Upcycling, a growing trend in the food industry, uses surplus food and food by-products to produce products such as dietary supplements, beauty products, nutraceuticals, or animal feed. Food businesses are looking at upcycling as one of the strategies to reduce the amount of food waste they generate. However, they face continued challenges around unmarketable ingredients, process costs, and consumer acceptance. To ensure success of this niche sector, fostering partnerships to collect food by-products, collaborating with government institutions for technical know-how along with initiatives that promote upcycled food waste products could go a long way.
Burgeoning need for upcycling food waste
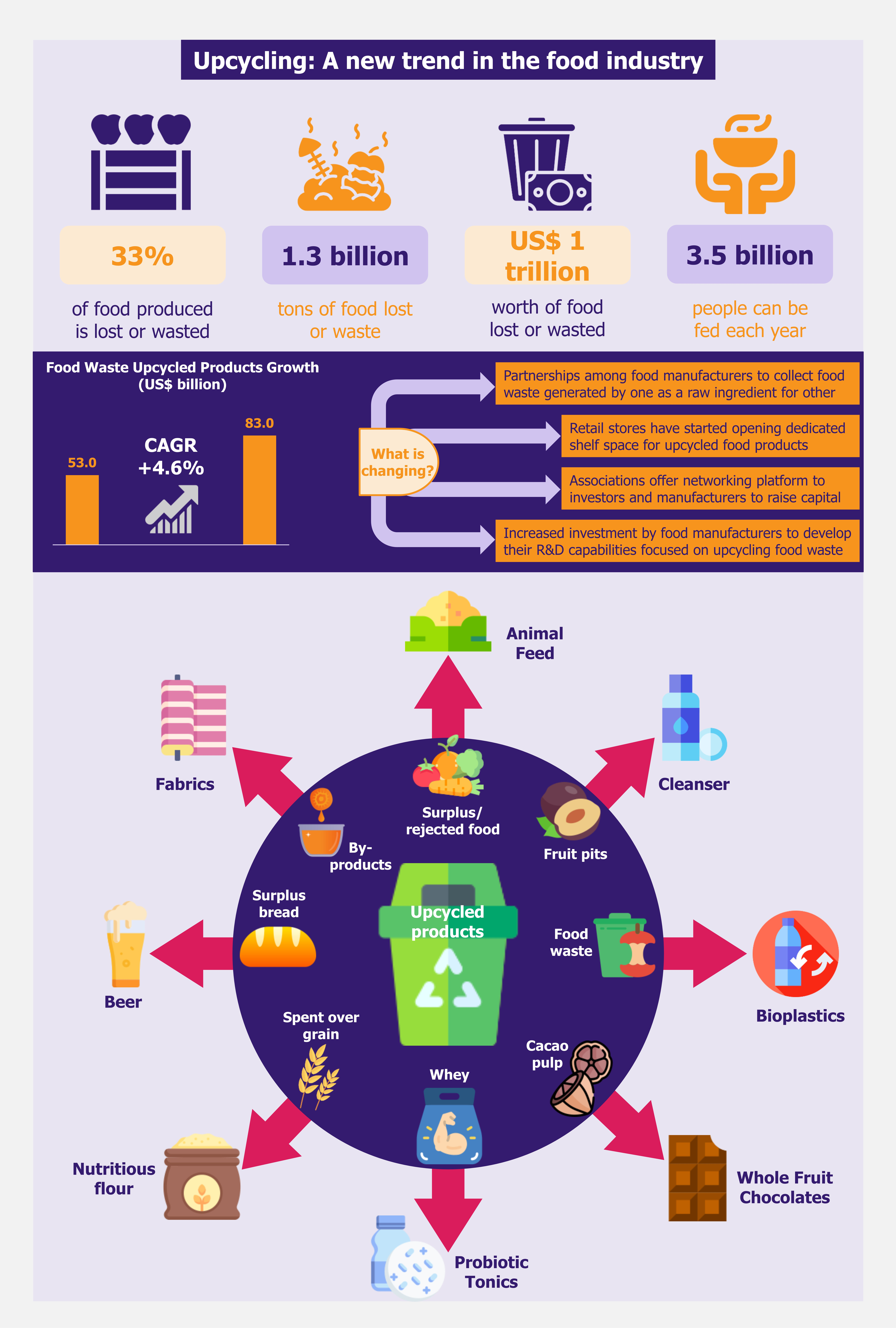
UN estimates that nearly 33% of the food produced globally each year is either lost (in the form of any edible food that goes uneaten, crops left in the field, food that gets spoiled in transportation or does not make it to the stores) or wasted (food discarded by retailers due to color or appearance, food left on the plate at restaurants, and scraps from food preparation at home). This accounts for 1.3 billion tons of food worth approximately US$1 trillion, enough to feed 3.5 billion people.
Moreover, food wastage contributes to 10% of global greenhouse gas emissions and is a huge burden on the environment and natural resources. As more and more food waste ends up in landfills, it produces methane, considered to be eight times more harmful than carbon, thus contributing more to global warming than automobile emissions.
Upcycling is one way that can help mitigate the ill effects of food waste, to a certain extent. Upcycling uses food by-products, produce with visual imperfections (produce often unattractive to sell due to color or appearance), food scraps, and surplus food to make new products. It is forecast that, in 2022, the market size for products made from food waste will be approximately US$53 billion and is expected to reach US$83 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 4.6%.
Repurposing food waste into value-added products
Driven by sustainability, repurposing food waste offers a plethora of opportunities for start-ups and other players to make value-added products such as beverages, food products, dietary supplements, nutraceuticals, animal feed, cosmetics, and personal care products. Companies are coming up with innovative solutions to convert food by-products and surplus produce into something reusable and resalable.
Upcycled food
In 2021, Nestle Australia launched a carbonated soft drink called “Nescafe Nativ Cascara”, which uses cascara, the husk of the coffee berry fruit which is discarded in coffee production. Another interesting upcycling initiative taken by Nestle Japan is “Cacao Fruit KitKat” which uses the white pulp surrounding the cacao beans (70% of the cacao fruit is wasted and only the beans are used to produce chocolate). Moreover, in June 2022, Barry Callebaut, a Belgian-Swiss chocolate manufacturer, also launched whole fruit chocolate made from 100% pure cacao fruit.
Taking a step ahead, companies are also investing to set up research centers and business verticals that focus entirely on food waste upcycling. Nestle invested approximately US$4 million and expanded its R&D center in Singapore to focus on upcycling food waste and plant-based innovation. Another American-Irish agricultural corporation, Dole, is partnering with the Singapore Economic Development Board and has formed “Dole Specialty Ingredients”, a new business arm that uses food waste to produce specialty ingredients such as enzymes, seed oils, fruit extracts, etc.
Bakery industry is another sector that holds significant potential for upcycled food waste products. For instance, ReGrained, a food technology company, based in the USA, is using leftover spent grain from brewing beer and turns it into nutritious flour called ReGrained Supergrain+, which is then used to produce snacks bars. The company also sells this flour to other food producers. Another US-based food company Renewal Mill, uses byproducts of plant-based milk to develop high fiber, gluten-free flours which are used in cookie mixes.
Food waste is also used in beverage processing. WTRMLN WTR, a food processing firm based in the USA, uses watermelons that are discarded due to aesthetic reasons and upcycle them to make flavored water. WTRMLN WTR is currently available at 35,000 retail stores across the USA. Another UK-based brewing company, Toast Ale, uses surplus bread from bakeries to brew beer. To date, the company has salvaged approximately 2.6 million surplus bread slices that would have otherwise gone to waste.
Several companies also upcycle the not-so-appealing fruit or vegetables to produce food products such as sweet and savory snacks, condiments, etc. For instance, Barnana, a US-based banana snack company, uses bruised bananas and produces snacks such as dehydrated banana bites, plantain chips, and crisps. The company has used roughly 50 million metric tons of not-so-good-looking bananas and plantains since its inception in 2013. Rubies in the Rubble, a UK-based company, produces condiments such as plant-based mayo, apple relish, and spicy tomato relish from imperfect produce rejected due to size and aesthetics.
While most of the applications for upcycled food waste ingredients have been in baking, beverages, and snacks, other interesting applications are also emerging. For instance, Scraps, a start-up based in New York, USA, uses excess or bruised basil leaves and odd-shaped peppers to make frozen pizzas. Unilever uses ice cream, not used in the primary production process, and mixes it with chocolate sauce and white chocolate chips to create a new flavor called “Cremissimo”. White Moustache, a US-based yogurt company, makes probiotic tonics from whey, a by-product of yogurt. Austria-based Kern Tec, a fruit seed producer and processor, uses the pits of cherry, apricot, and plum, and transforms them into protein powders and oils.
Beyond food
Food waste can also be used to make products beyond food. Wastelink, a food upcycling start-up based in India, collects food waste from 300+ distributors and factories across India and converts it into nutritional-rich feed for animals. Over the past two years, the company has upcycled over 5,000 metric tons of food waste. Wastelink raised over US$1.2 million in seed funding in June 2022.
Food by-products are also finding its acceptance in the textile industry. Orange Fibre, a sustainable textile company based in Italy, has partnered with Lenzing Group, a producer of wood-based specialty fibers, to produce Lyocell fiber made from orange juice and wood pulp.
Japan-based PEEL Lab started in 2021, is another innovative start-up that upcycles plant and fruit waste into plant-based leather. The company’s products include bags and wallets (made from apple and pineapple leather), yoga mats (made from bamboo leather), and apple leather coasters.
TripleW, a biotech company based in Israel, utilizes food waste for the production of polymer grade lactic acid, which is further used to make Polylactic acid (PLA) bioplastics used in food and beverage packaging, car parts, toys, textiles, and kitchenware, among others.
Upcycling food waste has also found applications in the beauty industry. Circumference, a New York-based skincare brand started in 2018, sources unused olive leaves from California-based olive oil company Brightland, to produce an antioxidant extract, which is used in the brand’s cleanser. The company previously launched a moisturizer using leftover grape leaves. Another US-based skincare company, Farmacy, uses left-over apple extract in its cleansing balm. Klur, a US-based beauty brand, utilizes avocado and tomato seed oils discarded by the food businesses to produce cuticle oil. Another interesting use of food waste in the beauty industry is adopted by France-based beauty brand Kadalys, wherein they extract bio-actives from bruised bananas to be used in their skincare products.
Challenges concurrent with upcycling food waste
Upcycling food waste poses many challenges. Most companies in this space are small and have limited product mix due to lack of consistent supply of upcycled ingredients. Another concern is maintaining the quality or freshness of the ingredients throughout the product lifecycle. Since these are mainly by-products or scraps, doubts on how these are stored (whether in a temperature-controlled environment or what sort of hygiene procedures are followed, if any), transported, and handled prevail.
Consumer acceptance is another challenge pertaining to upcycled foods. Consumers are often reluctant to buy upcycled food products owing to concerns about the quality of the ingredients used. Educating consumers that upcycled food is not just made from food scraps or leftovers but also from by-products which are nutritious and safe to consume is a daunting task. Moreover, the general perception that upcycled products are often priced higher further reduces consumers’ willingness to buy them.
EOS Perspective
Upcycling food waste is slowly but surely gaining acceptance, but still needs to go a long way to get established as a mainstream market. Owing to its environmental and economic benefits, the trend of upcycling is here to stay. ReFed, a non-profit organization in the USA, which strives to reduce the food loss and waste across the USA, claims that just by converting food by-products such as spent grains, fruit or vegetable pulps, and rinds into a new ingredient or an edible food product could save nearly 1.87 million tons of food waste diverted to the landfills resulting in financial benefits of US$ 2.69 billion each year.
Food waste industry offers multitude of opportunities for partnerships and cross-sector collaborations among start-ups, established food brands, food producers, philanthropic organizations, and technology and supply chain solution providers. For instance, ReGrained, in partnership with USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) developed a patented technology to convert spent grain into flour.
Several companies are also partnering with food producers for a consistent supply of raw materials. For instance, Barnana is partnering with farmers across Latin America to procure bananas and plantains on a large scale. Food producers are also working together in order to reduce food waste. An example of this is Kellogg’s UK’s partnership with Seven Bro7hers Brewing, a brewery company based in the UK, to turn its waste corn flakes into beer. Moreover, retail stores such as MOM’s Organic Market, an organic grocery chain in the USA, have also started dedicating shelf space for upcycled food products.
In addition to partnerships, philanthropic organizations such as Upcycled Food Association (UFA) also play an important role in reducing food waste by educating and connecting upcycled food companies globally to become a part of the growing upcycled food economy. Formed in 2020, UFA strives to improve the upcycled food supply chain. Currently, the association is a network of more than 180 businesses from over 20 countries. Credited with launching the world’s first third-party certification program for upcycled food ingredients and products, “The Upcycled Certified Standard” in 2021, UFA has received preliminary approval (in February 2022) from USDA FSIS (The Food Safety and Inspection Service), to include their certification mark in the FSIS-regulated ingredients and products. As of February 2022, nearly 400 products are waiting to be certified by the UFA. This initiative aims at educating consumers about the impact of upcycled food on environment and the economic potential it holds.
Furthermore, in 2021, UFA together with ReFed also launched the “Food Waste Funder Circle”, a network platform for private, public, and philanthropic funders for educating, collaborating, and investing to raise capital needed to reduce food waste by 50% by 2030 within the USA. Such initiatives highlight that the upcycling food waste industry has immense growth potential.
In the long run, it seems that upcycled products made from food waste could become a part of day-to-day life. Global appetite for sustainability is increasing and so is the upcycled food waste industry. Eventually, it is all about building an all-inclusive food system for a sustainable future.