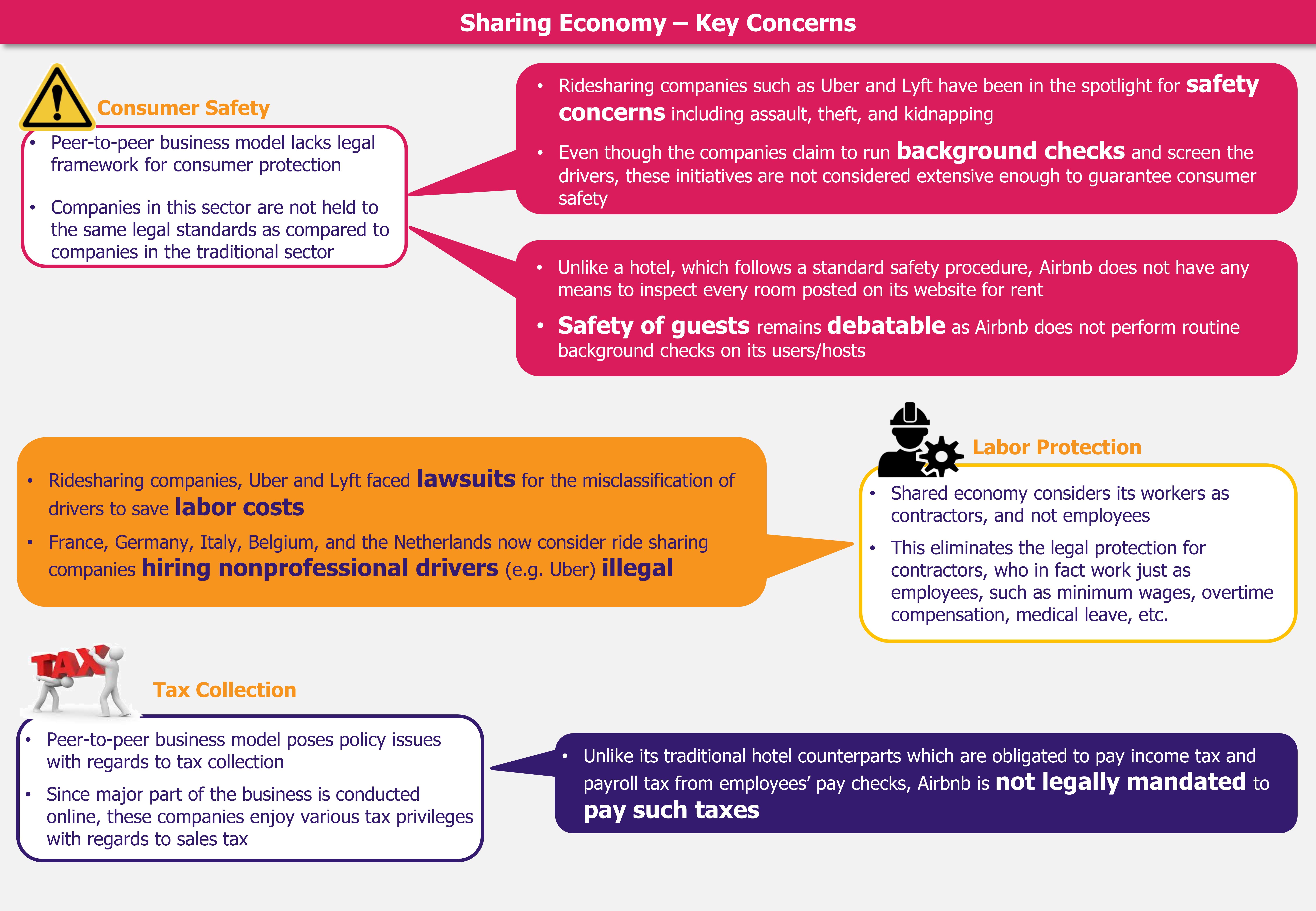
It is a well-known fact that China, today, is the largest and fastest growing e-commerce market globally. Accounting for close to half of the global e-commerce sales, China’s e-commerce industry is witnessing a double-digit growth, rising by about 26% in 2016. Leading the growth in China’s e-commerce sector is cross-border e-commerce (CBEC), which is currently witnessing close to double the growth compared with the overall industry and is expected to continue to grow robustly over the next five years. The government has not only been charging favorable duty to promote CBEC, but has also created special customs-clearing zones in 13 cities to support cross-border trade. However, in 2016, the government came up with a new set of taxation and a list of items that were allowed to be only imported. Following a significant industry pressure, the government has pushed the implementation of these rules to the end of 2018, and it now remains to be seen whether the industry will continue to receive government support which is instrumental for it to flourish.
Cross-border e-commerce (CBEC) has been creating quite a buzz globally, and leading this global trend is China, one of fastest growing markets with respect to CBEC. A plethora of social factors such as improved standards of living, increased awareness about foreign products through greater international travel as well as access to information online, increased quality consciousness among consumers, limited options available locally (especially in product categories such as infant milk formula and health supplements) have resulted in escalated demand for international products in China. All these factors, along with the ease of buying through e-commerce and the growing tendency of Chinese people to use their mobile phones to shop, have resulted in exponential growth of the CBEC sector in the country.
|
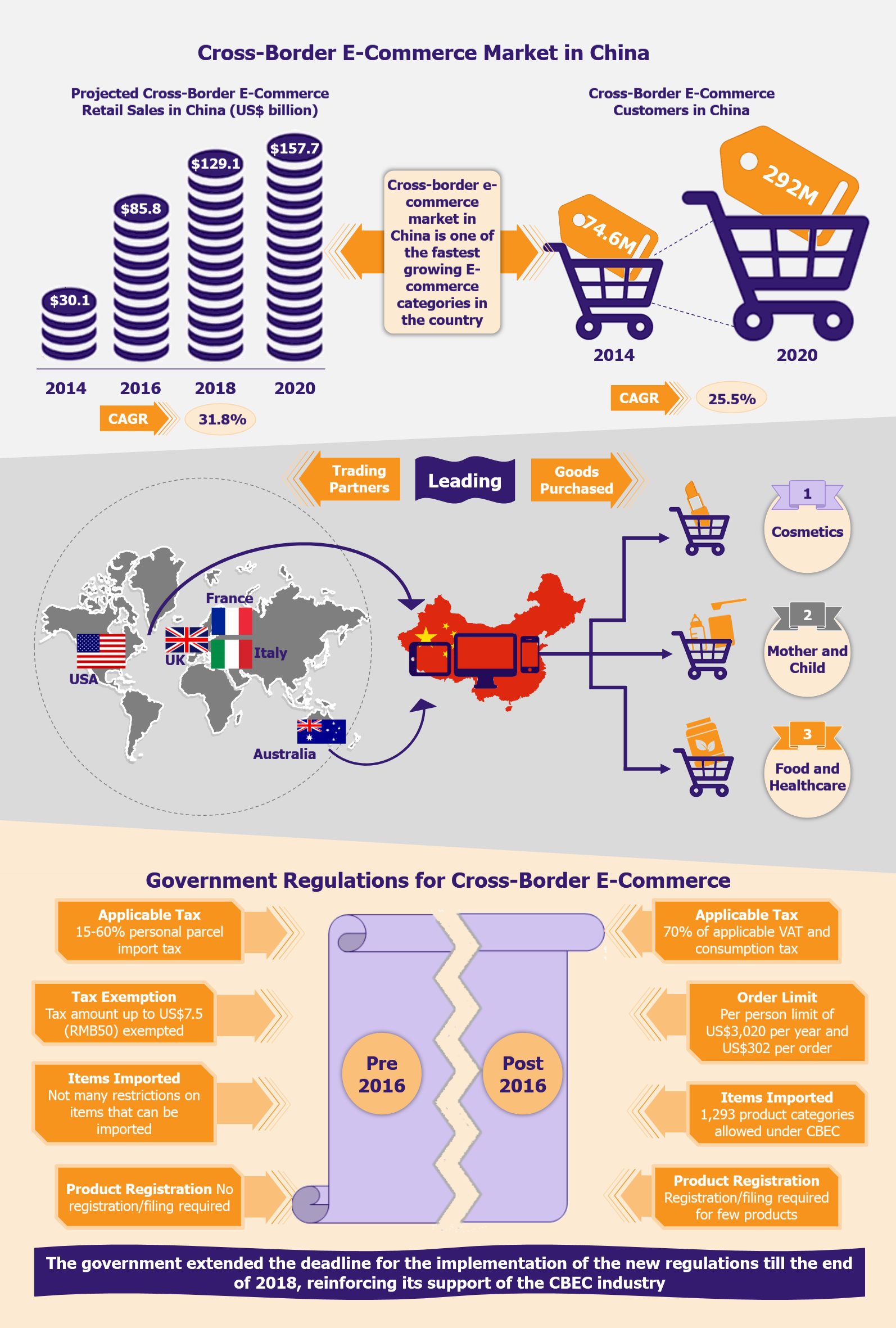
China’s CBEC Industry – At a Glance Retail Sales and Growth: The industry was estimated at US$85.8 billion in sales in 2016 and is expected to double up sales to about US$158 by 2020. The number of CBEC customers in China is estimated to rise from about 181 million in 2016 to close to 292 million in 2020. Trade Partners and Goods: The UK, USA, Australia, France, and Italy are some of China’s largest trading partners with regards to CBEC. Cosmetics, food and healthcare products, mother and child solutions (including infant formula), clothing and footwear are the most shopped categories through CBEC. Consumer Profile: About 65% of the customers are male and 75% are between the age of 24 and 40. Most of the customers are well-educated, with three-fourth of them having at least a graduate degree. The ticket size for about half of these purchases ranges between US$15 and US$75 (RMB100-500). Leading Players: Most cross-border online sales are undertaken through third-party online marketplaces such as TMall Global (owned by Alibaba group) and JD Worldwide (owned by JD Group, China’s second largest e-commerce player). Global e-commerce leader, Amazon is also becoming increasingly active in China. |
The government has also provided immense support to the CBEC sector, a fact that has been critical to the market growth. As an effort to weed out the illegal grey market imports and to promote e-commerce, China’s government relaxed cross-border e-commerce rules and the applicable custom rates (close to 15 to 60% depending on the item). Moreover, custom duty amounting to less than US$7.5 (RMB50) was exempted. The government also created 13 CBEC zones across the country in order to expedite custom clearing of foreign items ordered online. These zones house large warehouses where foreign brands and retailers stock items, which, upon being ordered, are put through custom clearance (under relaxed rules). This way the consumer receives foreign goods within few days of ordering it.
While this has been greatly benefiting the Chinese consumers who now have an access to a range of products that were once seemingly out of reach for the public at large, it is also revolutionizing how foreign players are operating in China. Traditionally, foreign companies (brands) required to have a legal entity in China (subsidiary, partner, or own manufacturer) to import goods through the general trade channels. These legal entities had the task to clear import customs and pay duties on goods imported into the country. However, under the CBEC channel, these foreign players are freed from the requirement of establishing a local entity before selling their goods in the Chinese market. This also relieves companies from several compliance procedures that they were required to follow in case they were entering the market through offline trade channels. Therefore, several players, who shied away from China in the past (owing to cumbersome product registration and approval process), are looking at this as their entry strategy in the market. Simpler compliance checks and reduced import taxes have also made it easy for companies to experiment and launch a host of products (on a hit and miss basis) in the Chinese market without much investment.
However, while CBEC has greatly supported the cause of promoting e-commerce and aiding international companies in accessing the Chinese markets, it has seriously hampered the business of several domestic players (especially in the cosmetics and health supplements industry) who have been protected from foreign competition in the past owing to strict import rules. Moreover, it has resulted in a major disadvantage for conventional retailers with a brick and mortar setup as goods sold through the CBEC route are levied with a lower number of taxes compared with similar goods sold through traditional trade channels in China.
Owing to these factors, in April 2016, the government revised the taxation rates for CBEC goods resulting in a marginal increase in taxes for few categories. Under the new rules, products would be temporarily levied with 0% import tariff but would be taxed at 70% of the applicable VAT and consumption tax rate, which changes based on the product category. For instance, cosmetics worth RMB500 (US$75) ordered through CBEC would be taxed 0% import tariff + VAT at 11.9% (i.e. 70% of applicable VAT rate for cosmetics – 17%) + consumption tax at 21% (i.e. 70% of applicable consumption tax for cosmetics – 30%), thereby, making the total amount equal to RMB664.5 (US$100). In addition to the changes in taxation, the government removed the waiver of custom duty of up to US$7.5 (RMB50) and set a limit of US$302 (RMB2,000) on a single transaction and of US$3,020 (RMB20,000) on purchase by a single person per year. It also released a list (termed as a ‘positive list’) of 1,293 products that were allowed to enter the Chinese market through CBEC. While the goods under the ‘positive list’ are exempted from submitting an import license to customs, few products from this list that come under China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA), such as cosmetics, infant formula, medical devices, health supplements, etc., require registration before import. This entails the same tedious registration or filing requirements required for products imported through the traditional trade channels. This greatly limits the inherent benefits of the CBEC model for these products.
While the government had initially intended and aimed for immediate implementation of these new regulations, protests and pressure from Chinese e-commerce companies and the ultimate objective of promoting the country’s e-commerce sector resulted in the government agreeing to a one-year transitional phase for these rules (which was to end in 2017). However, in September 2017, the government decided to extend the transitional period until the end of 2018 and to set up new trade zones for CBEC, reinforcing its support for the cross-border e-commerce sector. While changes in the regulation do seem to be a certainty in the future, the timeline for their introduction remains ambiguous as several industry analysts anticipate that they may get pushed off again.
EOS Perspective
The cross-border e-commerce sector in China has been witnessing exponential growth and despite the looming new regulations, is expected to continue to grow at least over the next five years. While leading e-commerce companies in China (such as Alibaba group and JD group) have acted swiftly to benefit from this growing space, the greatest benefit has been for the foreign players who now have an easy access to Chinese consumers without the need of setting up a shop in the country. However, these benefits may be short-lived considering the new set of regulations. Few product categories such as infant formula, cosmetics, and health supplements (which have in actuality been the most popular categories for CBEC) will be subject to registration and filing requirements, thereby their so-called ‘honeymoon phase’ in the country is likely to end. Although a lot of products do not have to comply with registration/filing requirements and are only subject to a marginal increase in taxes (as per the new rules), this does not guarantee that future regulations will not impact their presence and sales in China. Therefore, while CBEC may be the smartest way for companies to test their products with limited investment in China, they may need a back-up plan in case the government further regularizes the industry to create a level-playing field for the traditional retail.