Globally, electronics are discarded at alarming rates, generating unprecedented amounts of e-waste. On the other side, finite resources such as minerals and metals, which are used to make these electronics, are getting depleted. To foster sustainability across the electronics value chain, many tech companies are adopting strategies such as incorporating long-lasting product design, using recyclable and biodegradable materials, using clean energy for power generation, etc. However, the sustainable electronics concept is still in a nascent stage of adoption, and a lot of work needs to be done. Strict legislation, cross-sectoral collaborations, organizations facilitating networking and knowledge sharing, and changes in business models are needed to implement sustainability across various business units in the electronics industry.
Growing need for sustainability in electronics
Global consumption of electronics is rising exponentially and is expected to double by 2050. This increase is set to adversely affect the environment, leading to more mining of raw materials, an unprecedented increase in e-waste, and increased carbon emissions during manufacturing.
Globally, people are discarding electronics sooner than before due to the availability of new electronics, owning outdated models, obsolescence, etc. Over the last few years, nearly 50 million tons of e-waste has been generated annually. Only 17% of this e-waste is recycled globally, and the rest is transported and dumped in developing countries such as Pakistan, Nigeria, and India, which do not have adequate facilities for processing and handling e-waste. This e-waste ends up in landfills, accounting for approximately 70% of hazardous chemicals, and pollutes the air and water streams. Moreover, e-waste generated globally contains recyclable or reusable raw materials, scrap rare earth metals, plastics, and valuable elements, which are valued at US$62.5 billion per year.
Given the economic and environmental cost of e-waste, as well as responding to growing consumer preference for sustainable products, several companies are looking to transition to sustainable electronics. Sustainable electronics are products that are made using recycled or reusable and biodegradable materials, as well as products that generate low carbon emissions during manufacturing and distribution.
Recycling, clean energy power, and modular design for sustainable electronics
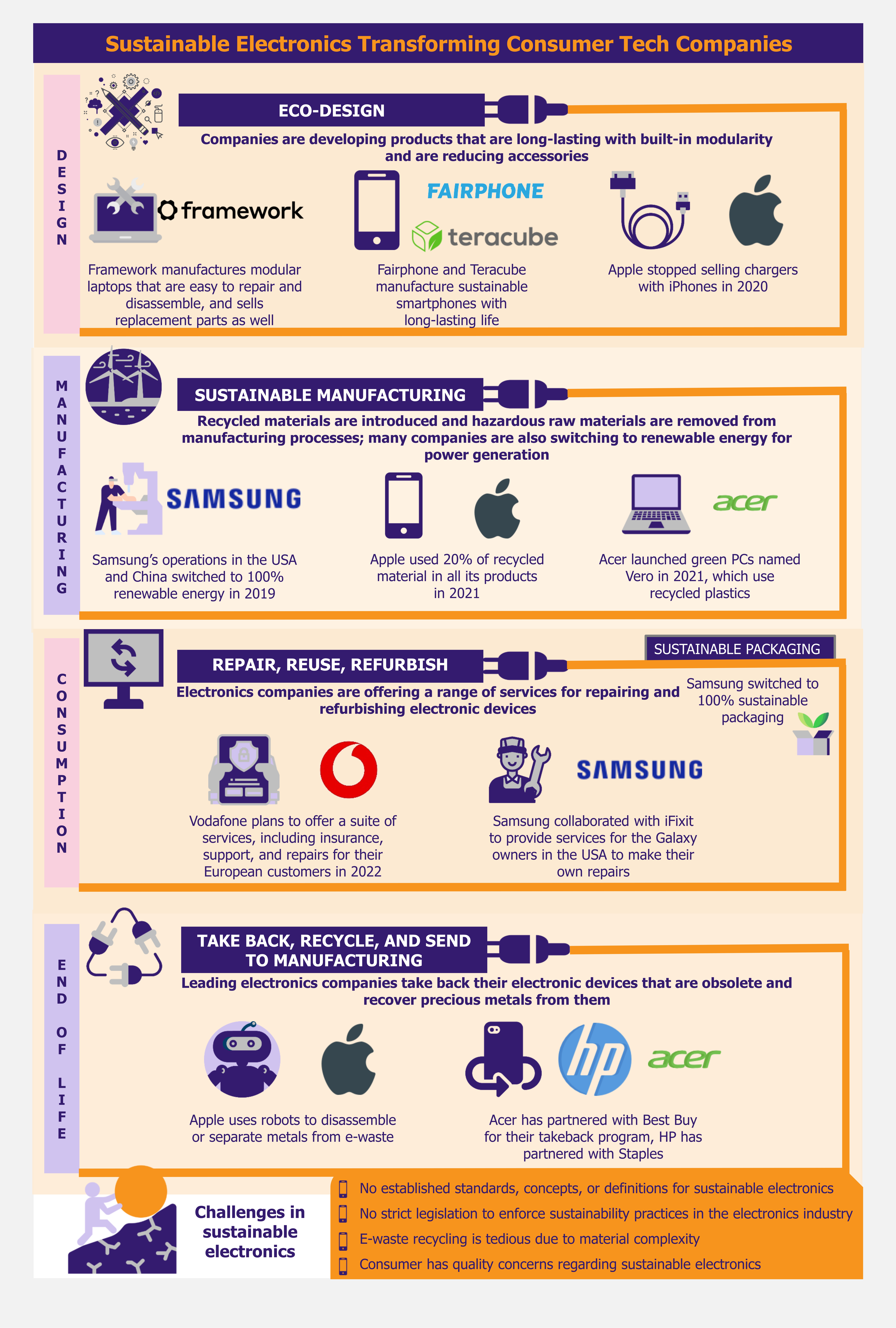
Over the last few years, consumer tech companies have been adopting many strategies for manufacturing electronics sustainably. In 2021, tech giants Cisco, Dell, Google, Microsoft, Vodafone, and many others together formed a “Circular Electronics Partnership (CEP)” to accelerate the circular economy for electronics by 2030 and to help businesses and organizations overcome barriers to sustainable electronics.
Several companies are looking to increase the life span of their smartphones to make them more sustainable. Increasing the phone’s life span by two years can reduce carbon emissions to a great extent, as 80% of the carbon emissions come during manufacturing, shipping, and the first year of phone usage. Fairphone, a Dutch-based smartphone manufacturer, has introduced smartphones with a lifespan of approximately 5 years, higher than the average lifespan of 2.5 years. Similarly, Teracube, a US-based sustainable smartphone manufacturer, has launched phones that can last up to 4 years.
Many companies are also designing their products with modularity, which allows users to repair, upgrade, customize, and disassemble their gadgets easily. For instance, Framework Computer, a US-based laptop manufacturer, sells laptops that can be upgraded. The company offers upgrading kits that contain laptop main boards and top covers to customize the device as per the user’s need. Similarly, Fairphone manufactures modular smartphones, which are easy to repair and upgrade. These kinds of gadgets eliminate the user’s need to buy new ones, saving both costs and wastage.
There is also an increased interest among consumer electronics companies to use recycled materials in various products. Sony, a Japan-based multinational corporation, has developed a recycled plastic, SORPLAS, and has been using it in a range of its products, such as audio systems and televisions, since 2011. In 2022, Logitech, a Swiss-American manufacturer of computer peripherals and software, used recycled plastic in 65% of its mice and keyboards. Similarly, in 2021, Acer, a Taiwan-based electronics corporation, launched a series of PCs named Vero, which uses recycled plastics for the chassis and keycaps. Acer also launched the Earthion program, an eco-friendly initiative, in the same year and started working closely with suppliers and partners to bring various sustainability measures in product design, packaging design, and production. Tech giant Apple stopped selling chargers and headphones along with the iPhone in 2020 to cut e-waste. The company used 20% recycled material in all its products in 2021 and uses robots to disassemble or separate metals from e-waste. There is 40% recycled content in the MacBook Air with Retina display, and 99% recycled tungsten is used for the iPhone 12 and Apple Watch Series. Samsung, a multinational electronics corporation, is using recycled plastics in refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners, TVs, monitors, and mobile phone chargers.
Due to this increased demand for recycled materials, recycling companies are receiving investments to a significant extent. In 2021, Closed Loop Partners, a US-based investment firm, invested an undisclosed amount in ERI, a US-based electronics recycler that supplies materials to companies such as Best Buy, Target, and Amazon, to extend the capacity for the collection and processing of electronics. Similarly, in 2022, the Australian Business Growth Fund (ABGF), an investment fund focused on small to medium-sized Australian businesses, invested US$7.5 million in Scipher, an Australia-based urban mining and e-waste recycling business.
Significant activity has been happening in the refurbished electronics market as well due to the rising consumer awareness of sustainability. Trade-in and refurbishment reduce e-waste piling up at landfills, as it limits buying newer gadgets and thereby paves the way for greater sustainability across the electronics industry. Back Market, a France-based marketplace of renewed devices (which provides refurbished devices with a one-year warranty), has raised over US$1 billion since its launch in 2014. In 2022, Verdane, a European specialist growth equity investment firm, announced an investment worth US$124 million in Finland-based Swappie, a re-commerce company that sells previously owned, new, or used smartphones. Vodafone also announced a major initiative to extend the life of new mobile phones and to encourage customers to trade in or recycle their old devices. The company is planning to provide customers in European markets with a suite of services, including insurance, support, and repairs for their devices, in 2022. Samsung collaborated with iFixit, an online repair community, for its self-repair program in 2022. The company said that under this program, Galaxy device owners in the USA can make their own repairs to the Galaxy Tab S7+, Galaxy S20, and S21 products using easy-to-repair tools available from iFixit.
Tech companies have also started transitioning to renewable energy and looking for ways to reduce their carbon emissions. Intel, a US-based technology company, uses green energy of up to 3,100,000 MWh annually in the manufacturing of processors and computer accessories. Samsung’s facility operations in the USA and China switched to 100% renewable energy in 2019. In 2021, Microsoft entered into a partnership with IFC, a member of the World Bank Group, to reduce carbon emissions in the organization’s supply chain. IFC is said to work with selected Microsoft suppliers in emerging markets, primarily in Asia, to identify technical solutions and financing opportunities to reduce emissions in the production process.
Legislation to aid the shift toward the circular economy in electronics
For years, many countries did not have appropriate policies enforcing sustainability across the electronics industry. Nevertheless, the trend is reversing with several countries adopting legislation for the circular economy. For instance, in 2020, the European Commission announced a circular electronics initiative that would promote eco-design (a design that considers environmental aspects at all stages of the product development), right-to-repair rules, including a right to update obsolete software, and regulatory measures on universal chargers, to name a few. France became the first European country to pass the Anti-Waste for a Circular Economy Act (AGEC) in 2020, which requires producers of electronic devices to provide details on how repairable their products are. According to AGEC, manufacturers are required to scale their products at a rate of 1-10 based on the reparability index. France also plans to introduce a durability index by 2024, whereby manufacturers would be asked to describe the full lifecycle of their products. Moreover, the US government passed an order in 2021 to draft regulations that protect the consumer’s right to repair electronic devices and other tools.
It is not easy to manufacture sustainable electronics
While sustainable electronics are the need of the hour, and several leading players have already started promoting and investing in this space, the sector faces many challenges. Currently, there are no established standards, concepts, or definitions concerning sustainable electronics, and there is no strict legislation to enforce sustainability practices in the electronics industry. There are some rating systems that identify energy-efficient products followed in the USA and Europe (for example, the USA’s ENERGY STAR program). However, registering and complying with the ratings and their requirements is up to the manufacturer and is not mandatory. Moreover, e-waste regulations in several countries are poorly enforced due to low financing, and illegal practices such as dumping e-waste and incineration by the informal sector still persist.
Most electronics companies are also not transparent about their environmental performance, and the impact is often hidden. The term ‘sustainable’ is widely misused as a promotional tactic by companies targeting environmentally conscious consumers.
The electronic industry also operates on a linear established model, wherein products are manufactured (with planned obsolescence) and sold to consumers. Incorporating circular strategies for recycling and reuse requires a lot of remodeling and reconfigurations across the supply chain, and the rising consumption of electronic devices makes it difficult to adapt to any new changes. Challenges, such as complex recycling processes, costs of recycling, and consumer perception of green electronics, also hamper sustainability development. Most electronics are not designed for recycling and are made of a complex mixture of materials such as heavy metals, highly toxic compounds, glass, plastics, ferrous and nonferrous materials, etc. Recycling these materials is tedious and involves several steps such as dismantling, removing the hazardous waste, shredding into fine materials, and sorting the materials into various types. The process is also resource and cost-intensive, requiring human labor, more processing time, and adequate infrastructure such as various material screening types of equipment. Recycling e-waste could also be polluting, with potential exposure to toxic metal fumes.
Finally, the perception of consumers about sustainable electronics also needs to be changed, which is challenging. There is a notion among customers that the use of recycled, sustainable materials in electronics means products would be of lower quality. A lot of investment would be required to educate and convince consumers about the benefits of sustainable electronics and to address any concerns about quality. In most cases, it is difficult to pass on these costs to the consumers as they are unlikely to accept higher prices. Thus, this cost would be required to be absorbed by the companies themselves. Due to this, most current initiatives toward sustainable electronics can be best described as half measures.
EOS Perspective
The economic benefits of sustainable electronics are enormous. The resource scarcity and the price fluctuation of various minerals and metals make them necessary to recycle, recover, and reuse in the circular economy. Over the last few years, consumer electronics manufacturers have taken many sustainability initiatives, such as reducing energy consumption, eliminating hazardous chemicals, introducing biodegradable packaging, incorporating recycled and recyclable materials in products, and investing in renewable energy projects. Also, the refurbished electronics segment is growing fast, while interest is surging in introducing devices with built-in reparability. While several small initiatives are being taken by leading players, electronics manufacturers mainly do not know how to introduce sustainability across their products in a mainstream fashion.
Sustainability in electronics has still a long way to go. Several legislative initiatives are underway toward a circular (sustainable) electronics economy, and it is high time for electronics manufacturers to be proactive and rethink their business models. A complete business model transformation is required to integrate sustainability across every unit. Cross-sector collaborations with stakeholders such as product designers, manufacturers, investors, raw material producers, and consumers are crucial to understanding the technical know-how. It is essential to analyze the entire life cycle of products, from choosing raw materials to their disposal, and to prioritize circular strategies for such products. Electronic manufacturers also need to come up with creative and rewarding ways for consumers to be willing to choose sustainable products, as, in the end, the industry cannot flourish without consumer acceptability. The future of sustainable electronics can be bright, and manufacturers who see this as a potential business opportunity rather than a problem will benefit in the long term.