Estonia, a small Baltic country with a population of 1.4 million, is in the news for all the right reasons: its burgeoning fintech sector. With a market size of €15.2 billion in 2023 and projected growth of 5.7% CAGR from 2023 to 2028, Estonia’s number of fintech companies has increased by 23% from 2020 to 2023. The country has 264 fintech startups, half emerging between 2020 and 2022. Strategic investments in digital infrastructure, a progressive regulatory environment, and a tech-friendly culture make Estonia a leading hub for fintech innovation in Europe.
Estonia has become an important name in the fintech sector ever since its financial institutions started using fintech in the early 2000s. It has become the leading fintech hub in Europe, with 2.3 fintech unicorns (startups with a valuation exceeding US$1 billion) per million population.
Most fintech startups, accounting for 87% of all fintech companies in Estonia, fall into six categories: digital asset exchange (33%), digital lending (15%), enterprise technology provisioning (14%), digital payments (11%), wealthtech (9%), and digital capital raising (6%).
Startups dominate Estonia’s fintech landscape with fewer established companies, indicating a favorable environment for new players. Digital asset exchange services that facilitate the trade of cryptocurrencies or digital currencies for other assets form the lion’s share of these startups. This includes Tallinn-based companies such as AsicVault and Guardtime.
Finding customers is a concern for Estonia’s fintech sector
Fintech is flourishing in Estonia despite various challenges that players must navigate. Typically, these challenges affect the smallest and newest entrants to the market the most.
One of the significant challenges that businesses can expect is finding loyal customers for their solutions, according to the 2023 report by the TalTech School of Business. In their research, the respondents indicated finding customers as the most critical problem in two survey editions, 2021 and 2023.
Since Estonia has a small population of 1.4 million, the domestic market is relatively small. Businesses across sectors, including fintech, often face limitations in expanding their customer base. This can force companies to look beyond national borders to achieve significant growth, which can be difficult for new players.
Rising costs are affecting smaller and newer players
The financial side poses a substantial challenge for players with limited budget planning to start and expand a fintech firm in Estonia. Estonia used to be a place of low living costs and cheap labor since its independence in 1991. However, the rising operation costs now affect the fintech landscape. A 2023 report published by the European Commission indicated that in the fourth quarter of 2022, compared to the same period in the previous year, Estonia saw a 10.1% increase in hourly wage costs. This can harm small new players looking to enter Estonia’s fintech landscape.
Competition with Big Tech in foreign markets can challenge expansion
Estonian fintech companies attempting to expand into more mature markets can face several hurdles. For example, a high degree of sophistication and regulation characterizes the UK financial services sector, a desired expansion target, leaving little room for new entrants without an established brand presence or a solid track record.
Establishing trust is paramount for fintech startups, as consumers and businesses often prefer providers with known reputation, selecting them through word of mouth or established market presence. As a result, new entrants must devise comprehensive (and often cost-intensive) marketing strategies to overcome these initial credibility barriers.
Increased competition from established financial institutions that leverage their substantial resources to compete with startups can exacerbate these challenges. Big Tech firms such as Google, Amazon, and Apple have also begun to venture into the financial services sector. These companies possess strong brand recognition, customer trust, and rich data sets, enabling them to overshadow smaller fintech operations.
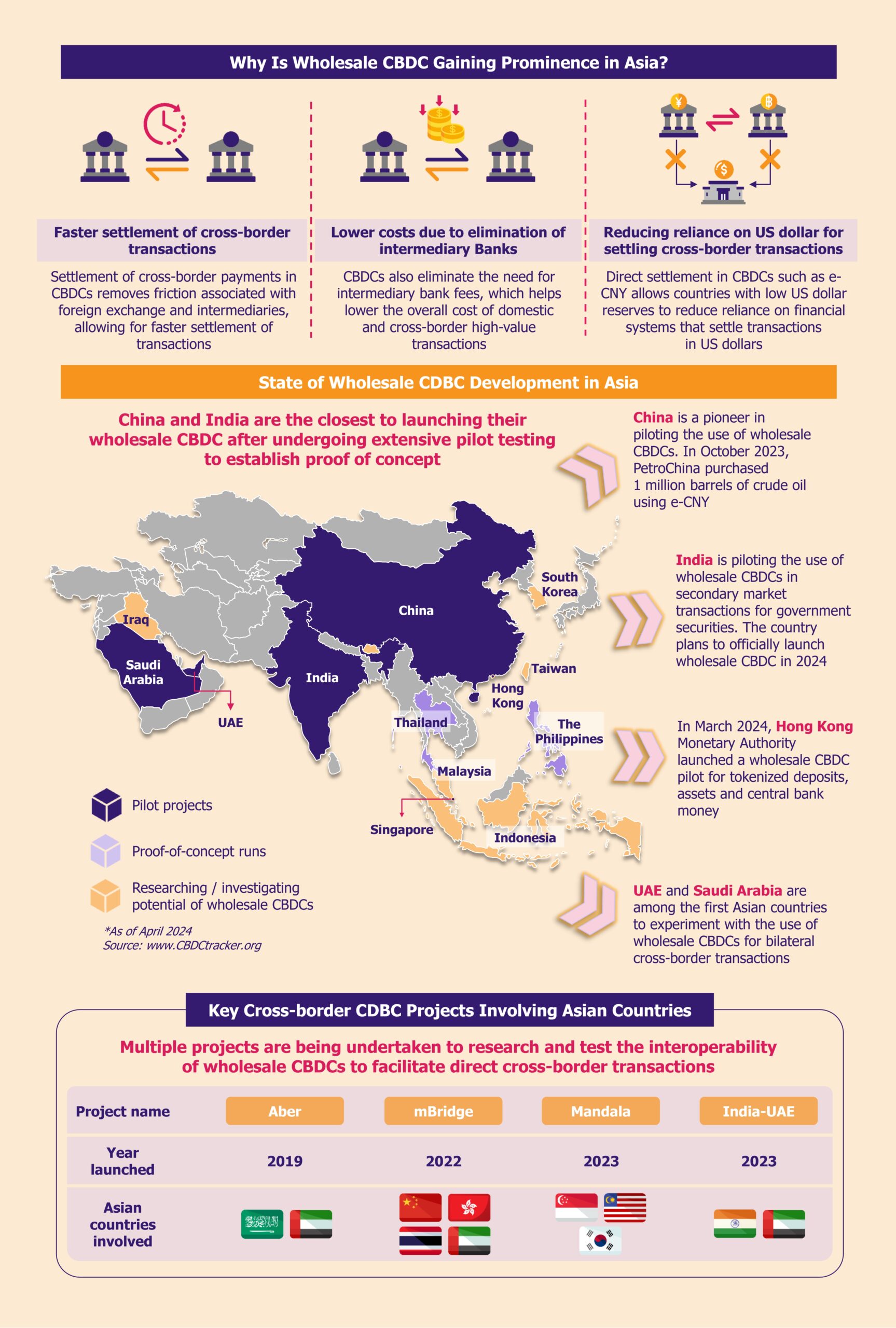
Cross-border expansion signals Estonia’s thriving fintech sector
Estonia’s cross-border expansion activities highlight its flourishing fintech sector. Fintech ranks as the second largest industry within the Estonian startup ecosystem, following business software and human resources, accounting for 13% of the nation’s startups. In terms of revenue, it also holds the second position, generating €196 million in turnover as of 2023.
Estonian fintech startups are actively pursuing opportunities beyond national borders. For instance, the financial cybersecurity firm Salv, based in Estonia, has extended its operations to Latvia and is planning further expansion to Lithuania and the UK. The firm aims to promote its AML solution, Salv Bridge, in these markets.
Additionally, in June 2024, Depowise, a startup located in Tallinn, announced its plans to expand into Ireland and the UK to enhance its market presence in the region.
Estonian fintech startups are increasingly seeking opportunities outside their home market, demonstrating the sector’s robust success and appetite for expansion.
Several catalysts are fueling the growth of Estonian fintech
Ease of doing business
The country ranks 18th in the World Bank’s ease of doing business index, beating more developed countries such as Germany (22nd), Canada (23rd), and Ireland (24th) as of 2019. This favorable business environment in the country is one of the main factors making it an attractive location for fintech businesses. According to the World Bank, the country has a highly conducive tax system, ranked 12th in the ease of paying taxes.
Efficient corporate tax systems
Due to its efficient tax policy and straightforward tax compliance frameworks, Estonia holds the top spot in the 2023 International Tax Competitiveness Index published by Tax Foundation, a US-based think tank. This allows companies to spend considerably less time (five hours per year in Estonia compared to 42 hours per year in an average OECD country) on tax-related tasks.
The Estonian tax system also boasts a similarly low compliance burden (resources and costs associated with complying with regulatory requirements) for other taxes, including value-added tax (VAT).
The country’s corporate tax rate is 20%, but it only applies to distributed profits. This means that if a company reinvests its profits back into the business, it does not pay any corporate income tax until it distributes those profits as dividends. This has significantly encouraged reinvestment, growth, and expansion of businesses, including fintech companies.
Internet freedom
Internet freedom is robust in Estonia, and the country is known for its numerous e-government initiatives. For the past several years, Estonia has maintained the second position globally in the Freedom on the Net reports by the US-based NGO Freedom House, indicating a very high internet freedom rating in the country. This minimal restriction on online content facilitates easy information and idea transfer and helps businesses, including fintech companies, to flourish.
Cybersecurity
Though online activities have minimal restrictions, the Estonian authorities have implemented proactive measures to ensure cybersecurity. The 2020 Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) published by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) ranks Estonia as the third most cybersecure nation. This is especially beneficial for fintech companies since most of their operation is online.
Estonia is a cashless society with around 99% of transactions occurring digitally. This creates a significant demand for innovative fintech solutions. Startups and established companies take this as an opportunity and offer services such as digital wallets, payment gateways, and peer-to-peer lending, among others, to which strong cybersecurity is essential.
E-residency scheme
Estonia’s e-residency program supports fintech investments by allowing foreign entrepreneurs to establish businesses remotely without a physical office. This program provides online business owners, digital entrepreneurs, and freelancers with a digital Estonian ID, granting access to various local services such as business registration, banking, payment processing, and tax management.
Since its introduction in 2014, the e-residency program has grown significantly, with 117,000 individuals from 185 nationalities obtaining e-resident status and creating over 31,800 Estonian companies. This represents roughly one in five new companies annually and links 38% of startups to e-residents. The initiative has also contributed €244 million to Estonia’s economy, generating €67.4 million in direct revenue in 2023 alone, with associated costs of €7 million, achieving a nearly tenfold return on investment.
Regulatory sandboxes
A regulatory sandbox (RS) is a framework established by regulators that allows businesses to test new products, services, or technologies in a controlled environment for a specified time. This concept is prevalent in various sectors, including finance, transportation, and healthcare.
In March 2024, Estonia expanded its RS through the Accelerate Estonia program to support non-fintech startups, inviting a medical startup, Your Cue, and a clean energy startup, O-Innovations. While regulatory sandboxes are more common in the US fintech sector, European countries such as the UK, Poland, and Spain are also developing their own. As of October 2023, there were 14 fintech sandboxes in 12 EEA countries, including Estonia, which launched its sandbox in August 2023 but has yet to invite any fintech participants.
Technological advancements dictate the direction of development
The use of newer and more innovative technologies is on the rise. Many Estonian fintech startups now use technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), the Internet of Things (IoT), etc.
An example is Depowise, which has developed innovative AI-powered solutions to automate critical functions for financial institutions, including compliance oversight, cash flow monitoring, and digital asset safekeeping.
Companies such as Value.Space, an insurtech firm founded in Estonia and currently headquartered in London with an operating office based in Tallinn, uses deep tech (advanced technologies engaged to address and revolutionize the fields they are used in) such as InSAR (Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar), AI, predictive analytics, and satellite imagery to help businesses monitor and assess the risk of damage to commercial assets.
Open banking and embedded finance are the budding trends in Estonia’s fintech solutions developments. BaaS (Banking as a Service) enables secure data sharing and collaboration between financial institutions, technology companies, and customers. Open banking facilitates the entry of new players into the Estonian market through strategic partnerships with local fintech companies. This dynamic allows fintech and technology companies to challenge traditional financial models, creating innovative customer engagement methods with financial institutions. Furthermore, open banking grants developers access to an extensive financial data repository. This accessibility has spurred the emergence of novel fintech business offerings, including budgeting applications, robo-advisors, and automated savings solutions.
Embedded finance involves fluidly incorporating financial services and products into non-financial platforms, such as e-commerce websites, mobile apps, or other digital landscapes. One of the leading examples of fintech companies in Estonia leveraging embedded finance is Inbank, which has developed a portal for solar panel installers to provide financing solutions to their customers.
Opportunities for financial cybersecurity players emerge with increasing crime
Online financial crime and money laundering protection are also gaining traction in the development of fintech solutions. This has particularly accelerated following the 2007 mass cyberattack on a range of institutions and the 2017 money laundering scandal involving Danske Bank’s Estonian branch. Since those events, Estonia has seen a surge in demand for services and products providing solutions in compliance and AML measures.
An example of a solution meeting this demand is SalvBridge, Salv’s anti-money laundering solution, which uses advanced analytics and ML to detect and prevent financial crimes in real time. It also helps financial institutions meet increasingly stringent regulatory requirements and combat money laundering effectively.
Similarly, Tallinn-based Veriff offers solutions to help reduce fraud and ensure regulation compliance. Veriff protects against identity fraud and theft by automatically verifying customer identities through an AI system that assesses various technological and behavioral factors, including facial recognition.
Serokell is another Tallinn-based R&D company offering cybersecurity solutions for fintech companies. Its solutions use functional programming, making it ideal for the complex fintech sector.
Demand for such solutions will likely continue to grow, offering lucrative opportunities for players operating and innovating in this space.
Estonia’s fintech scene is shifting towards sustainable investing
As with many other industries, sustainability and environmental awareness have entered the fintech playing field. Some players attempt to improve their sustainability score while expanding their investment portfolios to include sustainable exchange-traded funds.
Companies that operate using carbon credits and sustainability fintech players are some of the newer market entrants. An example is Grünfin, founded in 2020, which facilitates investments in sustainable stocks.
Several fintech companies are also increasingly leveraging carbon credits to enhance their sustainability practices and offer financial solutions to clients. A notable example is the partnership between XTCC, an Estonia-based company specializing in exchange-traded carbon credits, and Finmaal, a UAE-based fintech platform. This collaboration allows customers purchasing financial products, such as insurance and banking, to offset their carbon emissions at the point of sale, thus integrating sustainability measures with financial transactions.
These activities reflect a broader trend in which fintech firms are leveraging cloud technologies and financial instruments to maintain a lower carbon footprint while contributing to carbon neutrality goals. It is fair to expect that the trend of focus on the environment and sustainability will gain more traction in the future.
EOS Perspective
Estonia is emerging as a strong and resilient ground for fintech startups as well as established fintech businesses. Given the country’s favorable conditions, this growth will likely continue. Industry experts expect the market to advance further in key areas such as digital payments, blockchain technology, and AI-driven financial services.
While no single company has a dominant market share, notable players such as Wise, Guardtime, and Bolt are likely to continue strengthening their positions. These companies have the financial resources, established brand presence, and technological capabilities to drive innovation and expand their market reach. Players can also expect increased competition from established financial institutions, such as banks, which are likely to enter the space.
New players and startups can expect a better level playing field in niche fintech areas, such as financial security or climate fintech, and other related areas often working in tandem with fintech, e.g., insurtech or regtech.
With several countries, including China, Egypt, Qatar, Oman, Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia, banning bitcoin or other cryptocurrency mining due to high energy use and safety issues, climate fintech startups can use this opportunity to expand their operations to offer more sustainable financial solutions.
Fintech startups offering cyber protection and customer data safety are expected to grow significantly in the coming years, especially with large financial institutions such as US-based Evolve Bank & Trust experiencing cyberattacks and a subsequent data breach in 2024.
The new tax policies scheduled to take effect in 2025 will increase individual and corporate tax rates from 20% to 22%. These changes are likely to create some ripples in the fintech sector, at least in the portion of players’ profits that are not reinvested. The new tax laws may increase the operating costs for fintech companies, which could somewhat stifle innovation. This new development may curb investment, especially for small, budding players.
Over time, consolidation is likely to occur as the Estonian fintech market will head towards maturing. Larger companies may acquire smaller startups to expand their product offerings and increase their market share.
While development is rife in the global fintech sector, with its tech-savvy culture, strategic digital infrastructure investments, and progressive regulatory conditions, Estonia will likely carve out an even more prominent place in the fintech landscape.