SARS-COV-2 has brought the world to a standstill. Technology and its creative uses have been playing a pivotal role in sustaining lives during the pandemic as well as combating the crisis. One such technology that has been at the forefront of the pandemic is blockchain. From mitigating supply chain issues with medicines and protection gear to facilitating transparency in donations to effectively tracking the spread of the virus and protecting patient privacy, blockchain technology is being applied across the spectrum to contain and manage the outbreak.
The current pandemic has brought to light many inefficiencies and limitations of the existing global healthcare systems, wherein governments across the globe are grappling to control the outbreak, challenged by the lack of a unified, interconnected, and trusted network to share data and track cases. Blockchain has several inherent properties, such as decentralized ledger, transparency, and immutability, that make it suitable for handling and managing various aspects of containing the pandemic.
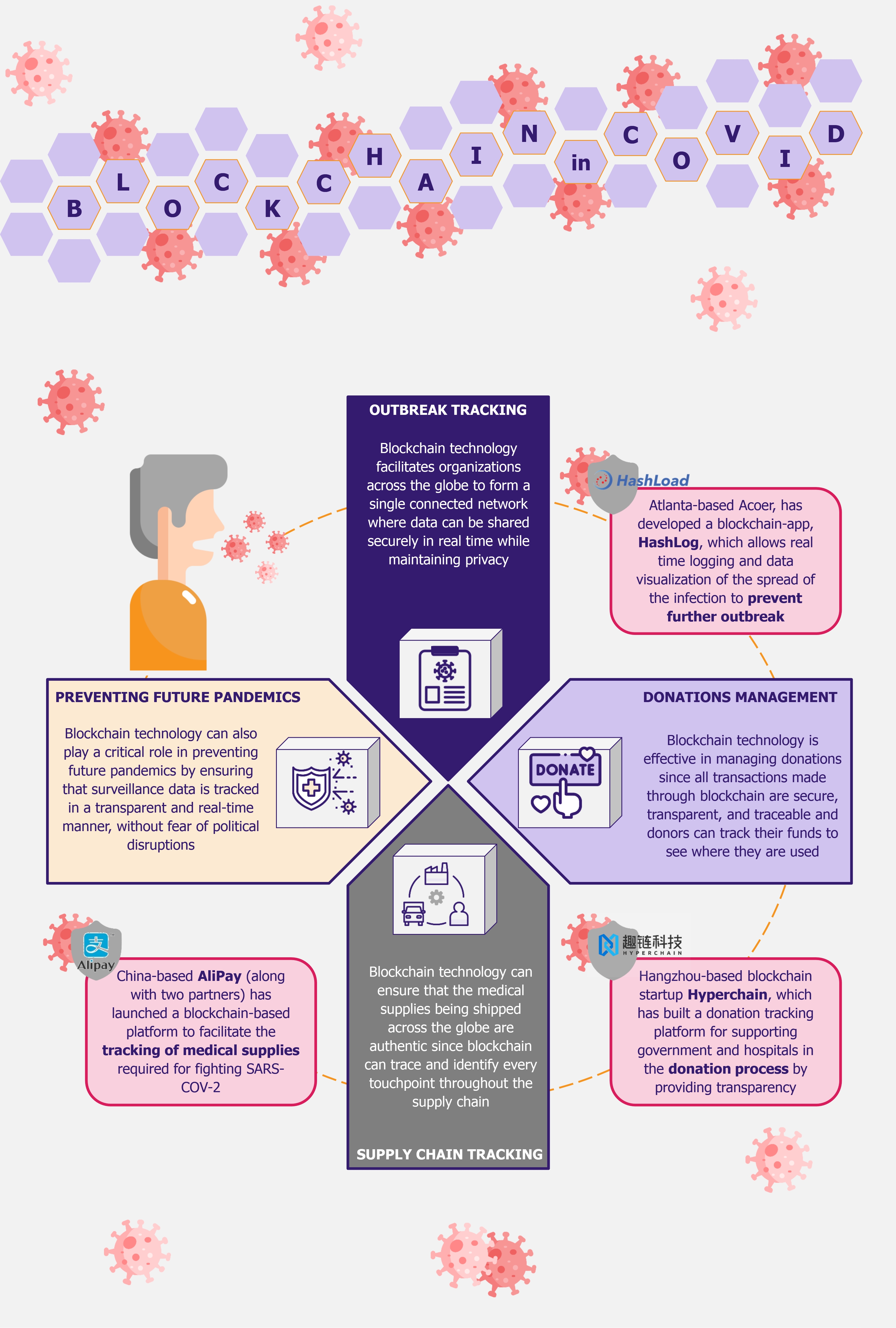
Outbreak tracking
Global health authorities and governments across the globe are having a hard time gathering authentic data regarding tests and patient numbers, hospital beds, recoveries, etc. Currently, most of the data circulating is disparate and comes from multiple sources, such as hospitals, labs, the public, and media, instead of one authorized source. This is extremely damaging since it results in the creation of a great amount of inaccurate and duplicate data, which, if trusted, makes the process of tracking and containment both time-consuming and ineffective. This is counter-productive to the management of a disease that is as fast-spreading as COVID-19.
Blockchain technology can come into play in effectively tackling this issue. Owing to its distributed and immutable nature, blockchain can provide a feasible solution for tracking the outbreak. Blockchain-based apps facilitate organizations across the globe to form a single connected network where data can be shared in real time and securely. Moreover, since data stored in the blockchain is immutable, it is protected against unauthorized changes, and its distributed nature ensures protection against fraudulent data (since each entry requires consensus algorithms and smart contracts). Lastly, blockchain efficiently manages high volumes of data (as in the cases of the COVID-19 pandemic) on a real-time basis, which cannot be managed using human resources.
However, in addition to these factors, the aspect that stands out the most and makes the blockchain technology ideal for monitoring and managing outbreak-related information is the level of privacy it offers. People do not wish for their information to be shared publicly or be used for other purposes. Thus, it is a challenge to get patients to collaborate with governments and healthcare institutions to share information regarding their condition and wellness. For instance, the Israeli government recently permitted healthcare institutions to track citizens’ mobile phones to control the spread of coronavirus. This has raised concerns from human rights organizations as citizens are not comfortable with sharing their personal information.
Since blockchain uses a distributed ledger, which ensures accountability and transparency with regard to access to its stored data, the information shared through blockchain cannot be extracted or misused. Moreover, information stored in a blockchain cannot be hacked. This encourages patients to share information regarding their condition, symptoms, location, and underlying health conditions without fear of the information being misused or shared with any third party.
Furthermore, information shared by patients in a blockchain network may not only be used for tracking the outbreak but also facilitate health centers’ study of the disease characteristics and patterns to develop treatment and solutions.
For instance, WHO has been using a blockchain-based data streaming platform, called MiPasa, which facilitates the sharing of information amongst need-to-know organizations such as state authorities and health officials. The platform is built on top of Hyperledger Fabric and partners with IBM for blockchain and cloud platforms. The application cross-references siloed location data with health information to track and prevent the spread of the outbreak, all while protecting patient privacy.
In another example, an Atlanta-based developer of blockchain-enabled healthcare applications, Acoer, developed an application called HashLog, which allows real-time logging and data visualization of the spread of the infection. HashLog provides real-time updates on the spread of the disease by tracking the movement of infected people to identify potential outbreaks and prevent further spread. The application uses the Hedera Hashgraph distributed ledger technology, and each entry is recorded through a verified hash reference on the ledger, ensuring that the data is correct.
Donations
In addition to tracking and preventing outbreaks, blockchain also plays an important role in securing donations. From hospitals and state authorities with insufficient funds for medical supplies to economically weaker sections of the population losing sources of income due to lockdown, the current pandemic has displaced a huge number of people across the globe. Thus, in such times, donations play a critical role in sustaining livelihoods and providing healthcare supplies to the affected people. However, given the fraud associated with donations in recent times, lack of trust is a common factor affecting the success of donations. Several individuals want to help and donate, however, are discouraged due to fear of their money being misused.
For instance in India, the government and police warned citizens against several fake relief schemes that have been floating in the name of COVID-19 relief, some even mirroring the Prime Ministers Relief Fund. These kinds of activities deter willing people from donating.
Blockchain technology can be used to effectively combat this issue. Since all transactions in the blockchain are secure, transparent, and traceable, donors can track their funds and see where they are utilized. This gives confidence to donors that their funds are being used for the exact purpose that they intended.
One such example is Hangzhou-based blockchain startup Hyperchain, which built a blockchain-based donation tracking platform for supporting government and hospitals (such as Tangshan People’s Hospital, Jiayu People’s Hospital, and Xiantao No. 1 People’s Hospital) in the donation process. The platform has attracted more than US$2 million in donations.
Supply chain tracking
Blockchain technology has been deemed extremely useful in managing and tracing the supply chain in several sectors as retail (for more insights on this, read our article Blockchain Paving Its Way into Retail Industry). However, given the current pandemic, the technology can also utilize similar functionalities and play a significant role in tracking of medical supplies.
Given the pace of the spread of COVID-19, authorities and healthcare organizations across the globe have faced a shortage of medical supplies, such as masks, sanitizers, PPE kits, ventilators, testing equipment, as well as some medicines. This drastic increase in demand has resulted in the distribution of a large number of counterfeit and faulty products. Blockchain technology can play a significant role to combat this. Given the data provenance in blockchain and its immutable nature, it is possible to identify and trace back every touchpoint of the medical supplies to ensure its authenticity.
In addition to filtering counterfeit products, blockchain also helps streamline the supply chain process to ensure hospitals and doctors secure timely supplies to treat patients. Blockchain can provide real-time updates regarding demand so that medical manufacturers can adjust production levels accordingly. In addition, it can help fast-track supply chain contracts through the use of smart contracts and facilitate faster payments, thereby improving overall efficiency.
In February 2020, China-based AliPay, along with the Zhejiang Provincial Health Commission and the Economy and Information Technology Department, launched a blockchain-based platform to facilitate the tracking of medical supplies required for fighting SARS-COV-2. The platform has improved trust within the medical supply chain since it records and tracks the entire provenance of preventive supplies, including masks, gloves, and PPE kits.
Apart from the medical supply chain, blockchain can also help limit supply chain disruptions faced by several other industries due to lockdowns in several parts of the world. However, companies that are using blockchain for managing their supply chain have an advantage as they have better visibility into their complete supply chain and thereby can identify points of disruption in a timely manner.
Avoiding future pandemics
Blockchain is on the front line for fighting the current pandemic, but it also has the potential to prevent future disease outbreaks. Most of the current healthcare surveillance systems across the globe are outdated and lack the required timeliness and efficiency in sharing information with local as well as international health enforcement organizations. Moreover, sometimes there is a question of deliberate delay in the sharing of critical information.
To this effect, blockchain-based health surveillance systems can help mitigate future outbreaks. Since they operate on a decentralized ledger, the surveillance data is transparently available to health organizations across the globe in a real-time manner, without the fear of any political disruptions. Timely knowledge of a potential outbreak is the first and most critical step in preventing a similar situation in the future.
In addition to the above-mentioned applications, blockchain companies, along with institutions, are developing creative solutions that help reduce challenges faced by people due to COVID-19 in their day-to-day lives. For instance, Toronto-based blockchain company Emerge launched a public safety app called Civitas, which assists citizens and local authorities across Latin America. This app matches one’s official ID to confidential medical records stored in the blockchain to identify whether the person is allowed to leave the house or not. Thus, the app allows police to verify if the person has travel permission just on the basis of their government ID and without gaining access to the person’s medical records. The app also determines the safest time and day for going out for essentials for people who are experiencing COVID-like symptoms.
Moreover, as discussed in our previous article (Blockchain Scores Well in the Education Sector), blockchain is also extremely useful in the virtual education scenario, which is now the new way of schooling for a large part of students across the globe.
EOS Perspective
Blockchain technology has several inherent properties that make it ideal for helping to manage and combat the current pandemic. Its decentralized, traceable, and immutable properties make it especially desirable for managing contact tracing and outbreak tracking, which are critical in handling a pandemic efficiently. Moreover, the benefits of blockchain are further amplified when used alongside other technologies, such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and big data.
However, despite its several uses, the issue of scalability plagues blockchain adaption at a larger scale. Blockchain is still a nascent technology and lacks high-level scalability. With COVID-19 affecting most of the world, the current blockchain companies do not have the level of scalability to provide all-encompassing global-level solutions.
Furthermore, blockchain technology does not operate alone, and it needs to be configured with the operating legacy system of companies and other stakeholders. However, most legacy systems are relatively old and, therefore, do not support blockchain technology. Updating or reconfiguring a legacy system is a tedious process (both in terms of time and money), and companies may not want to tie up resources for that at the current time.
Given these drawbacks, blockchain may not be deployed at a global-scale level during this pandemic, however, its inherent benefits have made companies, authorities, and global health organizations ponder, explore, and evaluate its potential in managing such situations in the future. While the COVID-19 pandemic has caught the world largely unprepared, organizations and companies across the globe are gearing up to ensure this history is not repeated, and blockchain technology has emerged as a critical part of the solution.