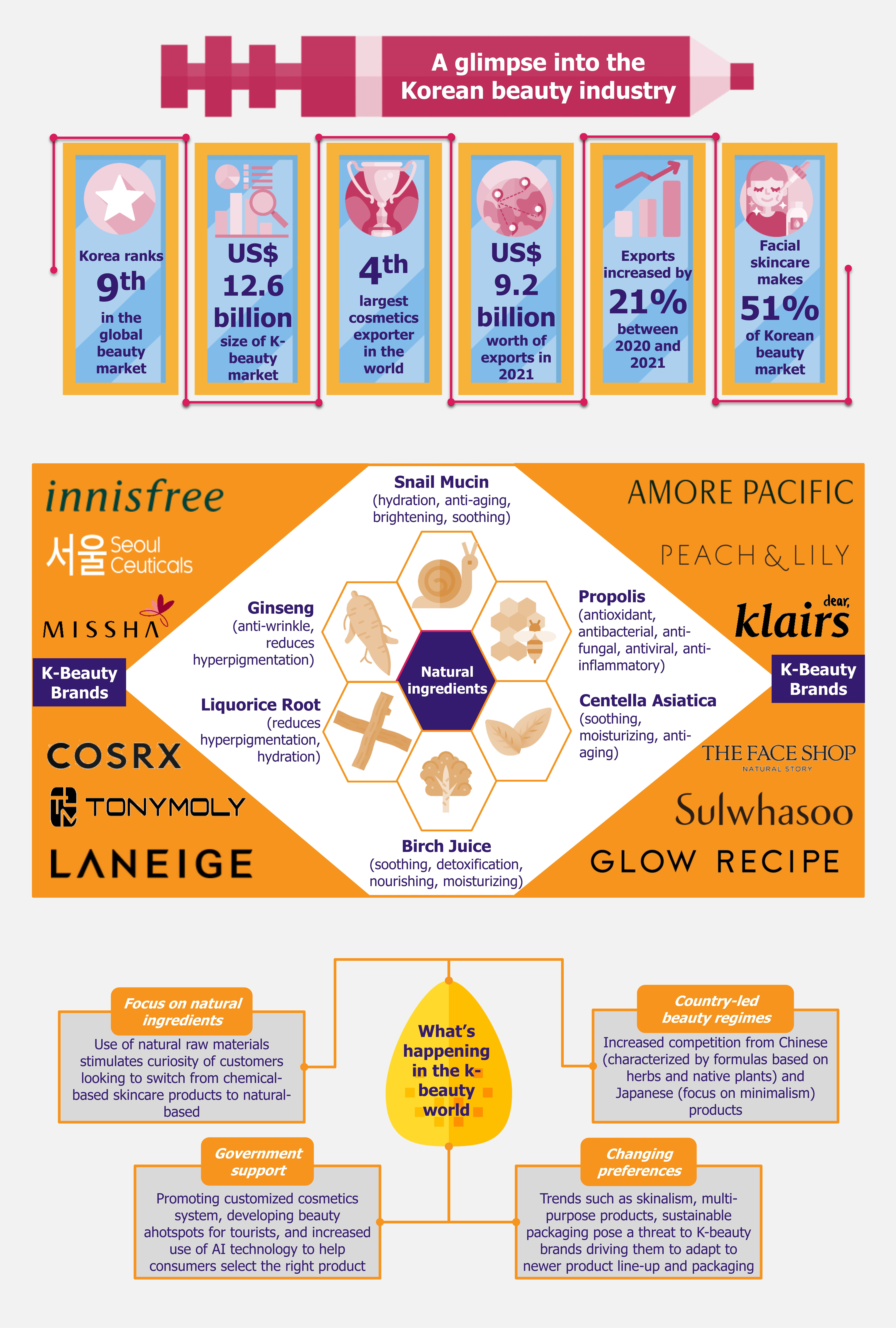
South Korea is the 9th largest cosmetic market globally with a market size of nearly US$ 12.6 billion. Innovative and affordable products made using exotic natural ingredients that focus on enhancing skin health and prevent skin concerns drive the success of K-beauty brands. Moreover, the launch of the first global customized cosmetics regulatory guidelines, along with support from the government to enhance R&D capabilities and to improve infrastructure, seem to reinforce further stability to the already growing sector. However, rising trends such as minimalism and concerns about sustainability might pose a challenge for the Korean beauty brands that thrive on the tenets of long product lines, multiple products pushed on a daily basis, and focus on packaging that tend to use plastic.
K-beauty brands are uniquely well-known due to the use of natural and unusual ingredients such as snail mucin, bee venom, ginseng, pearl, mushrooms, carrot seed oil, royal honey, and yuzu, among others, in their skincare and beauty products. Products incorporated with such ingredients may, at first, sound too out of the ordinary to be a part of one’s beauty regime but they are believed to be effective.
Korea’s beauty and cosmetic sector backed by strong government support
Korean domestic cosmetics industry, which offers growth prospect of more than 5% per year on average, draws huge support from the government. In November 2021, the South Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare declared plans for 2022 to support the cosmetics industry through technology development, preparation of legal system, overseas expansion, and professional manpower training.
On the technology side, the government is focusing on developing a ‘skin genome data platform’ that can collect and utilize skin characteristics and genomic information by country and race. The government will also continue to make mid-to-long term R&D investments towards development of local and sustainable innovative raw materials.
Additionally, plans are underway to complete the construction of the K-Beauty Comprehensive School and Academy in Osong, North Chungcheong Province, for providing professional and comprehensive training to beauty professionals by 2023; the school is to provide comprehensive consulting and train workforce for the industry’s needs.
Another way the government supports the domestic Korean beauty companies is by offering tax breaks if they have an all-export business model.
With an aim to promote the growth of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in cosmetics industry in Korea, the South Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare along with Foundation of Korea Cosmetic Industry Institute, launched a pilot concept of ‘K-Beauty Experience and Promotion Center’ in September 2021. The center is a comprehensive exhibition space for domestic SMEs in Seoul, allowing SMEs to promote their innovative cosmetic products that they would otherwise be unable to promote due to lack of funds. This is expected to not only enhance brand awareness among domestic consumers but also to strengthen export competitiveness among foreign tourists visiting Korea as potential customers. A monthly event is to display more than 100 products from 30 companies (selected through monthly application process).
In another initiative to promote the beauty sector, the Seoul Metropolitan Government conducted an online beauty industry branding conference in September 2021. Held under the theme ‘Branding Seoul’s K-beauty Industry’, the conference was attended by domestic and international experts and content creators active in the fields of beauty and tourism. Aiming at expanding the K-beauty industry through the Seoul city brand, which constitutes 45.7% of the country’s domestic cosmetics distributors, plans are underway to develop beauty specific tourism products and tourism courses by partnering with beauty creators and beauty flagship stores.
In September 2022, the government also plans to set up K-Beauty consumer hotspots or zones, a place with several K-beauty shops offering discounted deals on beauty and cosmetic products in areas frequented by tourists.
New initiatives: customized cosmetics regulations and product refills
The South Korean Ministry of Drug and Safety (MFDS), in March 2020, introduced the world’s first regulatory guidelines on custom cosmetics. This will allow manufacturers to provide consumers with cosmetics made on the spot by mixing ingredients based on personal preferences. The regulations came into effect in October 2020 and aim at ensuring that businesses (manufacturers or retailers) comply with safety management standards for the formulation of custom cosmetics.
The authorities also encourage cosmetic companies to offer cosmetic product refill services keeping in mind environmental benefits as well as cost effectiveness. People can purchase refill products at 30% to 50% lower prices when compared to a newly packaged product. As of June 2021, the country had 150 custom cosmetic stores, out of which 10 stores offered refill services where consumers could refill products such as shampoo, conditioner, body wash, and liquid soap. The program will allow consumers to refill products on their own without the need of a customized cosmetics dispensing manager. To make this initiative more effective, a pilot program, which will run for two years, is being conducted wherein existing store staff (who have been trained to work at refill stores) can replace the customized cosmetics dispensing managers.
A customized cosmetics system, wherein certified individuals can mix cosmetics according to a consumer’s individual skin condition and preference at stores, is a revolutionary change in the beauty industry where any concerns related to product usage or suitability can be minimized, if not eliminated completely.
International brands and PE firms investing in Korean beauty brands
Innovation is at the forefront of the Korean beauty industry. A number of consumer goods and international beauty players have invested in innovative Korean beauty brands.
Estée Lauder, a multinational beauty company, acquired Have & Be Co. Ltd., a Korean beauty company, for nearly US$ 1.1 billion in 2019. The deal was made with a key focus on acquiring Dr. Jart+ brand, an innovative high-performing skin care brand, and Do The Right Thing (DTRT) men’s grooming brand.
In October 2021, Glow Recipe, a Korean skincare brand whose products are made with fruit extracts, received an investment from the US-based private equity firm North Castle Partners (for an undisclosed amount). The brand aims at using the investment funds for marketing and global expansion.
Private equity firms are also investing in local brands based in Korea. Helios Investment Partners, a London-based emerging markets-focused private equity firm, signed a stock purchase agreement (SPA) in October 2021, to acquire management rights with a 67% stake in Soleo Cosmetics, a cosmetics and household goods development and production company. The value of the transaction is said to be around US$ 32.5 million. Additionally, in September 2021, JKL Partners, South Korean private equity firm, announced that they will acquire Perenne Bell, a domestic brand that offers organic and sensitive skin products to consumers, and will help the brand focus on entering new markets, including the USA, Japan, and the Middle East.
Not everything is as ideal as it seems
Despite beauty brands claiming their products to be well-researched, organic, and environment friendly, issues exist. In early 2021, sunscreens from Korean brands such as Purito, Dear Klairs, and Keep Cool were under scrutiny when, on the basis of independent lab tests, it was found out that their sunscreens have far lower SPF that what was indicated on the packaging. Following the controversy, the brands withdrew their sunscreen products from the international markets and issued refunds to the customers.
In another incident, Innisfree, a cosmetic brand owned by Korean firm AmorePacific, was called out for misrepresenting the product’s eco-friendly credentials – on the packaging, the product was wrongly labelled as “paper bottle” whereas it actually came in a plastic bottle wrapped in paper.
Loyalty and trust are important in the beauty business and while it might be incorrect to write-off all Korean beauty brands based on a few bad incidents, consumers would not shy away from exploring other brands that offer what they claim.
EOS Perspective
Over the years, South Korea’s cosmetics industry has built a stronger position on the global map especially with the use of innovative and natural ingredients, and a shorter product development cycle. The quality of Korean beauty products, sold with a promise of flawless and crystal-clear skin, is the biggest selling point in a hyper-competitive beauty market.
The popularity of Korean skincare brands is definitely growing but it is not just driven by innovation or quality but also propelled by the mounting fascination for everything Korean, be it culture, entertainment, food, or beauty. Right now, the charm of Korean wave is so prominent that anything Korean will sell and Korean beauty brands are leveraging this opportunity to make big bucks. However, they might not to be able to ride the tide forever.
Since COVID-19, beauty industry has undergone momentous changes. As lifestyles changed and staying indoors and wearing masks became the new normal, the demand for make-up products decreased and the need for skincare products increased. The trend is here to stay. People want healthier skin but prefer to achieve it through easier, minimal, and effective skincare routines and K-beauty brands might be popular for a lot of things but minimalism. By updating their product lines with the strangest of ingredients, discontinuing products, and asserting the use of multiple products on a daily basis, Korean beauty brands tend to over-tire the consumers. Rising trends such as skinalism that focuses on single multi-functional products and sustainable packaging that demote the use of plastic pose further challenge for Korean beauty brands.
In the ever-changing beauty industry, beauty regimes change rapidly and country-led beauty regimes are no exception. With new beauty trends and regimes such as J-beauty and C-beauty quickly catching up among consumers, the novelty of K-beauty products will definitely wear off sooner or later.
K-beauty can perhaps be considered just a fad that stayed and resonated with consumers for more than a decade. For now, the appeal of this trend is not expected to fade very soon. As for the time when the ‘all things Korea’ fascination is over, only players who have been able to build their brand awareness and gain consumers’ trust are likely to successfully continue when the Korean tag will no longer be a pass for high sales.