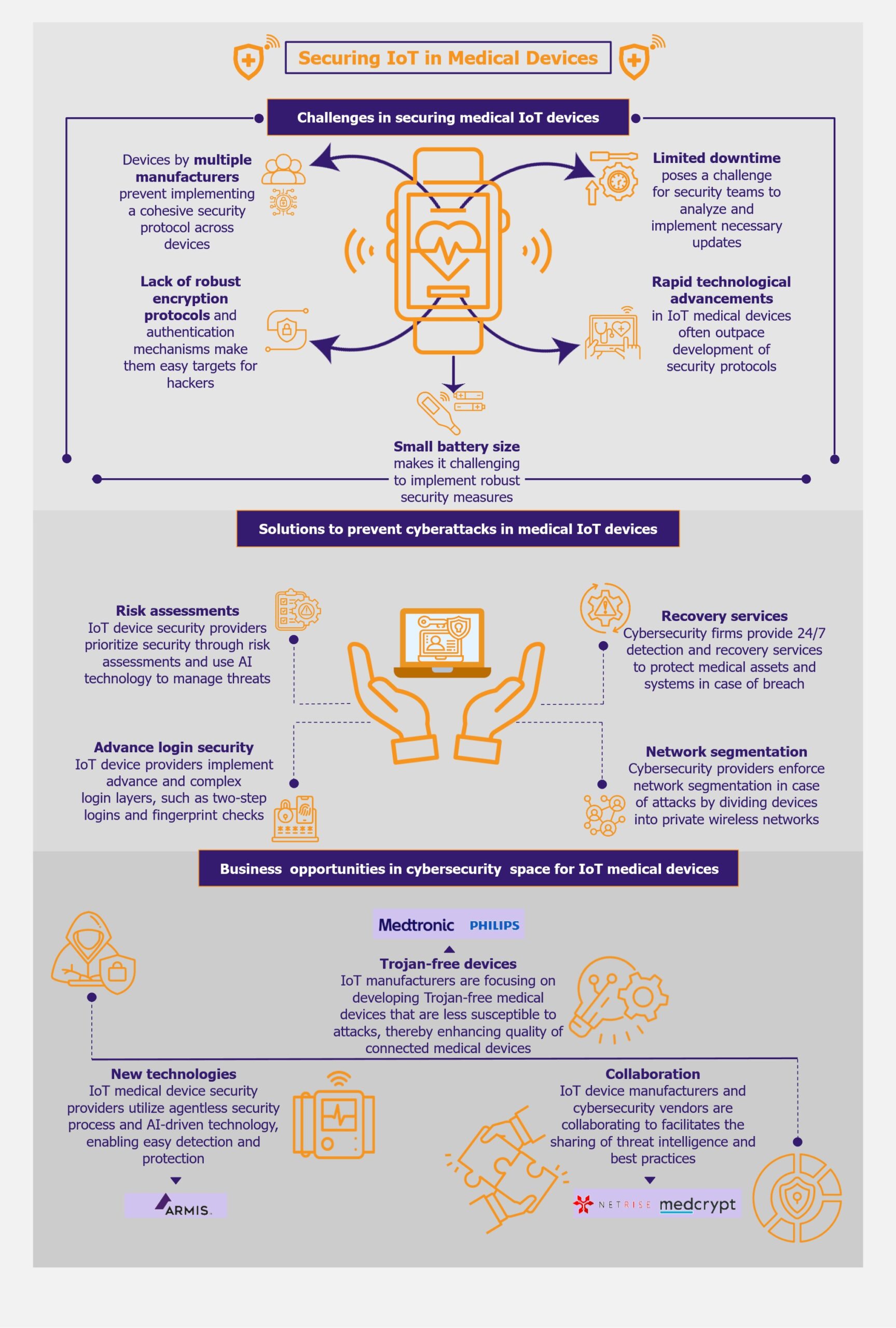
Continuous glucose monitors (CGM) represent a disruptive innovation that has transformed the diabetes management landscape. In recent years, the CGM market has seen remarkable growth, becoming an integral part of diabetes care with the potential to supplement or even replace traditional blood glucose monitoring methods. Opportunities in the CGM sector are endless, as the market remains under-penetrated. Market leaders such as Dexcom and Abbott leverage this potential to establish their foothold while continuously innovating their offerings.
CGMs provide accurate readings that can be used for insulin dosing decisions, eliminating the need for traditional fingerstick tests. The devices offer high ease of use and convenience, with many integrating seamlessly with smart devices. Additionally, the increasing use of AI and machine learning has led to the development of algorithms that customize health-related data for users.
Read our related Perspective:
Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices: Overcoming Barriers in LMICs
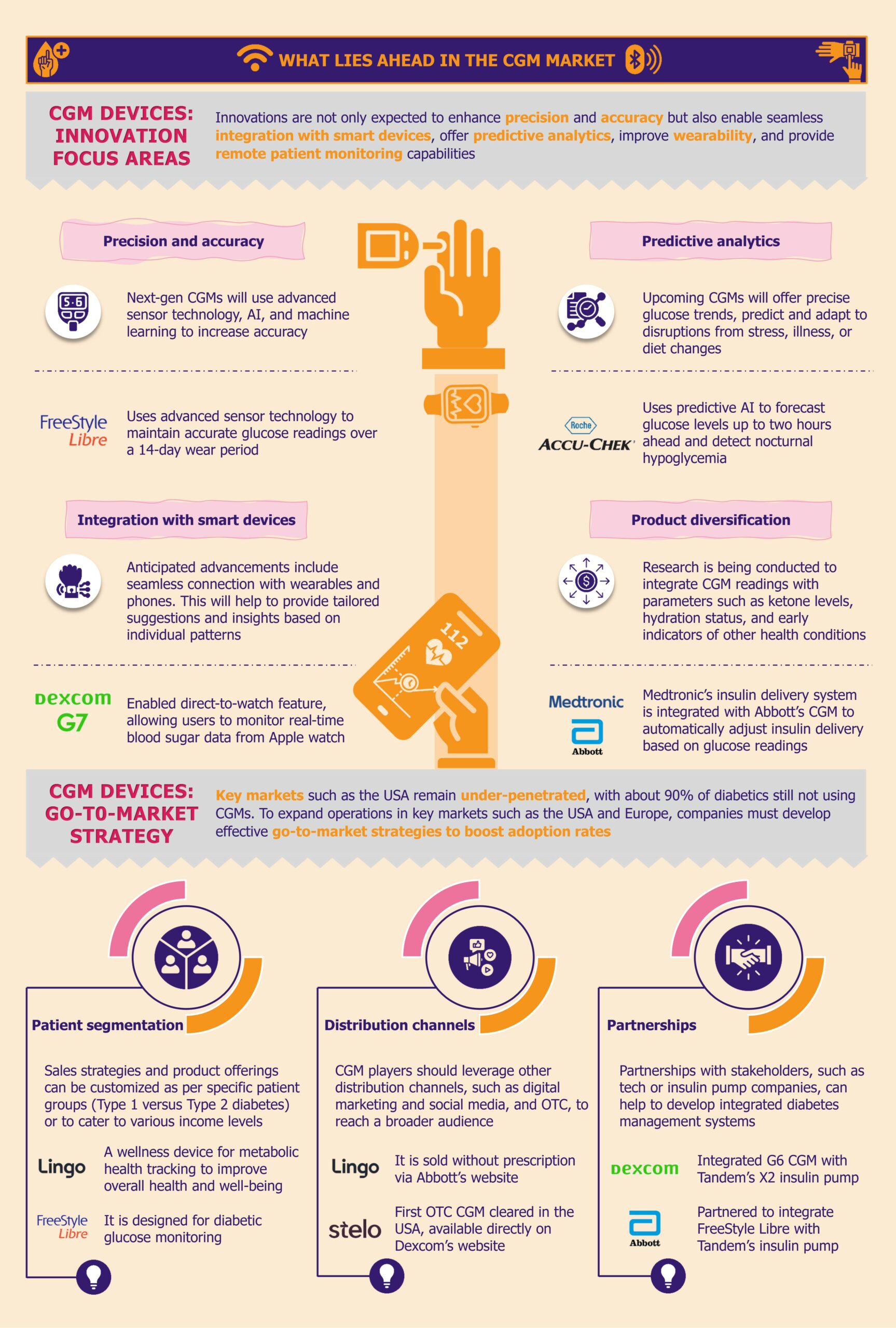
As we expect the next generation of CGMs, revolutionary advancements promise to transform diabetes management with these devices. The ongoing innovations aim to enhance precision and accuracy, offer predictive analytics, provide continuous monitoring beyond glucose, and enable the integration of other health parameters into the CGMs.
Precision and accuracy
Building on the success of current CGMs, the next-generation devices are likely to offer unprecedented precision and accuracy. Upcoming CGMs will use next-generation sensor technologies, including advanced nanomaterials and multi-enzymatic systems, to detect glucose levels with higher sensitivity and specificity.
Sophisticated AI and machine learning will support the prediction of glucose trends and real-time data processing to increase accuracy. To further improve accuracy across diverse populations and glucose ranges, emerging CGMs will leverage personalized calibration algorithms that adapt to individual metabolic variations.
Integration with broader health ecosystems and cloud-based analytics will be industry players’ key focus, ensuring improvement through real-world data feedback. Clinical validation and regulatory supervision will ascertain that CGMs adhere to all safety and health standards.
Overall, players will aim to provide reliable glucose data to empower users with actionable insights for effective diabetes management. Leading industry players, such as Abbott and Dexcom, prioritize data accuracy and ensure that their devices track glucose trends accurately with minimal error. For instance, Abbott’s Freestyle Libre uses advanced sensor technology to maintain accurate glucose readings over a 14-day wear period. On the other hand, Dexcom’s G7 utilizes advanced algorithms to continuously calibrate and refine glucose readings based on real-time data and historical trends, eliminating the need for fingerstick calibrations. Both devices provide real-time alerts on glucose levels to help users take action.
The Future of Diabetes Care Key Innovations in the Continuous Glucose Monitoring Market by EOS Intelligence
Integration with smart devices
Anticipated advancements include seamless connection with smartphones, smartwatches, and other wearable devices for uninterrupted glucose monitoring. Such integration will not only elevate user experience but also allow real-time updates, such as alerts for glucose fluctuations, viewing historical trends, and sharing data with healthcare providers, thus facilitating proactive management of user’s condition.
In advanced CGMs linked with mobile applications, predictive algorithms will be able to foresee glucose levels, offering tailored suggestions and insights based on individual patterns. Recently, in June 2024, Dexcom enabled a direct-to-watch feature, allowing its G7 users to monitor real-time blood sugar data from an Apple watch, regardless of whether they are carrying their phone.
In the future, this synergy between CGMs and smart devices will not only improve the accuracy and accessibility of glucose monitoring but also empower users to make quick, informed decisions regarding their health and improve overall well-being.
Predictive analytics
The real-time and historical analysis of glucose data equips CGMs to predict blood glucose levels several hours ahead, notifying users about impending hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia before they occur. This proactive approach allows for timely interventions, such as regulating insulin dosage or dietary modifications to maintain optimal glucose level.
Predictive analytics integrated with CGMs is revolutionizing the diabetes care market, and key market players are increasingly prioritizing its incorporation into their devices to gain a competitive edge. Roche is gearing up to compete with Abbott and Dexcom with its Accu-Chek Smartguide, which will soon be launched in the European market following its approval in July 2024. The company is betting on robust predictive analytics to differentiate its product from competitors. The device aims to enhance glucose monitoring by employing predictive AI to forecast glucose levels up to two hours ahead, identify the risk of low blood glucose within 30 minutes, and detect nocturnal hypoglycemia.
Over the years, as predictive algorithms improve, CGMs will become increasingly suitable for mitigating risks, reducing glucose spikes in patients, and equipping patients to manage diabetes better and improve quality of life. In the future, enhanced personalization and seamless integration of CGMs with broader health ecosystems can transform diabetes management by providing more precise and accessible real-time insights and recommendations tailored to individual metabolic responses, lifestyle patterns, and environmental influences. It is likely that the next generation of CGMs will also predict and adapt to potential disruptions caused by stress, illness, or diet changes.
Product diversification
The evolution of CGMs is expected to go beyond glucose monitoring, embracing a holistic approach focused on personalized and preventive healthcare. Companies are conducting research to integrate CGM readings with health metrics such as ketone levels, hydration status, and early indicators of other health conditions.
Industry players are also developing targeted solutions for various customer segments. For instance, they are focusing on pediatric and geriatric populations by creating CGMs customized to meet these segments’ unique physiological and lifestyle needs. Another area of focus is developing CGMs to support gestational diabetes, helping pregnant women better manage maternal and fetal health.
Currently, companies such as Medtronic and Abbott have partnered to integrate Medtronic’s automated insulin delivery systems with Abbott’s CGM to create closed-loop systems. This system automatically adjusts insulin delivery based on real-time glucose readings, which helps patients improve glycemic index.
EOS Perspective
The next generation of CGMs is poised to help manage chronic diseases beyond diabetes. With key players such as Dexcom and Abbott maneuvering the industry, the future promises unprecedented advancements through the fusion of technology and healthcare. The impact on patient outcomes and the broader healthcare landscape will lead to a more personalized, proactive, and interconnected approach to care.
There is a significant opportunity for industry players across major markets such as the USA, where CGM adoption remains low, with about 90% of people with diabetes still not using these devices. To penetrate key markets including the USA and Europe, CGM companies need to develop effective go-to-market strategies to increase adoption rates. They should focus on patient segmentation, exploring multiple distribution channels, and forming alliances with key stakeholders.
Patient segmentation
Sales strategy and product offerings could be tailored around specific patient groups, i.e., Type 1 versus Type 2 diabetes or various income levels. For example, Abbott has strategically developed different CGMs to target varied patient groups. Its FreeStyle Libre is designed for users with Type 2 diabetes, while Lingo, a consumer wearable, is ideal for consumers trying to improve overall health and well-being.
Diversifying distribution channels
The CGM players must diversify their distribution channels, particularly by utilizing digital marketing and social media to reach a broader audience and increase awareness. Digital marketing can also serve as a crucial tool for connecting with diabetes online communities and educating patients.
Abbott and Dexcom are looking to explore new distribution avenues. In H2 2024, both companies rolled out their competing products (Abbott’s Lingo and Dexcom’s Stelo) over-the-counter in the USA, selling through their websites, with an aim to expand the reach and enhance market penetration. Expanding sales through the online channel also makes it simpler for consumers to purchase CGMs directly from producers simpler for consumers.
Partnerships
Forging strong alliances with key stakeholders can create improved and integrated diabetes management systems. Strategic partnerships with technology companies can help CGM players enhance products, expand market reach, and improve patient outcomes. On the other hand, partnering with insulin pump and insulin pen companies can streamline diabetes care by combining real-time glucose monitoring with automated insulin delivery.
Both Abbott and Dexcom have partnered with Tandem Diabetes Care to integrate FreeStyle Libre CGM and G6 CGM, respectively, with Tandem insulin pumps. These systems use real-time glucose readings to automatically adjust insulin dosing, improving diabetes management.
The opportunities in the CGM market are vast and continually expanding. As technology advances, CGMs will become more accurate, user-friendly, and integrated with other health management tools. Moreover, with the growing prevalence of diabetes worldwide, the demand for efficient and effective glucose monitoring solutions will only grow in the future, making the CGM market an attractive segment for continued investment and development.