1.9kviews
The idea of robots replacing humans has always seemed like talks of the future, however, it is not as distant as it seems, especially when it comes to the fast food industry. The fast food market, which is characterized by cut-throat competition and high share of low-skilled jobs, has recently been swept by a technology wave. Leading players, such as Domino’s, Starbucks, or KFC, are investing heavily in artificial intelligence (AI) to increase efficiencies and differentiate themselves in this overly crowded industry – some are integrating it with their back-end operations while others with the consumer interface. However, with investments in technology increasingly becoming an industry trend, the question remains if AI will provide the competitive edge to these players or are consumers yet not quite ready to lose the human touch.
Artificial intelligence has been the buzz word for some time and the fast food industry is also catching on the wave. With some market leaders claiming to be as much a technology company (owing to huge technology budgets) as a food business, these players are incorporating AI in several verticals to improve operational efficiencies and elevate consumer experience.
The wave of AI adoption is particularly prominent in the US market, where labor costs are increasing significantly, hence AI is being seen as a tool to reduce costs in the long run. Just recently, in the beginning of 2017, minimum wages have been increased in 19 states and will reach US$13.50/hour in Washington state and even US$15/hour in California by 2022 (the minimum wages in 2017 stood at US$11 and US$10.50 for Washington state and California, respectively).
Apart from the need to control costs, the interest in AI is driven by the fact that it provides food business with great advantage – the use of AI helps companies gather valuable data about customer choices, flavor trends, etc., and use this information effectively.
Leading players, such as Domino’s, Starbucks, KFC, and CaliBurger, have already started using AI is different verticals of their businesses to not only reduce costs but also to remain one step ahead of the changing consumer expectations.
Domino’s
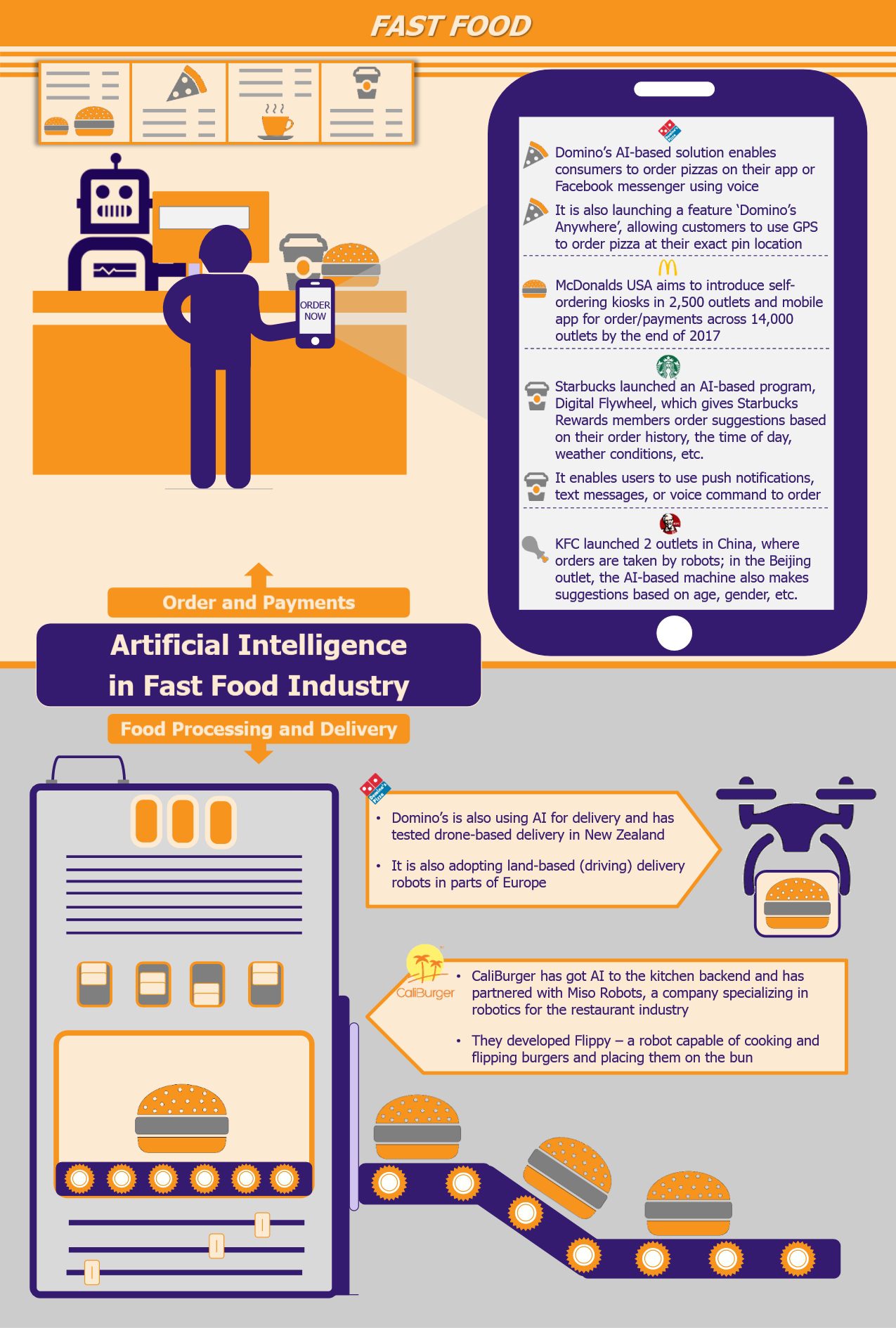
Domino’s can be easily slated as one of the most aggressive fast food players when it comes to adoption of technology. The company has embraced AI in several aspects of its operations aiming to smoothen both the ordering and the delivery sides of the business.
In early 2017, Domino’s launched an AI-based technology called the DRU (Domino’s Robotics Unit) Assist, which enables consumers to order a pizza on the app using their voice. The in-app AI assist, which was built in partnership with natural language company, Nuance, converses with customers in a human-like manner and discusses orders, menus, ingredients, store locations, and operating hours.
Along similar lines, the company has also launched its Facebook messenger bot, wherein customers can converse with the bot on the messenger app to learn about menu options, discount offers, and also order food. In addition, Domino’s is in the process of launching its ‘Domino’s Anywhere’ feature, through which customers can drop an exact location pin using GPS (as in case of Uber) when ordering pizza thereby facilitating delivery at various locations, such as parks, and other public places without providing an exact address.
Simultaneously, the company is also using AI to automate the delivery process. In November 2016, in New Zealand, Domino’s partnered with Flirtey, a drone company, to undertake the first commercial delivery of food by a flying drone. While this technology is largely futuristic for mass adaptation, the company is focusing on land-based autonomous delivery vehicles to deliver pizza to customers’ doorsteps. This technology went to trial in June 2016 in Australia and in 2017 in Germany, while the company plans to roll it out in the Netherlands for customers within the one-mile radius by the end of 2017. The technology, which is provided by Starship Technologies (a European start-up), has GPS tracking, computer vision and object detection capabilities, and can travel within a three mile radius, carrying up to 10kg weight for a cost as low as US$1.32 (£1).
McDonald’s
McDonald’s is one of the recent players to blend fast food with technology. The company stated that its investments in technology are to be one of its key strategies in 2017, calling it the ‘Experience of the Future’ strategy. As per its plans, McDonald’s aims to replace cashiers with self-ordering kiosks in 2,500 of its restaurants by the end of 2017 and in another 3,000 restaurants by the end of 2018. The cost of each kiosk is estimated at about US$50,000-60,000.
In addition to this, the company plans to roll out mobile ordering across 14,000 US locations by the end of 2017. Mobile ordering will not only ease the ordering process but also help the company gain access to valuable customer data, which in turn can be used to recommend additional dishes and personalized deals. McDonald’s has already launched mobile ordering in Japan and received a positive response with customers using the app ordering about 35% more than usual.
Since 2015, the company has also been rolling out digital menu displays across its stores in the USA as well as globally. They use AI to highlight weather-appropriate options. This feature has resulted in increased sales by 3-3.5% in Canada.
Starbucks
Starbucks has also developed an artificial intelligence program to improve customer ordering experience. The program, which is known as the Digital Flywheel program, links itself with the accounts of Starbuck Reward members and makes order suggestions based on order history, weather conditions, time of day, weekend/workday, and other such factors. In addition, it brings additional convenience to the ordering process for the Reward program members, who can order directly from push notifications or text message and collect their ready order from a nearby Starbucks.
Moreover, embracing the voice computing trend, the company has launched an AI-based ordering system on its app that allows customers to order and pay for their orders using voice. The company has also launched a ‘Starbucks Reorder Skill’ for users of the Amazon Alexa app, wherein users who have linked their Starbucks account to their Amazon Alexa account can re-order their usual drink (at one of the last 10 visited Starbucks stores) by simply saying “Alexa, order my Starbucks”. However, this service is currently limited to the order of the users’ usual designated drink instead of ordering anything off the menu.
Starbucks has made significant investments in technology on a continuous basis, having invested close to US$275-300 million in its partners and digital initiatives globally in 2016, an increase from an investment of US$145 million in 2015.
KFC
While most quick service restaurants players are using technology to elevate their app-based ordering experience, KFC in China is taking a different route to join the AI bandwagon. In April 2016, KFC (in collaboration with Baidu, China’s leading search engine) launched a robot-run restaurant in Shanghai called Original+. The restaurant is run by a robot named Dumi, which takes customer orders and is smart enough to handle order changes and substitutes. While the robot can understand the three main dialects of Mandarin spoken in China, it cannot distinguish other dialects and accents. The payment at the outlet is made through smartphones via mobile payment systems.
The collaboration opened another AI-enhanced café in Beijing in December 2016, wherein customers take pictures of themselves with a machine, which then recognizes the users face, sex, age, and mood, along with analyzing the time of the day to recommend suitable meal options and completes the ordering process. Moreover, upon revisit, the machine recognizes the user and shows order history as well as dining preferences to quicken the order process. However, unlike the Shanghai restaurant, this restaurant also offers the traditional ordering process. While these may seem futuristic, the company has expressed its plans to open more smart restaurants in the country.
CaliBurger
Apart from market leaders, smaller players, such as CaliBurger, are also investing heavily in technology in both the front and back end of their operations. The California-based burger chain has brought AI into their kitchens through the use of AI-enabled robot, called Flippy, which is capable of cooking/flipping burgers and placing them on the bun. The robot, which was launched in March 2017 in the chain’s Pasadena, California outlet is created by Miso Robotics, a pioneer in the robotics for restaurant business. The concept is currently in test run and if successful, it is expected to be rolled out in early 2018 with expansion plans to more than 50 outlets worldwide by 2019.
EOS Perspective
It remains no secret that most leading and few niche smaller players are turning to AI to elevate their service levels in this competitive industry. Companies which have traditionally not taken the digital route up till now are also joining the technology bandwagon. Pizza Hut, which has always been one step behind Domino’s with regards to technology deployment, has invested US$12 million in technology in Q2 2017 towards improving its digital and delivery services. The chain plans to invest US$180 million in a technology overhaul by the end of 2018.
It can be expected that at this stage of technology development most of the automation will be successfully implemented in the customer-facing side of the business, and will comprise technologies such as bots and voice recognition that can be integrated into apps and other ordering mediums. This not only helps consumers by easing the ordering process but also helps companies gather valuable data about customer preferences and ordering trends, which in turn can be used for providing complementing recommendations and thereby increasing sales. While AI-enhanced ordering and payment may be the path of the future, it will be far-fetched to say that it will eliminate the need for humans in this side of the industry altogether. With increased sales due to AI-based ordering, the need for humans will remain, however, their role may evolve from ordering to management.
The adoption of AI or automation at the food preparation and delivery end, on the other hand, still seems a little futuristic. While several players, such as Domino’s and CaliBurger, have started investing and launching this technology, the wide application of it seems distant. This is especially true in the food preparation tasks, due to an increasing trend towards customization of orders and the growing use of complex ingredients to cater to niche audiences that require dairy-free, vegan, gluten-free, or other such options. Till the time robots that can handle such complexities are developed, these jobs will largely be conducted by humans with maybe automating the easier aspects of the process (such as flipping the burgers). Moreover, with the fast changing consumers’ needs it will be hard for robotics companies to preempt the trends and develop robots that can match the required skill sets both now and in the future.
That being said, the use of AI by the restaurant industry is definitely on the rise and while we may not know the extent to which it will take over the current operations, we can definitely be sure that this is increasingly becoming the point of focus as well as innovation in this highly competitive space.