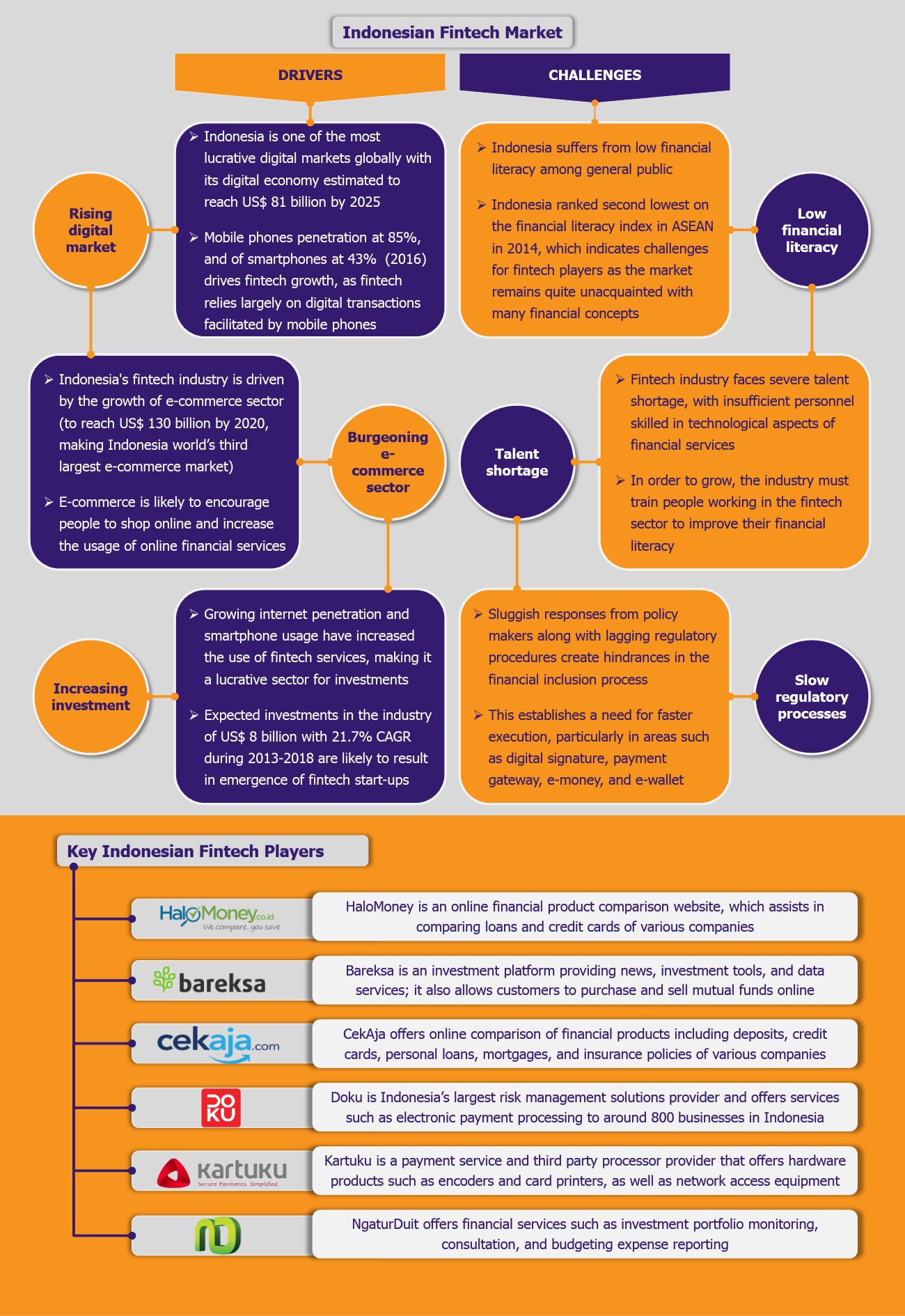
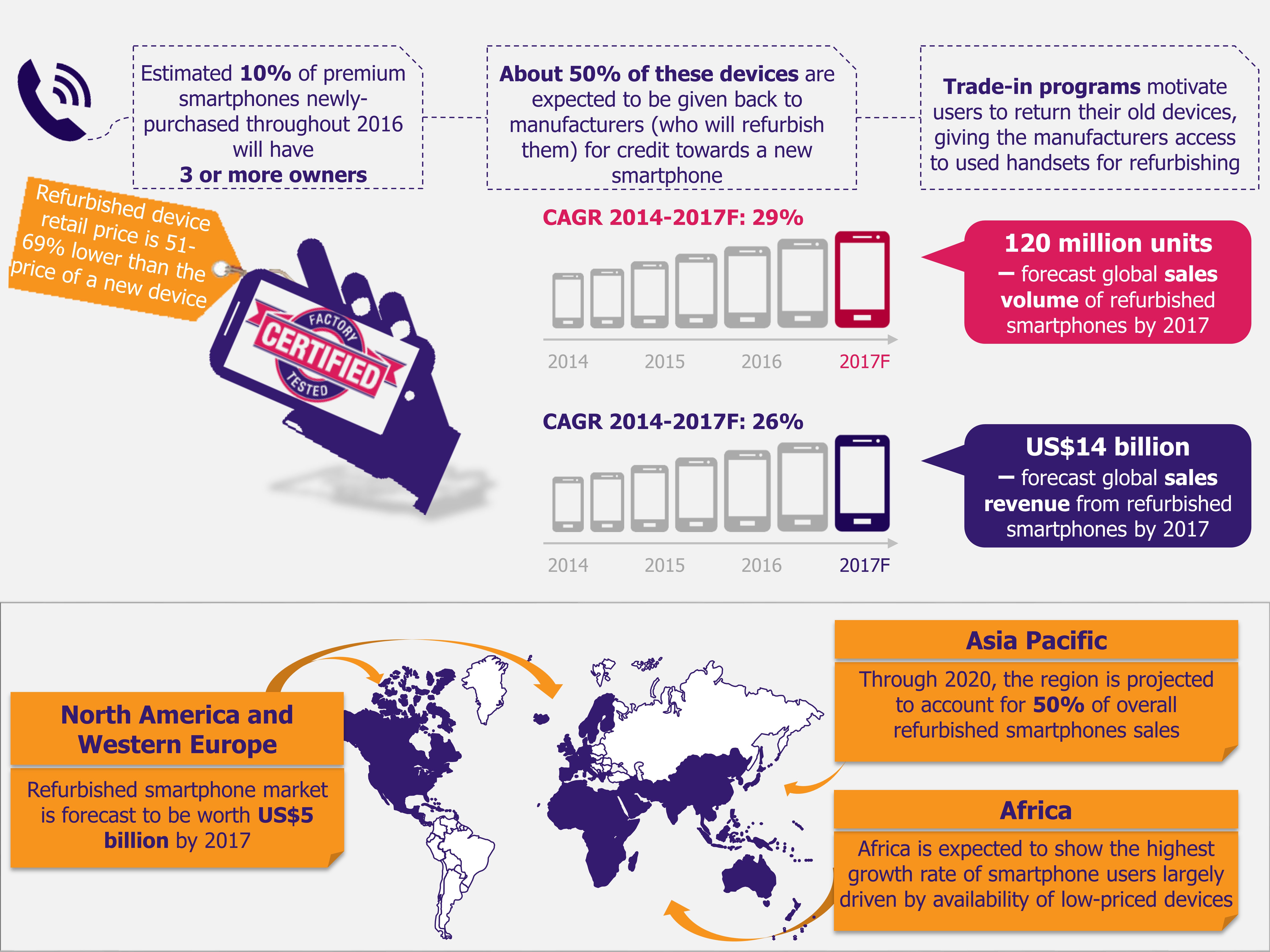
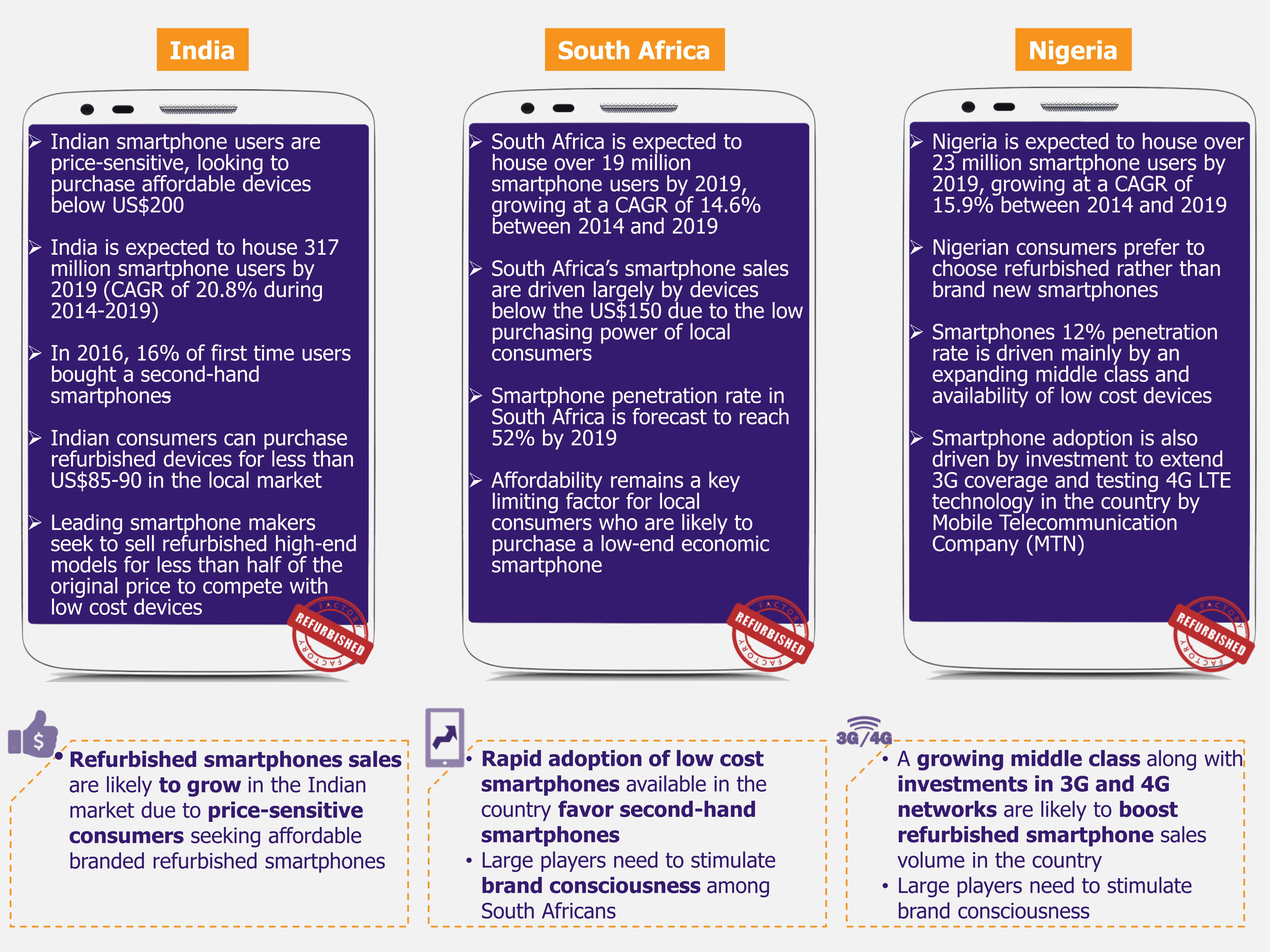
For the past several years, Amazon has been battling to break into the grocery retail market. After several experiments, Amazon has now embraced technology to differentiate its offerings and improve customer experience – a bold tech-fueled strategy to establish itself in the grocery market in the USA. Its latest innovations have shaken the traditional retail store concept and brought in revolutionary ideas of checkout-aisle free convenience stores, robot-controlled outlets, and voice-enabled online shopping.
Amazon is set to soon open its technology-powered brick and mortar stores in the USA, an idea that it once shunned, due to the strong belief that it could win over customers only through online channel. These stores have the potential to offer seamless store experience.
Amazon Go – Grocery store of the future
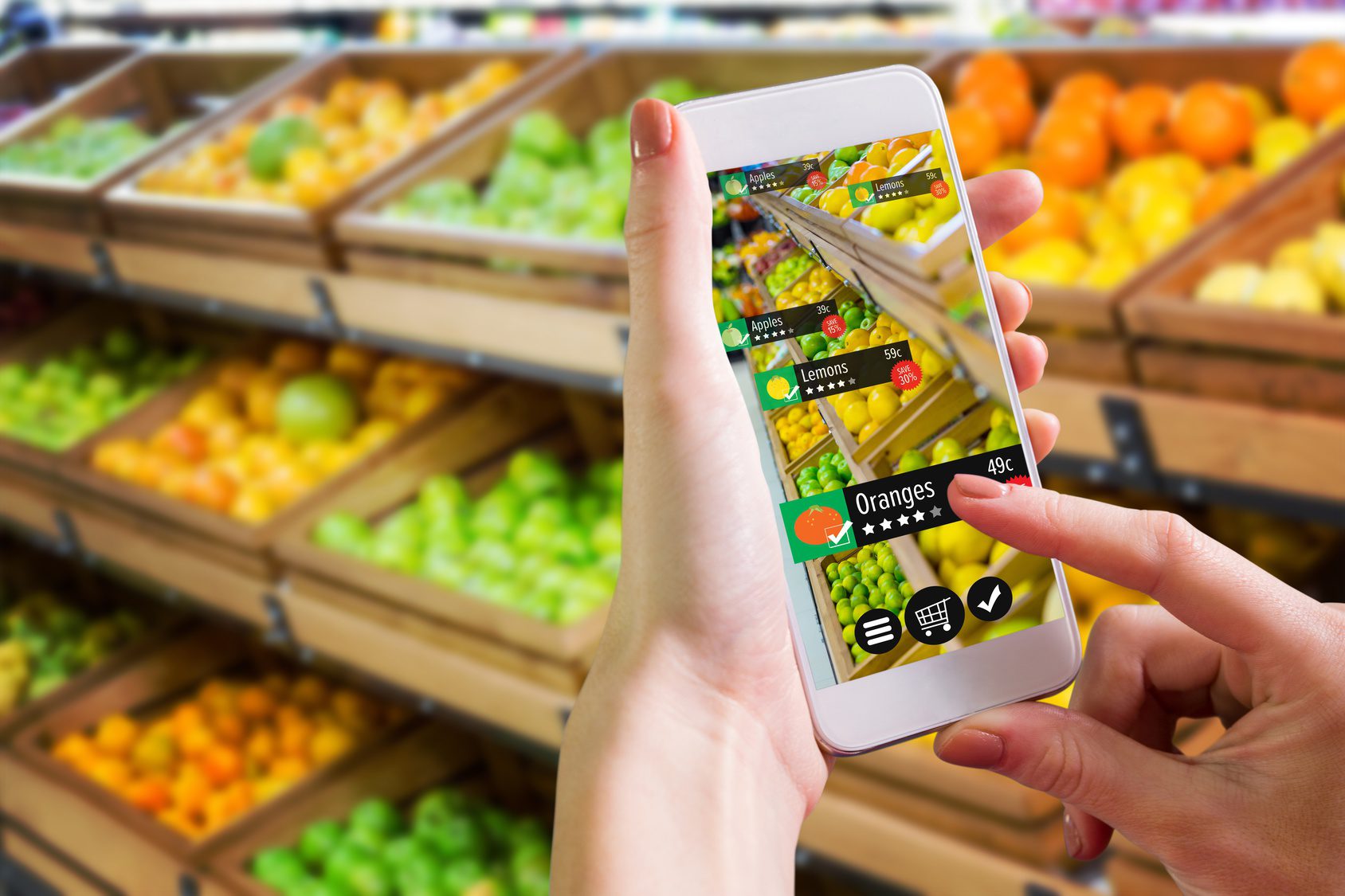
The company unveiled check-out free, Amazon Go store that ensures hassle-free and smooth shopping experience by eliminating the need to wait in queues to bill items – which was one of the key grievances of time-pressed customers. Launched in December 2016 in Seattle, the store is still in private beta mode and accessed only by Amazon employees. The public launch date is scheduled for early 2017.
The store operates on ‘just walk out technology’ that allows shoppers with Amazon Prime accounts to tap their phones on a turnstile while entering the store, and from then onwards, the technology tracks the selected items and adds them to a virtual cart, which is billed and sent to customer’s Amazon account.
The ‘just walk out technology’ has been developed using recent innovations such as computer vision, sensor fusion, deep learning, and artificial intelligence, among others. Products have embedded tracking devices – functioning through high-tech object recognition and inventory management systems – which pair with customers’ phones to charge their Amazon accounts. The weight sensitive shelves alert Amazon regarding restocking requirements.
Amazon has not yet commented on the number of stores it intends to open.
Robot-powered supermarket – Soon to be reality
A robot-operated supermarket is no longer just a figment of imagination with Amazon working towards opening such outlets soon. The supermarket is likely to be an extended colossal version of Amazon Go stores – the idea is to build two story, about 10,000-40,000 square foot store, stocked with over 4,000 items.
Shopping experience will be facilitated with robots that will pick up items from shelves and bag them in the first floor to deliver it customers waiting downstairs. Items will be charged automatically to customer’s account, replicating the Amazon Go’s check-out and billing concept.
Customers will have option of in-store shopping or to order online and pick-up items from the store later – offering both facilities is Amazon’s strategy to attract more customers.
The stores will be able to function with as few as six staff members to a maximum of 10 workers per location during any shift, against the industry average of 90 employees required to run a supermarket. The stores will only require a manager to sign up people for the Amazon Fresh service, a worker to restock shelves, two employees stationed at drive-through windows for customers collecting their groceries, and another two employees to help robots bag groceries, which would be sent down through conveyors.
Eventually, Amazon aims to introduce robot-run stores globally.
Alexa – Powering the age of hands-free shopping
In March 2017, Amazon successfully launched yet another innovative solution, Alexa, which is an artificial intelligence-powered voice assistant that facilitates shopping on Prime Now for its members (currently, limited to the USA). It ensures seamless, hands-free, and convenient shopping experience, as the user only has to give a voice command as ‘Alexa, order from Prime Now’ and the job is done.
Alexa is extremely versatile and a multi-tasker, it can search for items, re-order or track orders, add items to cart, and give product recommendations. Besides being a powerful shopping tool, it can also read kindle books, control selected smart home products, play music from Amazon’s own services, etc.
Voice-enabled shopping service is available through Amazon devices such Echo, Fire tablet, and Fire TV, and it has been integrated with Amazon’s Shopping app for iOS platform.
EOS Perspective
Will Amazon’s innovations threaten other players in the market?
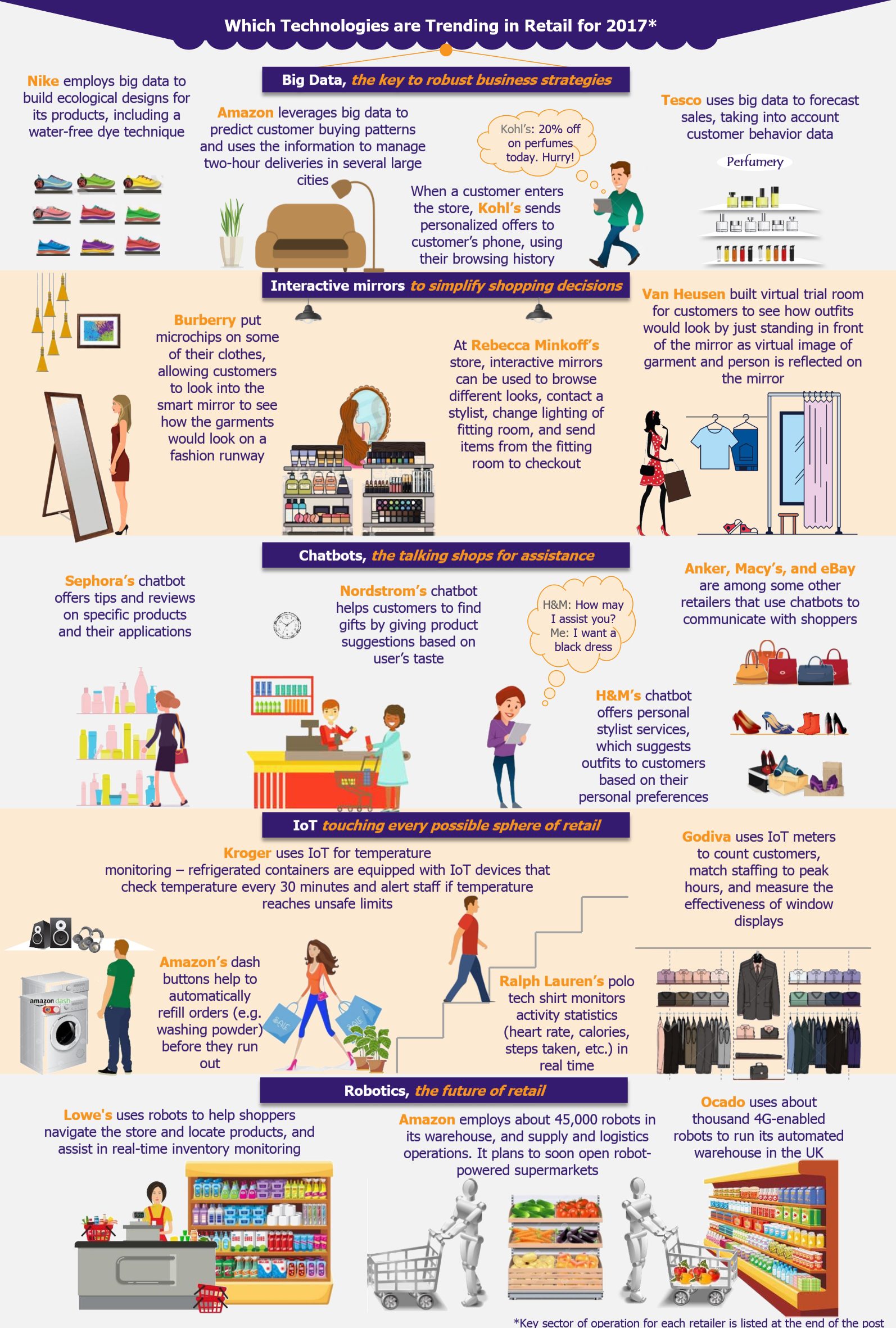
Other retailers feel the pressure to upgrade services to keep up with Amazon’s enhanced shopping experience. Kroger launched ClickList (an online grocery ordering service, where the customer needs to visit the store to pick up the items) across 500 stores and is using technology to analyze shopping habits of customers to generate relevant coupons for them.
In January 2017, Walmart launched Scan and Go app for Android users (already available for iPhone customers), to compete with Amazon. The app scans barcodes of items, customers can pay through the app, and show receipt at the gate before exiting the store. The prototype is still in testing phase and is likely to roll out by the end of 2017.
Amazon’s technology will not be easy to replicate nor will a lot of retailers have the capacity to implement technological innovation of such a massive scale, hence, Amazon is certainly likely to have an edge over its competitors when its stores open for public. Amazon’s competitors in the grocery business definitely feel threatened and have started to revamp strategies and use technology to reach more customers, however, the scale of their innovations still remains miniscule in comparison with Amazon.
Why is Amazon pushing for innovation?
After a decade of Amazon’s food retail experiments, with limited success through online channel, the company decided to launch physical stores. But cracking through the US$ 800 billion grocery market in the USA, already dominated with players such as Target, Walmart, Kroger, etc., is not so simple. Consequently, Amazon strategized to carve a niche for itself by differentiating its offerings, using technology to provide flawless, quick, and smooth shopping experience for customers. The move is expected to accelerate its penetration into the grocery business.
Amazon’s core business model is based on behavior modification, which revolves around attracting consumers to e-commerce website, and now also to physical stores, converting the customers into Prime members, and eventually driving them to spend more across categories.
All of Amazon’s new inventions, including Alexa, Amazon Go, and robot-powered outlets, will push consumers to eventually become Prime members, as holding a Prime membership is the basic requirement to be able to access these services. Prime members, besides paying an annual subscription fee, are likely to shop and spend four times more than the non-Prime members, which makes Amazon’s retail business profitable – in 2016, revenue from Amazon Prime and other subscription services such as e-books and videos stood at US$ 6.4 billion, growing by about 40% annually.
The other benefit of automation for Amazon includes minimizing labor cost, which accounts for lion’s share in a supermarket’s operating cost. Further, the robot-controlled supermarket’s design is likely to slash real-estate costs by reducing the need for aisles that typically occupy large areas of traditional supermarkets. Using robots on the first floor will also allow Amazon to stock more products in space smaller than in conventional stores. The store prototype is expected to yield profit margins above 20% against the industry average of 1.7%.
Further, Amazon envisions to open 2,000 stores in the USA over the next 10 years against the current 2,800 stores of Kroger, USA’s largest traditional supermarket chain. This indicates that, if these store openings are successful and if the profit margins are achieved as expected, Amazon could potentially be a real threat to conventional retailers over time.
Will these innovations be truly disruptive or have limited impact on grocery retail segment?
The path to building futuristic concepts and prototypes will definitely not be a cake walk for Amazon. It might face adversities such as increased chances of theft due to the store formats of Amazon Go and robot-driven supermarkets. Selling random weight items (fresh fruit and vegetables, sliced meats, etc.) can be difficult to incorporate in Amazon Go’s automatic checkout system.
Lastly, success of these stores will depend on their location and sales volume generated – opening stores in downtown areas might be difficult at the beginning because high rentals may not be covered by the sales achieved.
Certainly, the technology-driven stores are not a mass market option for Amazon today nor is the success of these prototypes guaranteed. Also, as grocery retail operates on wafer thin margins, lasting innovation is rare in this segment.
Amazon’s bold technological innovations might not be big enough to disrupt the industry yet. However, considering Amazon’s steady financials and relentless efforts towards automation, it is likely that the company could forge ways to make grocery retail more profitable and efficient in the future.