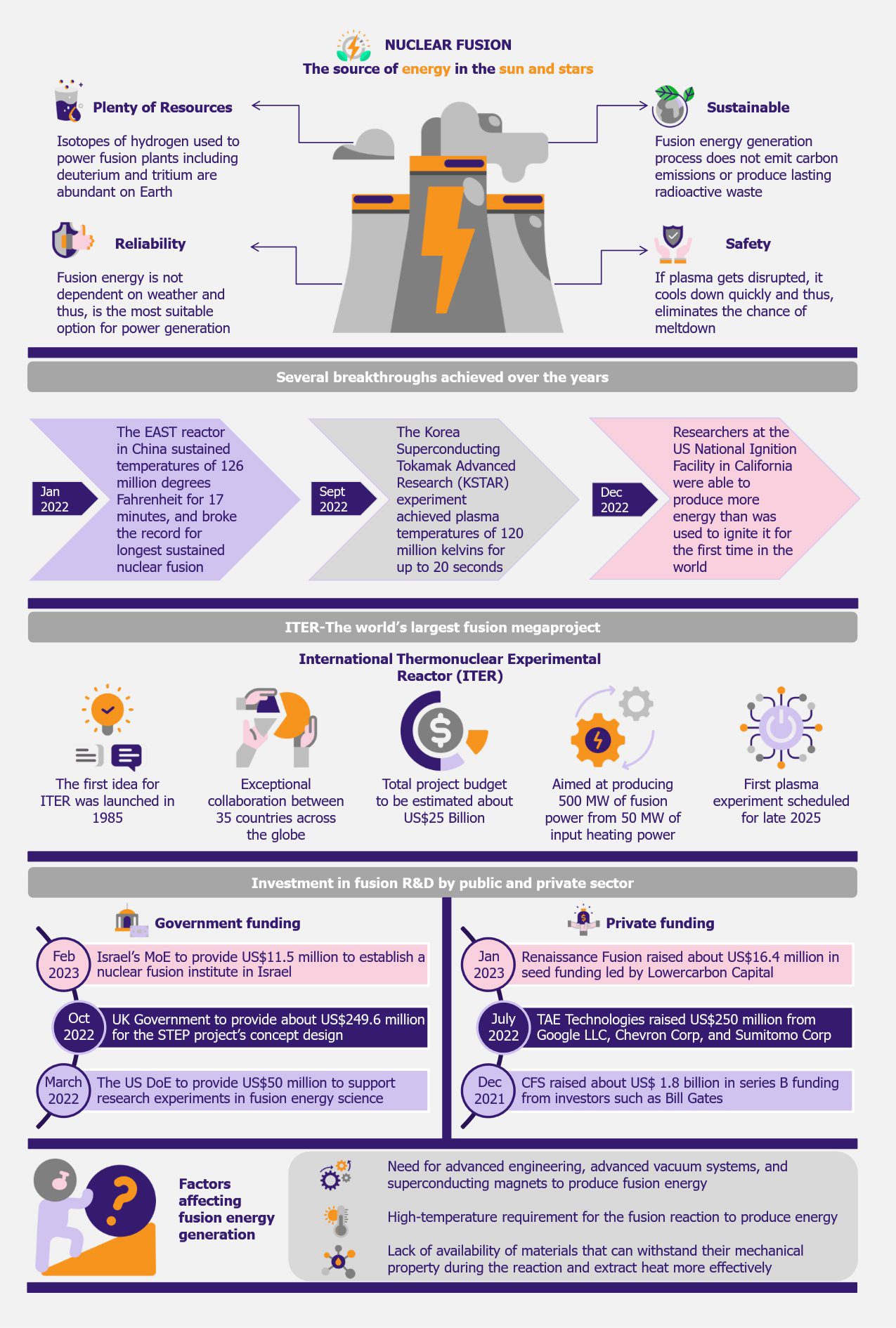
Nuclear fusion has recently gained attention as a potential source of clean energy. It was a result of the US National Ignition Facility in California achieving a major milestone in December 2022 in which researchers were able to produce more energy than was used to ignite it for the first time. Several countries are cooperating in the world’s largest fusion experiment project called ITER, focused on the construction and operation of an experimental fusion reactor located in France. Large-cap companies such as Google and the ministries regulating energy policies across the globe are also investing in fusion energy projects and start-ups to promote fusion energy generation. Despite huge investments, commercializing fusion energy still has a long way to go due to certain technological and operational challenges associated with the generation of this type of energy.
Ever-increasing carbon emissions due to the ongoing rise in energy consumption are driving the need for accelerating energy generation from renewable sources. As of October 2022, over 40% of global carbon emissions were caused by power generation. As per the International Energy Agency, carbon emissions from energy generation increased by 0.9% in 2022, in comparison with 2021, to reach 36.8GT.
Additionally, the energy crisis caused by the Russia-Ukraine war, particularly in Europe, further augmented the need for energy generation using renewable sources. The surge in energy demand from households and industries is putting pressure on the existing energy supplies, thus resulting in high energy prices.
So far, solar and wind energy sources have been prominently used across countries to meet the rapidly increasing energy demand. Nuclear fusion is another alternative renewable source as it does not emit carbon emissions or produce long-lived radioactive waste products, unlike nuclear fission.
Nuclear fusion is an energy-intensive process and requires high temperatures for fusion reaction. In the nuclear fusion process, energy is released by combining two atomic nuclei into one heavier nucleus. The released energy is then captured and converted into electricity by a fusion machine. This process is also the key source of energy in the sun and other stars.
Nuclear fusion releases around four million times more energy as compared to coal, gas, or oil, and four times more than nuclear fission technology. Nuclear fusion can provide energy to an extent that can power up homes, cities, and whole countries.
Current state of the nuclear fusion energy
The potential of generating nuclear fusion energy has been recognized since the 1950s. Countries across geographies have been involved in nuclear fusion research, led by the EU, USA, Russia, and Japan, along with vigorous programs underway in China, Brazil, Korea, and Canada. Various experimental fusion devices have been designed and constructed to advance and transform the way fusion energy is generated. These include tokamaks, stellarators, and laser-based technology devices. Tokamaks and stellarators have been used more commonly for fusion energy research experiments.
Some of the tokamaks and stellarators built across countries for generating fusion energy include the Joint European Torus (JET), started in the UK in 1978, the Wendelstein 7-X stellarator, started in Germany in 1994, Korea Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research (KSTAR) started in South Korea in 1995, the Mega Amp Spherical Tokamak- (MAST) initially started in the UK in 1997 and further upgraded to MAST-U in 2013, and Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) started in China in 2000, among others. Six countries, including China, India, Japan, Korea, Russia, the USA, as well as the EU, are cooperating in the world’s largest fusion experiment, ITER, an experimental fusion reactor currently under construction in France through EURATOM, the European Atomic Energy Community. ITER idea was first launched in 1985 and established in 2007. Its first experiment was scheduled to start in 2025 but is delayed due to Covid-19 disruptions. It is aimed at producing 500MW of fusion power from 50MW of input heating power.
Further, in 2017, China launched the China Fusion Engineering Test Reactor (CFETR) project as a follow-up to the ITER. This tokamak device is aimed at producing an extremely powerful magnetic field to confine plasma and generate fusion energy. This magnetic field can contain and control hydrogen gas ten times hotter than the core of the sun. CFETR is aimed at producing a peak power output of 2GW once completed in 2035, bridging the gap between scientific experiments and commercial use.
Extensive progress has been noticed in studying laser-based technology for fusion energy generation. Some of the facilities that use laser technology to produce fusion energy include the National Ignition Facility (NIF) at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) in the USA and the Laser Mégajoule (LMJ) in France.
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) also supports its member states in research activities related to fusion energy generation. It also organizes various workshops on fusion power plant concept demonstrations, technical meetings, and coordinates research activities.
Some of the breakthroughs achieved in fusion energy experiments to date
There has been significant progress in the research and development activities focused on nuclear fusion energy generation. Researchers are continuously emphasizing optimizing the condition of plasma through changes in density, temperature, and confinement time to achieve the required level of performance for a power plant. Several nuclear reactors were able to sustain high temperatures during the fusion process. For instance, in January 2022, the EAST reactor in China sustained temperatures of 126 million degrees Fahrenheit, which is nearly five times hotter than the sun, for 17 minutes, and thus, broke the record for longest sustained nuclear fusion.
In February 2022, the Joint European Torus (JET) achieved a record performance for sustained fusion energy of 59MJ over five seconds.
Also, in September 2022, the Korea Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research (KSTAR) experiment achieved plasma temperatures of 120 million kelvins for up to 20 seconds, a key demonstration of simultaneous high temperatures and plasma stability.
Recently, in December 2022, a major breakthrough was achieved at the US National Ignition Facility in California by using inertial confinement fusion, which released more energy than was pumped in by the lasers for the first time in the world. The laser shot released 3.15MJ of energy in comparison with the 2.05MJ pumped to the hydrogen isotope pellet by lasers. This breakthrough is likely to pave the way for abundant clean energy in the future.
Breakthroughs driving further investment in fusion energy R&D
Breakthroughs achieved over the past years in various projects have attracted significant investment by both the government and private sector in the research and development of fusion energy. For instance, in February 2023, Israel’s Ministry of Energy (MoE) proposed to provide US$11.5 million to establish a national nuclear fusion institute in Israel. This initiative includes major universities of Israel, namely the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, the Technion and Tel Aviv University, the Weizmann Institute of Science, as well as NT-Tao, an Israel-based start-up which is engaged in the development of a compact system for nuclear fusion.
Similarly, in October 2022, the UK government announced to provide US$249.6 million of funding for the Spherical Tokamak for Energy Production (STEP) project’s first phase, which will include concept design by the UK Atomic Energy Authority by 2024. STEP is a program aimed at designing and constructing a prototype fusion energy plant by 2040.
In March 2022, the US Department of Energy (DOE) proposed to provide around US$50 million of federal funding to support US scientists involved in conducting experimental research in fusion energy science. Of this, US$20 million was to support tokamak facilities and US$30 million to support fusion research to improve the performance of fusion and increase the duration of burning plasma. In addition to this, the US government’s budget for the financial year 2023 included US$723 million for the Office of Science Fusion Energy Sciences research in enabling technologies, materials, advanced computing and simulation, and new partnerships with private fusion efforts. This amount included US$240 million for the ongoing construction of ITER tokamak. Also, the budget for the financial year 2024 includes US$16.5 billion to support climate science and clean energy innovation, including US$1 billion to advance fusion energy technology.
Private funding in fusion companies has also increased significantly in the recent past. As per the Fusion Industry Association Report 2022 published in July, private sector funding amounted to about US$4.8 billion in total, witnessing an increase of 139% since 2021. Fusion companies also received an additional US$117 million in grants and other funding from governments. Big resource groups such as Equinor, based in Norway, Google, and Chevron, based in the USA, have also invested in fusion energy research. For instance, in July 2022, Chevron, together with Google and Japan-based Sumitomo Corporation, invested in TAE Technologies, a US-based nuclear fusion start-up, in a US$250 million fundraising round to build its next-generation fusion machine.
In addition to this, entrepreneurs, including Bill Gates and Jeff Bezos, are also providing financial support. In December 2021, Commonwealth Fusion Systems (CFS) raised around US$1.8 billion in series B funding from various key investors, including Bill Gates, DFJ Growth, and Emerson Collective, among others, to commercialize fusion energy.
Companies engaged in nuclear fusion energy generation
More than 35 companies are engaged in fusion energy generation for commercial use, such as Tokamak Energy, General Fusion, Commonwealth Fusion Systems, Helion Energy, Zap Energy, and TAE Technologies, among others. These fusion companies are increasingly emphasizing collaborations and experimenting with new technologies to produce fusion energy and make it available for commercial use.
In March 2023, Eni, an energy group based in Italy, and Commonwealth Fusion Systems (CFS) based in the USA, a spin-out of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), signed a collaboration agreement aimed at accelerating the industrialization of fusion energy.
In February 2023, TAE Technologies achieved a breakthrough in its hydrogen-boron fusion experiment in magnetically confined fusion plasma. This experiment was a collaboration between Japan’s National Institute for Fusion Science (NIFT) and TAE Technologies.
Also, in February 2023, Tokamak Energy proposed to build a new fusion energy advanced prototype at the United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority’s (UKAEA) Culham Campus, UK, using power plant-relevant magnet technology. It also built the first set of high-temperature superconducting magnets for testing nuclear fusion power plants. This supermagnet can confine and control extremely hot plasma created during the fusion process.
Certain breakthroughs achieved over the years in the nuclear fusion energy field have encouraged the entry of various start-ups across geographies. For instance, Princeton Stellarators, a US-based start-up focused on building modular, utility-scale fusion power, was founded in 2022. Another start-up named Focused Energy, a Germany-based fusion company, was founded in 2021 to develop a fusion power plant based on laser and target technology. In September 2021, the company raised US$15 million in seed funding led by Prime Movers Lab, along with additional investment from various entrepreneurs.
Start-ups are also emphasizing raising funds to create new fusion technologies and make a significant impact on the industry. In February 2023, NT-Tao, an Israel-based nuclear fusion start-up founded in 2019, raised US$22 million in a series A funding round aimed at developing a high-density, compact fusion reactor to provide clean energy.
Additionally, in January 2023, Renaissance Fusion, a France-based start-up founded in 2020, raised US$16.4 million in a seed funding round led by Lowercarbon Capital. The company is engaged in the development of a stellarator reactor for fusion energy generation.
Challenges to nuclear fusion energy generation
Although a lot of companies and governments across geographies are investing in nuclear fusion energy generation experiments, building full-scale fusion-generating facilities requires advanced engineering, advanced vacuum systems, and superconducting magnets. One of the key challenges in the fusion process is the requirement of extremely high temperatures to produce energy. Also, it becomes difficult to control plasma at such high temperatures.
Additionally, the lack of availability of materials that can extract heat more effectively while withstanding their mechanical properties for a longer duration is another challenge affecting the fusion energy generation process.
Moreover, fusion research projects are also facing capital and financing challenges due to high upfront costs, return uncertainty, and long project duration. The capital investment involved in building and operating a fusion reactor is high due to complex technology that requires significant investment in R&D, high energy requirements, use of advanced materials, and regulatory requirements aimed at ensuring the safety and low environmental impact of the fusion reactor. The cost of building a fusion reactor ranges between tens to hundreds of billions of dollars. It can vary depending on various factors such as size, design, location, materials, and technology used.
Since fusion energy is a new technology, there is uncertainty about when nuclear fusion will become a viable and cost-effective energy source, such as other energy sources, including wind and solar. This makes it difficult for investors to invest in fusion projects and predict the return on investment.
However, ongoing research and development activities aimed at building advanced, highly efficient, and cost-effective fusion reactors and commercializing fusion energy generation at a large scale are likely to overcome these challenges in the long term.
EOS Perspective
Accelerating climate crisis is driving the investment in nuclear fusion research and development as it does not create carbon emissions and long-lasting nuclear waste products. Over the past several years, various fusion research projects, university programs, and start-ups have achieved breakthroughs in the fusion energy field. The most recent breakthrough at the US National Ignition Facility in California, which released more energy than was pumped in by the lasers, has paved the way to the nuclear fusion gold rush and sparked excitement among investors, companies, and researchers.
Many fusion companies, such as Commonwealth Fusion Systems and TAE Technologies, are claiming to exceed breakeven by 2025 and commercialize fusion energy by 2030. Billions of dollars have been invested in nuclear fusion energy generation experiments but no company or projects have been able to achieve breakeven yet.
Several new fusion projects are planning on using advanced materials and putting a new generation of supercomputers to tweak the performance of ultrahigh-temperature plasma, but commercializing fusion energy is still far from reality. Moreover, the fusion process is very complex, requires extreme temperatures for fusion reactions, and involves huge energy costs. Thus, alternative clean energy sources such as wind and solar will likely remain the near-term methods to meet sustainable energy demand. At the same time, it should be expected that the increasing government support and investment by large cap organizations and entrepreneurs are likely to help set up viable fusion power plants in the future.