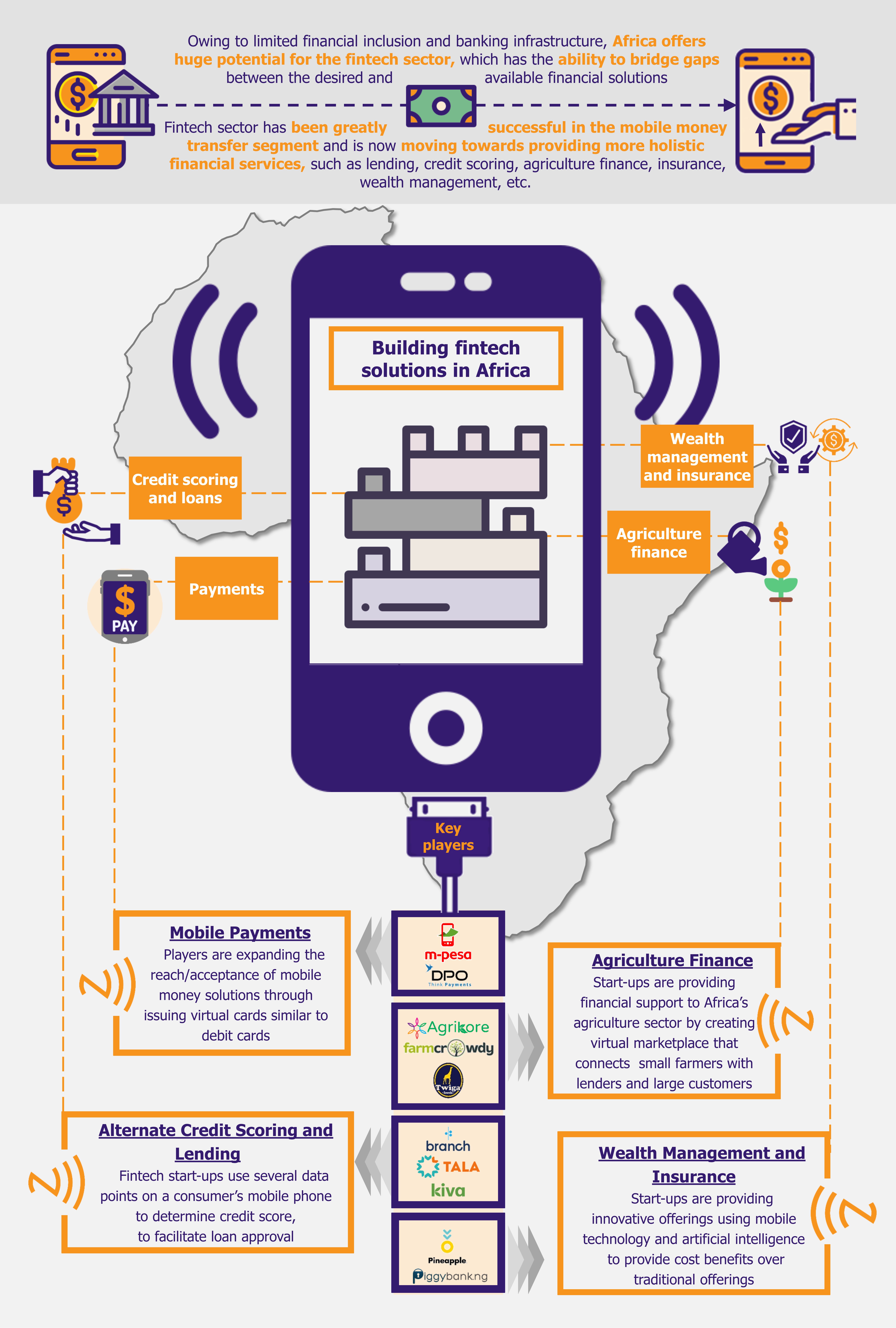
Africa carries the world’s highest burden of disease and experiences a severe shortage of healthcare workers. Across the continent, accessibility to primary healthcare remains to be a major challenge. During the COVID-19 pandemic, several health tech companies emerged and offered new possibilities for improving healthcare access. Among these, telemedicine and drug distribution services were able to address the shortage of health workers and healthcare facilities across many countries. New health tech solutions such as remote health monitoring, hospital automation, and virtual health assistance that are backed by AI, IoT, and predictive analytics are proving to further improve health systems in terms of costs, access, and workload on health workers. Given the diversity in per capita income, infrastructure, and policies among African countries, it remains to be seen if health tech companies can overcome these challenges and expand their reach across the continent.
Africa is the second most populated continent with a population of 1.4 billion, growing three times faster than the global average. Amid the high population growth, Africa suffers from a high prevalence of diseases. Infectious diseases such as malaria and respiratory infections contribute to 80% of the total infectious disease burden, which indicates the sum of morbidity and mortality in the world. Non-communicable diseases such as cancer and diabetes accounted for about 50% of total deaths in 2022. High rates of urbanization also pose the threat of spreading communicable diseases such as COVID-19, Ebola, and monkey fever.
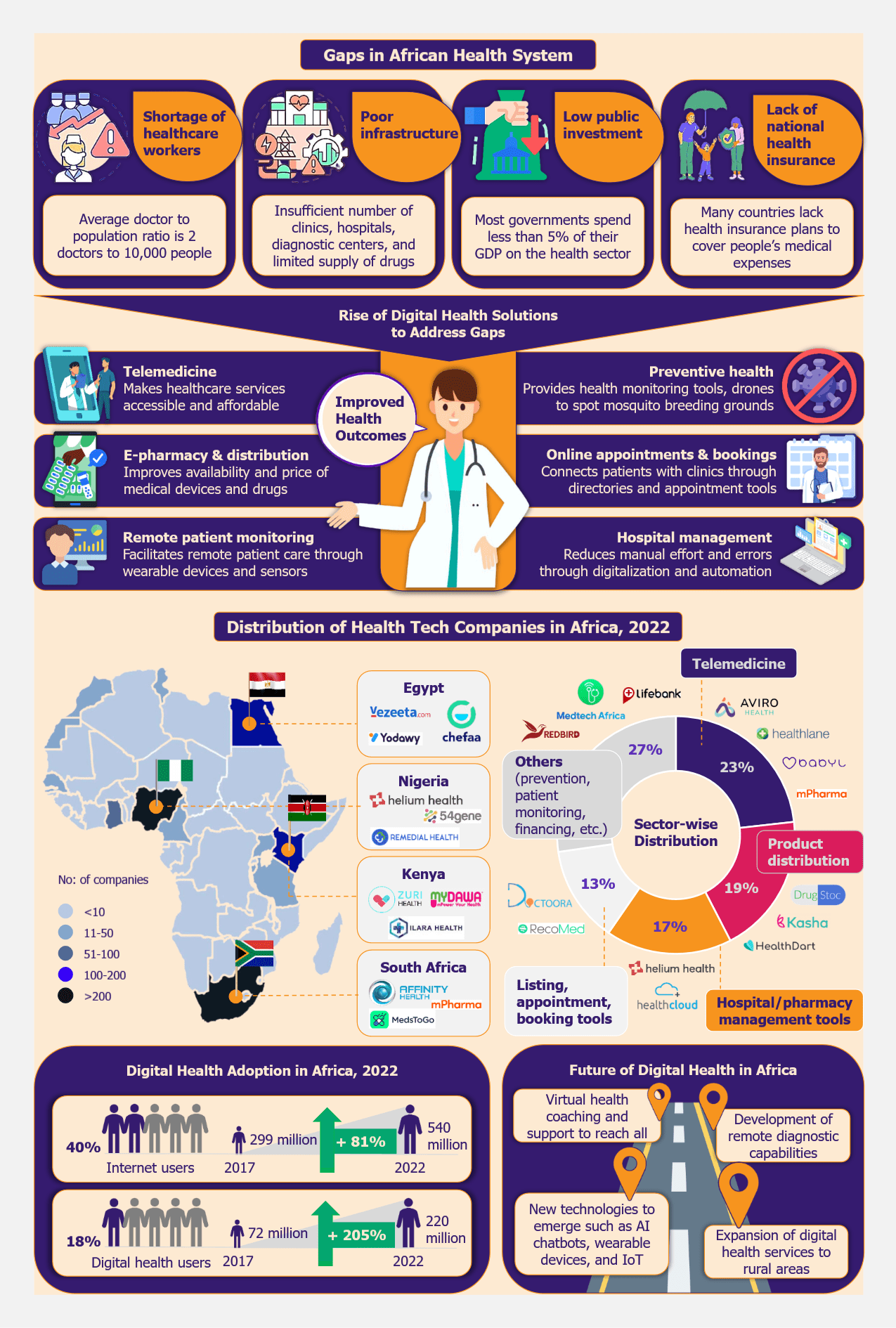
A region where healthcare must be well-accessible is indeed ill-equipped due to limited healthcare infrastructure and the shortage of healthcare workers. According to WHO, the average doctor-to-population ratio in Africa is about two doctors to 10,000 people, compared with 35.5 doctors to 10,000 people in the USA.
Poor infrastructure and lack of investments worsen the health systems. Healthcare expenditure (aggregate public healthcare spending) in African countries is 20-25 times lower than the healthcare expenditure in European countries. Governments here typically spend about 5% of GDP on healthcare, compared with 10% of GDP spent by European countries. Private investment in Africa is less than 25% of the total healthcare investments.
Further, healthcare infrastructure is unevenly distributed. Professional healthcare services are concentrated in urban areas, leaving 56% of the rural population unable to access proper healthcare. There are severe gaps in the number of healthcare units, diagnostic centers, and the supply of medical devices and drugs. Countries such as Zambia, Malawi, and Angola are placed below the rank of 180 among 190 countries ranked by the WHO in terms of health systems. Low spending power and poor national health insurance schemes discourage people from using healthcare services.
Health tech solutions’ potential to fill the healthcare system gaps
As the prevailing health systems are inadequate, there is a strong need for digital solutions to address these gaps. Health tech solutions can significantly improve the access to healthcare services (consultation, diagnosis, and treatment) and supply of medical devices and drugs.
Health tech solutions can significantly improve the access to healthcare services (consultation, diagnosis, and treatment) and supply of medical devices and drugs.
For instance, Mobihealth, a UK-based digital health platform founded in 2017, is revolutionizing access to healthcare across Africa through its telemedicine app, which connects patients to over 100,000 physicians from various parts of the world for video consultations. The app has significantly (by over 60%) reduced hospital congestion.
Another example is the use of drones in Malawi to monitor mosquito breeding grounds and deliver urgent medical supplies. This project, which was introduced by UNICEF in 2017, has helped to curb the spread of malaria, which typically affects the people living in such areas at least 2-3 times a year.
MomConnect, a platform launched in 2014 by the Department of Health in South Africa, is helping millions of expectant mothers by providing essential information through a digital health desk.
While these are some of the pioneers in the health-tech industry, new companies such as Zuri Health, a telemedicine company founded in Kenya in 2020, and Ingress Healthcare, a doctor appointment booking platform launched in South Africa in 2019, are also strengthening the healthcare sector. A study published by WHO in 2020 indicated that telemedicine could reduce mortality rates by about 30% in Africa.
The rapid rise of health tech transforming the African healthcare landscape
Digital health solutions started to emerge during the late 2000’s in Africa. Wisepill, a South African smart pill box manufacturing company established in 2007, is one of the earliest African health tech success stories. The company developed smart storage containers that alert users on their mobile devices when they forget to take their medication. The product is widely used in South Africa and Uganda.
The industry gained momentum during the COVID-19 pandemic, with the emergence of several health tech companies offering remote health services. The market experienced about 300% increase in demand for remote healthcare services such as telemedicine, health monitoring, and medicine distribution.
According to WHO, the COVID pandemic resulted in the development of over 120 health tech innovations in Africa. Some of the health tech start-ups that emerged during the pandemic include Zuri Health (Kenya), Waspito (Cameroon), and Ilara Health (Kenya). Several established companies also developed specific solutions to tackle the spread of COVID-19 and increase their user base. For instance, Redbird, a Ghanaian health monitoring company founded in 2018, gained user attention by launching a COVID-19 symptom tracker during the pandemic. The company continues to provide remote health monitoring services for other ailments, such as diabetes and hypertension, which require regular health check-ups. Patients can visit the nearest pharmacy instead of a far-away hospital to conduct tests, and results will be regularly updated on their platform to track changes.
Start-ups offering advanced solutions based on AI and IoT have been also emerging successfully in recent years. For instance, Ilara Health, a Kenya-based company, founded during the COVID-19 pandemic, is providing affordable diagnostic services to rural population using AI-powered diagnostic devices.
With growing internet penetration (40% across Africa as of 2022) and a rise in investments, tech entrepreneurs are now able to develop solutions and expand their reach. For instance, mPharma, a Ghana-based pharmacy stock management company founded in 2013, is improving medicine supply by making prescription drugs easily accessible and affordable across nine countries in Africa. The company raised a US$35 million investment in January 2022 and is building a network of pharmacies and virtual clinics across the continent.
Currently, 42 out of 54 African countries have national eHealth strategies to support digital health initiatives. However, the maximum number of health tech companies are concentrated in countries such as South Africa, Nigeria, Egypt, and Kenya, which have the highest per capita pharma spending in the continent. Nigeria and South Africa jointly account for 46% of health tech start-ups in Africa. Telemedicine is the most offered service by start-ups founded in the past five years, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. Some of the most popular telemedicine start-ups include Babylon Health (Rwanda), Vezeeta (Egypt), DRO Health (Nigeria), and Zuri Health (Kenya).
Other most offered services include medicine distribution, hospital/pharmacy management, and online booking and appointments. Medicine distribution start-ups have an immense impact on minimizing the prevalence of counterfeit medication by offering tech-enabled alternatives to sourcing medication from open drug markets. Many physical retail pharmacy chains, such as Goodlife Pharmacy (Kenya), HealthPlus (Nigeria), and MedPlus (Nigeria), are launching online pharmacy operations leveraging their established logistics infrastructure. Hospitals are increasingly adopting automation tools to streamline their operations. Electronic Medical Record (EMR) management tools offered by Helium Health, a provider of hospital automation tools based in Nigeria are widely adopted in six African countries.
Medicine distribution start-ups have an immense impact on minimizing the prevalence of counterfeit medication by offering tech-enabled alternatives to sourcing medication from open drug markets.
For any start-up in Africa, the key to success is to provide scalable, affordable, and accessible digital health solutions. Low-cost subscription plans offered by Mobihealth (a UK-based telehealth company founded in 2018) and Cardo Health (a Sweden-based telehealth company founded in 2021) are at least 50% more affordable than the average doctor consultation fee of US$25 in Africa. Telemedicine platforms such as Reliance HMO (Nigeria) and Rocket Health (Uganda) offer affordable health insurance that covers all medical expenses. Some governments have also taken initiatives in partnering with health tech companies to provide affordable healthcare to their people. For instance, the Rwandan government partnered with a digital health platform called Babylon Health in 2018 to deliver low-cost healthcare to the population of Rwanda. Babylon Health is able to reach the majority of the population through simple SMS codes.
Government support and Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
With a mission to have a digital-first universal primary care (a nationwide program that provides primary care through digital tools), the Rwandan government is setting an example by collaborating with Babylon Health, a telemedicine service that offers online consultations, appointments, and treatments.
As part of nationwide digitization efforts, the government has established broadband infrastructure that reaches 90% population of the country. Apart from this, the country has a robust health insurance named Mutuelle de Santé, which reaches more than 90% of the population. In December 2022, the government of Ghana launched a nationwide e-pharmacy platform to regulate and support digital pharmacies. Similarly, in Uganda, the government implemented a national e-health policy that recognizes the potential of technology in the healthcare sector.
MomConnect, a mobile initiative launched by the South African government with the support of Johnson and Johnson in 2014 for educating expectant and new mothers, is another example of a successful PPP. However, apart from a few countries in the region, there are not enough initiatives undertaken by the governments to improve health systems.
Private and foreign investments
In 2021, health tech start-ups in Africa raised US$392 million. The sustainability of investments became a concern when the investments dropped to US$189 million in 2022 amid the global decline in start-up funding.
However, experts predict that the investment flow will improve in 2023. Recently, in March 2023, South African e-health startup Envisionit Deep AI raised US$1.65 million from New GX Ventures SA, a South African-based venture capital company. Nigerian e-health company, Famasi, is also amongst the start-ups that raised investments during the first quarter of 2023. The company offers doorstep delivery of medicines and flexible payment plans for medicine bills.
The companies that have raised investments in recent years offer mostly telemedicine and distribution services and are based in South Africa, Nigeria, Egypt, and Kenya. That being said, start-ups in the space of wearable devices, AI, and IoT are also gaining the attention of investors. Vitls, a South African-based wearable device developer, raised US$1.3 million in funding in November 2022.
Africa-based incubators and accelerators, such as Villgro, The Baobab Network, and GrowthAfrica Accelerator, are also supporting e-health start-ups with funding and technical guidance. Villgro has launched a US$30 million fund for health tech start-ups in March 2023. Google has also committed US$4 million to fund health tech start-ups in Africa in 2023.
Digital future for healthcare in Africa
There were over 1,700 health tech start-ups in Africa as of January 2023, compared with about 1,200 start-ups in 2020. The rapid emergence of health tech companies is addressing long-running challenges of health systems and are offering tailored solutions to meet the specific needs of the African market.
Mobile penetration is higher than internet penetration, and health tech companies are encouraged to use SMS messaging to promote healthcare access. However, Africa is expected to have at least 65% internet penetration by 2025. With growing awareness of the benefits of health tech solutions, tech companies would be able to address new markets, especially in rural areas.
Companies that offer new technologies such as AI chatbots, drones, wearable devices for remote patient monitoring, hospital automation systems, e-learning platforms for health workers, the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), and predictive analytics are expected to gain more attention in the coming years. Digitally enabled, locally-led innovations will have a huge impact on tackling the availability, affordability, and quality of health products and services.
Digitally enabled, locally-led innovations will have a huge impact on tackling the availability, affordability, and quality of health products and services.
Challenges faced by the health tech sector
While the African health tech industry has significantly evolved over the last few years, there are still significant challenges with regard to infrastructure, computer literacy, costs, and adaptability.
For instance, in Africa, only private hospitals have switched to digital records. Many hospitals still operate without computer systems or internet connections. About 40% of the population are internet users, with countries such as Nigeria, Egypt, South Africa, Morocco, Ghana, Kenya, and Algeria being the ones with the highest number of internet users (60-80% of the population). However, 23 countries in Africa still have low internet penetration (less than 25%). This is the major reason why tech companies concentrate in the continent’s largest tech hubs.
On the other hand, the majority of the rural population prefers face-to-face contact due to the lack of digital literacy. Electricity and internet connectivity are yet to reach all parts of the region and the cost of the internet is a burden for many people. Low-spending power is a challenge, as people refuse to undergo medical treatment due to a lack of insurance schemes to cover their medical expenses. Insurance schemes provided in Africa only cover 60% of their healthcare expenses. Even though health tech solutions bring medical costs down, these services still remain unaffordable for people in low-income countries. Therefore, start-ups do not prefer to establish or expand their services in such regions.
Another hurdle tech companies face is the diversity of languages in Africa. Africa is home to one-third of the world’s languages and has over 1,000 languages. This makes it difficult for companies to customize content to reach all populations.
Amidst all these challenges, there is very little support from the governments. The companies face unfavorable policies and regulations that hinder the implementation of digital solutions. Only 8% of African countries have online pharmacy regulations. In Nigeria, regulatory guidelines for online pharmacies only came into effect in January 2022, and there are still unresolved concerns around its implementation.
Lack of public investment and comprehensive government support also discourage the local players. Public initiatives are rare in providing funding, research support, and regulatory approval for technology innovations in the health sector. Private investment flow is low for start-ups in this sector compared to other industries. Health tech start-ups raised a total investment of US$189 million in 2022, which is not even 10% of the total investments raised by start-ups in other sectors in Africa. Also, funding is favored towards the ones established in high-income countries. Founders who don’t have ties to high-income countries struggle to raise funds.
EOS Perspective
The emergence of tech health can be referred to as a necessary rise to deal with perennial gaps in the African healthcare system. Undoubtedly, many of these successful companies could transform the health sector, making quality health services available to the mass population. The pandemic has spurred the adoption of digital health, and the trend experienced during the pandemic continues to grow with the developments in the use of advanced technologies such as AI and IoT. Telemedicine and distribution have been the fastest-growing sectors driven by the demand for remote healthcare services during the pandemic. Home-based care is likely to keep gaining momentum with the development of advanced solutions for remote health monitoring and diagnostic services.
Home-based care is likely to keep gaining momentum with the development of advanced solutions for remote health monitoring and diagnostic services.
With the increasing internet penetration and acceptance of digital healthcare, health tech companies are likely to be able to expand their reach to rural areas. Right policies, PPPs, and infrastructure development are expected to catalyze the health tech adoption in Africa. Companies that offer advanced technologies such as IoT-enabled integrated medical devices, AI chatbots, drones, wearable devices for remote patient monitoring, hospital automation systems, e-learning platforms for health workers, and predictive analytics for health monitoring are expected to emerge successfully in the coming years.