In the past few years, food tech (online food delivery) industry in India has seen substantial growth in terms of daily order volumes (DOVs), revenue, and funding. While the business is growing for all players, they are still posting losses. A closer look into their financials and business models reveals that the current operating margins are very thin, and much of the recent rapid growth has been on the back of heavy discounting offered by players to attract customers. At present, the growth strategy is loud and clear: to acquire new customers, enter new markets, and expand current market share at any cost. This has raised a question whether such a model is sustainable in the long run or is it another tech bubble just waiting to burst?
Less than five years ago, the way Indians consumed food was completely different. Eating out was predominantly occasion-driven, while ordering food was limited to calling local restaurants or ordering a pizza from Dominos or Pizza Hut through their own websites. Online food ordering through apps was not at all a part of consumers’ culinary vocabulary.
However, this has been transforming over the past few years. There is a growing trend among Indians to order their food online via food aggregation apps. Today, Indian consumers, especially in metro and larger cities, are ordering food online more often than before. As a result of this, food tech has become one of the fastest growing internet sectors in India with an astonishing triple-digit growth rate in gross merchandize value (GMV) and DOVs in 2017 and 2018.
Huge potential waiting to materialize
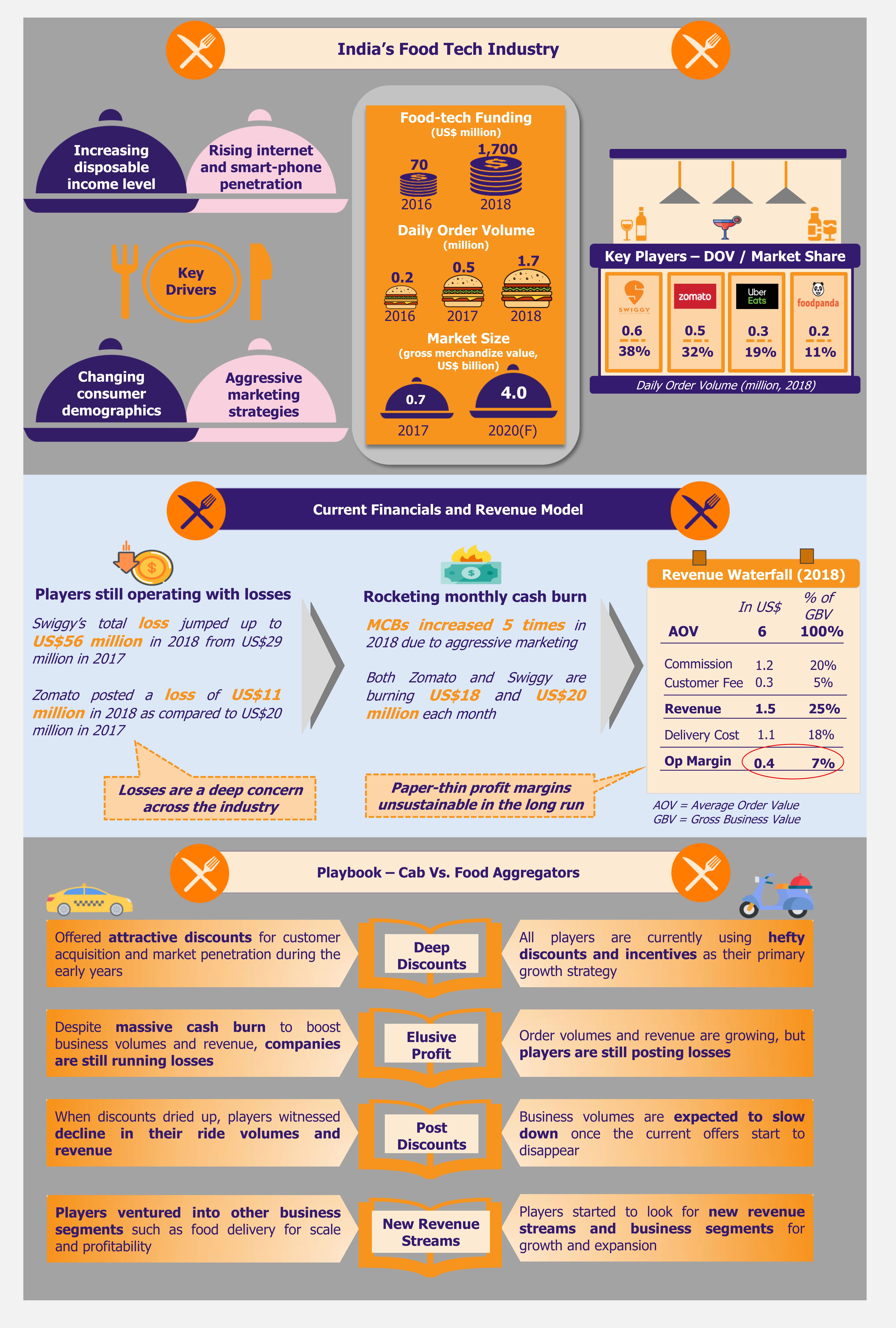
After an initial hype among entrepreneurs and investors in 2015, the food tech industry saw a slump and market consolidation in 2016 and 2017. Yet in 2018, India’s food tech industry rekindled investors’ appetite for the sector with huge spending spree. Driven primarily by rising disposable income, rapidly growing internet and smart-phone penetration, urbanization, and a young and working-class consumer base, India’s food tech industry stood at around US$700 million in 2017 and is expected to reach US$4 billion by 2020. In 2018, DOVs went up to 1.7 million orders from 0.2 million in 2016. The current market consists of four key players. Leaders Swiggy and Zomato currently hold a combined market share of ~70%.
The market still in its infancy
While order volumes have gone up significantly in the last 12-18 months, the industry is still in its infancy considering its outreach and adoption rates across the nation. At present, online food ordering is available in just over 200 cities across India and contributes to merely around 5% of the total food delivery business.
Further, India’s US$1.7 billion food tech market is pretty small compared to US$10.5 billion in the USA and US$36 billion in neighboring China. Out of the 90 meals consumed each month, Indians eat out or get their food delivered less than five times a month as compared to around 40-50 meals in countries such as Singapore, China, and the USA. In a nutshell, food aggregators have just begun to scratch the surface in India and there is a long road ahead for the industry to develop and grow further.
Growth driven by deep discounts
While the recent growth numbers draw a compelling picture of the industry, it should be noted that much of the current growth is driven primarily by deep discounts that are offered by the players to attract customers onto their platforms. With the recent funding boom, all players are deep-pocketed. In a fierce battle for market share, companies are spending heavily on advertising, low-cost and complimentary deliveries, and discounts as their primary growth strategy. Given the huge potential of the internet economy, even investors are willing to throw in money and keep the incentives going. However, recent history in India as well as similar experiences from other internet companies globally reveal that while this can be a good strategy to attract customers and penetrate markets, it is unlikely to be sustainable.
The recent growth is not entirely organic. A significant part of it is inorganic, pushed by discounts and offers, as players focus more towards acquiring new customers, increasing their order frequency, and entering new geographies.
– Satish Meena, Senior Analyst, Forrester
Again, customer loyalty is very hard to come by in the food tech industry. With India being a price-sensitive market, consumers will often flock to the platform that offers the best deal. Just like in India’s cab aggregation industry, it will be interesting to see how the food aggregators find their revenue and DOVs impacted once these offers will start to disappear.
Penetration beyond tier-II cities
Till 2018, orders were highly concentrated among top ten cities of India. These markets accounted for around three-fourths of the total business for all players. In order to move away from these gradually saturating markets, and to scale up their outreach across India, food tech players are pushing to capture the untapped potential in tier-III cities and smaller towns with first-mover advantage. While they consider these markets to be lucrative with improving demand appetite, rising spending power, and profitability, these cities are very different from metros in terms of size and customer preferences. E-commerce adoption rates as well as user base in these cities are relatively small, and therefore it will be challenging for food aggregators to create demand here, as consumers are not acquainted to online food ordering.
On the demand side, it will be difficult for aggregators to generate order volumes from smaller cities in India. Considering that Indians are very price sensitive, once these offers are gone, the drop-out rates will be much higher in these markets as compared to metros. –
Satish Meena, Senior Analyst, Forrester
Back in 2016, Zomato tested the potential in smaller cities and had to shut down its business in four cities including Lucknow, Coimbatore, and Indore due to poor demand. Similarly, Grofers, an online grocery delivery platform expanded into several tier-II and tier-III cities. But they also had to suspend operations in nine cities, citing the same reason. While the advent of Jio (an Indian mobile network operator) and its cheap internet data packages are proving to be a boon for e-commerce players, the question still remains how food aggregators will be able to create a sustainable demand in cities where population prefers to cook its food every day.
In addition, unorganized players dominate food delivery in these markets. It will be tough for aggregators to compete with them, especially in terms of pricing, since the local players operate with very low overhead costs without the need to worry too much about hygiene, safety, and other quality standards.
Weaker financials and unit economics
With the ongoing discounts and offers, the cost of customer acquisition is very high at present. A closer look at the financials of Zomato and Swiggy reveals that their monthly cash burn has increased five times within 2018, as they resort to aggressive discounting to grow further across the country. At present, all players are posting losses. This is very common even in the global food tech industry where most players are still operating with losses. For example, China’s Meituan-Dianping and ele.me are still far from reaching the break-even point, even after 10 years in the business. The story is the same even in developed markets such as USA and the UK. The aggressive cash burn model requires food aggregators to keep raising funds at regular intervals in order to further scale up and grow. This is a major concern raised by many industry experts.
Look at China! The top two players have still not managed to turn profitable even with far superior market penetration and order volume rates as compared to India. – Former Executive, Swiggy
Another major challenge faced by all the players are the inefficiencies in their operations, a fact that has a direct impact on their unit economics and thereby profitability. Although food delivery logistics is slowly getting better, it still constitutes a major chunk of the overall cost. Players are in a dire need to leverage innovative technologies and processes to streamline their logistics operations and make the most out of their logistics infrastructure and assets.
In order to improve their unit economics and operational margins, everyone is trying to streamline their logistics operations and to make the most out of their current infrastructure and assets. –
Vaibhav Arora, Former Associate General Manager,
RedSeer Consulting
Playing by the same playbook?
For the Indian market, food tech industry’s current growth story may seem to be a flashback from the ride-hailing industry, which really took off in the early days. On the back of heavy discounts and attractive offers, it looked like a win-win situation for all. In recent years, when cab aggregators slowly started to move away from discounts, at the same time increased fares for customers on one hand, while reducing incentives for drivers on the other, they started to witness challenges on both demand and supply sides of their business.
Strategies such as surge pricing, hike in fares, cutting-down driver salaries and incentives, etc., have impacted their businesses and resulted in unhappy customers and driver partners, unreliability in services, and a tussle with local associations. Cab aggregators in India have still not found the right balance to continue to grow without leaking money.
Many industry experts believe that food aggregators will also face the same set of challenges in the coming years, as players will start moving away from discounts along with hike in delivery charges and restaurant commission in order to improve their operating margins. This is already becoming evident as delivery partners from Swiggy in Chennai went on a strike for wage-related demands in December 2018, while UberEats faced a similar situation in April 2019 in Ahmedabad.
You can connect the dots with cab aggregation business and foresee similar challenges coming up for the food tech sector. In the long run, they will start charging higher delivery fees from customers and higher commissions from partner restaurants. –
Vaibhav Arora, Former Associate General Manager,
RedSeer Consulting
EOS Perspective
In recent years, food aggregators in India have definitely created a market for themselves by inculcating consumers with online food ordering concept. There is no doubt that the Indian food tech market is still developing and has a huge potential. But it is also a difficult one to crack. As seen in the past few years, many start-ups folded up early on. Similarly to India’s cab aggregators and e-tailers, food tech companies have started to believe that discounts are the way to a customer’s heart and eventually increasing their market shares.
None of the major players within the Indian internet sector is profitable yet. Even for Indian food tech players, profitability looks elusive, at least in the short to medium term. They will require massive funding injected regularly to finance their aggressive growth strategies. Uber in its recent initial public offering (IPO) prospectus made a bold statement admitting that if may never be profitable. This is one of the deepest concerns across the industry, and many industry experts are not sure whether sustainable growth can be achieved with the present business models.
In India, it looks like a certainty that both Swiggy and Zomato will be still posting losses for at least the next two to three years. –
Former Executive, Swiggy
There are many areas which are not streamlined enough, and therefore a significant amount of money is lost there. In order to grow, players will have to address the fundamental issues around unit economics and operational efficiencies. Companies will have to find multiple ways to improve their operational efficiencies such as looking at alternative revenue streams, monetizing their fleets, building other businesses, etc. Therefore, Swiggy has ventured into hyperlocal business by starting deliveries of groceries and medicines to further optimize its current delivery fleet. Similarly, Zomato has started Hyperpure, a service wherein they deliver food products to restaurant partners in order to grow further.
On the one hand, the above mentioned strategies seem to be logical for food aggregators and the way forward to scale up their businesses. On the other hand, this approach also raises concerns whether they are trying to juggle too many balls with just one pair of hands. Are players diversifying too early and rapidly, considering that they have not yet mastered the trade of online food delivery? Will these diversifications shift their focus away from the core business? Do they have the bandwidth as well as the expertise to manage these new businesses?
Furthermore, it will be also difficult for players to continue their current growth momentum beyond 2019, since they have penetrated all metros as well as tier-I and tier-II cities in India. Growing in smaller cities with low e-commerce penetration will be a daunting task, especially without the discounts. All these challenges are likely to cause the industry growth to slow down. To continue the growth momentum, food aggregators will also have to customize their strategies for smaller towns in India. Since availability of cuisines and quality of food is the biggest pain-point in these markets, players will have to compete by offering more choices with higher quality standards. Variety and quality of food will be one of the key differentiators for them to succeed in these markets.
In order to succeed in the long run, players will have to leverage the vast consumption pattern data at their disposal, and convert them into insights. By harnessing technologies, they can smartly identify the demand-supply gaps in each market, and address them by launching relevant products and services. For example, aggregators can assess and identify particular cuisines, dishes, order time-slots, etc. that are trending in each market, based on which they can either collaborate with restaurants and push them to expand their offerings and outreach to meet the increasing demand, or themselves start to move up the value chain by setting up own cloud kitchens (delivery-only kitchens) to fill such gaps, and thus further improve their profitability.
Additionally, players will have to further innovate their offerings. For instance, since migrant workers and students are the prime target, introducing subscription based meals in this segment could allow players to gain customer loyalty as well as earn steady stream of revenue. Similarly in the B2B (business-to-business) space, they can forge partnerships with small and medium enterprises (e.g. Indian Railways) to supply meals to their employees and customers. This is another market segment with huge latent demand where variety and quality of food is the need of the hour.
While these are early days to comment on the long-term growth potential of the industry, we can expect the market and current players evolve over the next few years. Considering that no one in the Indian aggregation space is profitable yet, and the fact that the path followed by food aggregators closely resembles to the one followed by cab aggregators in India, who have found it to be bumpy, unless players can build a solid business model with a clear path to profitability, for now, the rapid rise of food tech sector looks like another tech buzz that will eventually slowly down over the years to come.