For years, tech adoption has been relatively slower in the education sector than in many other sectors. This considerably changed when COVID-19 hit in early 2020 and triggered the closure of educational institutions all over the world. With classroom doors closed and conventional methods of education taking a setback, e-learning gained momentum like never before. From virtual classes to tutoring and conducting meetings online to learning new skills, the pandemic propelled EdTech into the spotlight, putting it on a growth trajectory.
Changing face of the EdTech market
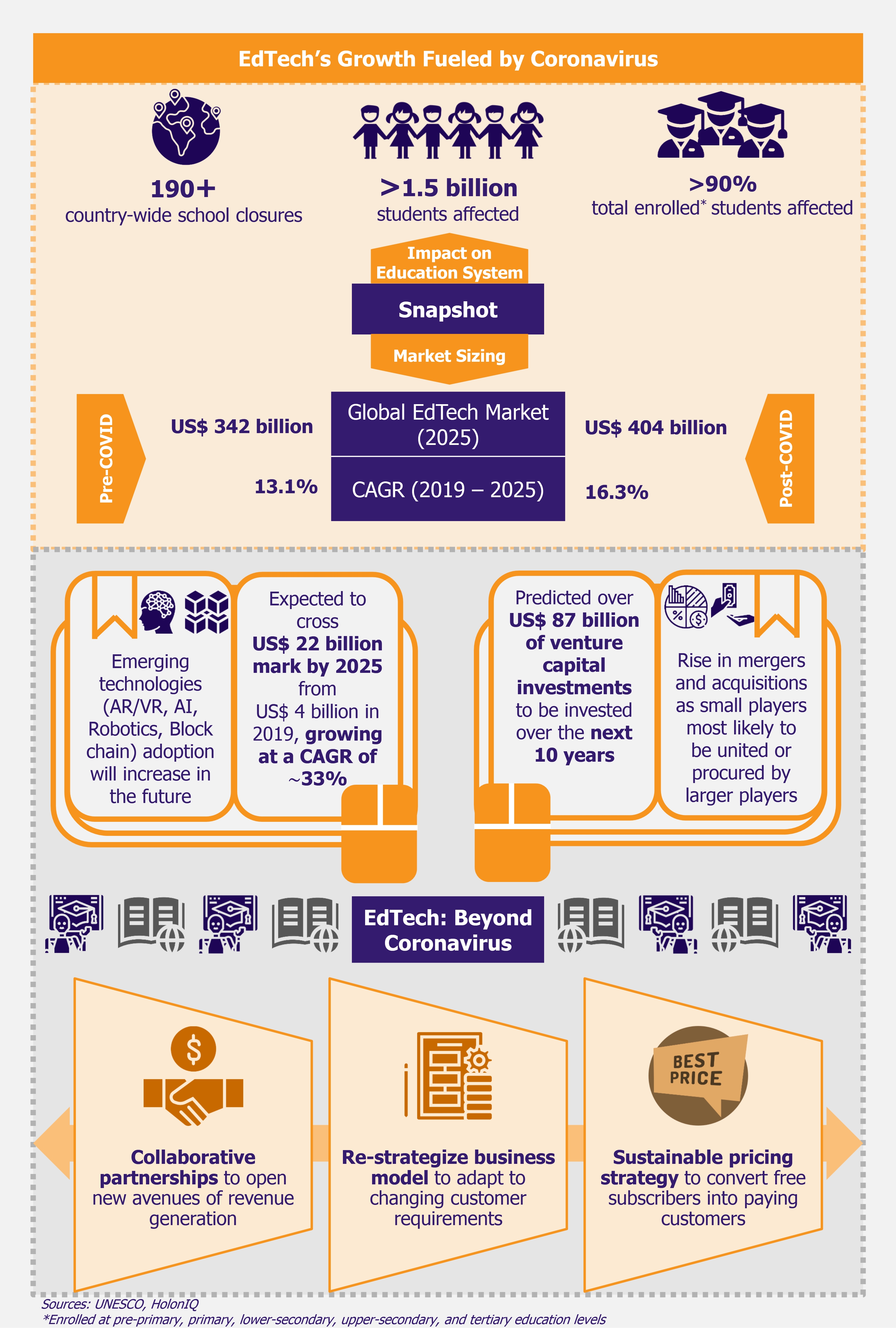
To control the spread of coronavirus, nearly 190 countries had implemented temporary school closures by the end of March 2020, disrupting education of more than 1.5 billion students. Over the coming days, as the count of people affected by the virus multiplied hourly, all educational institutions (including schools, colleges, universities, vocational training centers, and skill development institutions) were directed to remain shut until the situation improved, driving students to shift to online learning. This sudden change away from classroom learning has led to the adoption of online learning on a large scale.
Before the coronavirus pandemic, the EdTech sector was estimated to reach a value of US$ 342 billion, growing at a CAGR of 13.1% between 2019 and 2025. The forecast revisions accounting for the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic predict the global EdTech market to reach US$ 404 billion, with a CAGR of 16.3% by 2025. The sudden adoption of e-learning across educational institutions, as well as an increasing need for upskilling courses by working-class individuals, are driving the tech embracement in the COVID-19 pandemic scenario.
Moreover, with uncertainty still looming on the reopening of educational establishments, technology will need to play a critical role across all aspects of education – content generation, knowledge consumption, and assessments. This is expected to intensify the pace at which digitization happens in the education sector.
Investment at an all-time high
Over the last decade (from 2010 to mid-2020), global EdTech venture capital funding stood at US$ 36.8 billion, of which more than 50% occurred since 2018. Investment in EdTech has sky-rocketed over the last few years – the sector witnessed investment of merely US$ 0.5 billion in 2010 but reached a striking figure of US$ 7 billion in 2019, 14 times more in a span of nine years. Even during the COVID-19 pandemic, companies globally attracted US$ 4.5 billion in funding between January and July 2020, which is the highest ever funding raised during a comparable period in the last decade. It is expected that the trend will follow, and the investments will grow further, anticipated at US$ 87 billion over the next decade.
During the coronavirus outbreak, the demand for e-learning increased manifold, accelerating the investment spree in EdTech. While the USA is home to nearly 43% of the world’s EdTech companies (followed by India – 10%, Brazil – 9%, the UK – 8%, and China – 3%), as of 2020, the companies that received the high-value funding deals during COVID-19 period were situated elsewhere.
India-based online tutoring firm Byju’s raised more than US$ 1 billion from January through September 2020 (US$ 200 million in January from Tiger Global Management, USA-based investment firm; US$ 200 million in February from General Atlantic, USA-based equity firm; US$ 23 million in June from Bond Capital, USA-based investment firm; US$ 122 million in August from DST Global, Hong Kong-based investment firm; US$ 500 million in September from Silver Lake, USA-based equity firm) to become the first company in the EdTech domain to reach a valuation of US$ 10.8 billion.
The second company was China-based Yuanfudao, an online live course platform, which raised US$ 1 billion in March 2020 from Hillhouse Capital (a China-based private equity firm) and Tencent Holdings (a China-based technology conglomerate).
Another noteworthy deal was also scored by China-based Zuoyebang, an online education tutoring provider, which received US$ 750 million in funding from FountainVest Partners (a private equity firm based in Hong Kong) and Tiger Global Management.
Moreover, mergers and acquisitions are also likely to grow in the near future, considering many small players will not have the necessary finances and expertise to revamp their business model to the changing market needs and are likely to merge with or acquired by larger players.
Increased adoption of advanced technology
The short-term rush in additional demand for EdTech solutions brought by COVID-19 is also expected to give headway to increased adoption of advanced digital technologies in the future. Solutions based on technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR), and blockchain (we wrote about the role of blockchain in virtual education in our article Blockchain Scores Well in the Education Sector) are likely to gain more momentum and be integrated into core education delivery.
It is expected that by 2025 AR/VR market in EdTech will reach US$ 12.6 billion from US$ 1.8 billion in 2019, growing at a CAGR of 38.3%. AI is expected to observe a CAGR of 40.29% between 2019 (from US$ 0.8 billion) and 2025 (to US$ 6.1 billion). Other technologies that will see a spike include robotics (expected to grow from US$ 1.3 billion to US$ 3.1 billion during the six-year period) and blockchain being increasingly incorporated into learning processes (expected to grow at a CAGR of 34.8% from US$ 0.1 billion to US$ 0.6 billion).
EOS Perspective
COVID-19 has proved to be a turning point for the EdTech industry and acted as a push for change that was already underway in the education sector. The pandemic downrightly disrupted the education system, making online learning an essential part of the way we learn; however, it is unlikely that digital learning will become the new norm. Now, whether e-learning becomes the sole mode of education or blends with physical classes, the EdTech market has growth potential, and the investment angle also looks bright.
Whilst a large number of players in the EdTech sector were able to capitalize on the need for education during the pandemic, not all digital learning platform providers will stick around. In the long term, players with a clear-product concept and a well-defined monetization policy will emerge winners. They must also be thoughtful of the fact that the unforeseen growth the sector witnessed during the pandemic is only transient and once educational institutes reopen, the demand for online learning is likely to shrink (even if by a small percentage).
In terms of user adoption, EdTech companies saw significant growth by offering free access to their platforms. However, this is not a sustainable strategy that firms can adopt in the long run. Once things get back to normal and the free trials end, companies will need to attune their product pricing and come up with more affordable plans. Nevertheless, emerging on the winning side of the pandemic will not be easy for the players as they walk a very thin line between offering innovative learning models and meeting market demands while still being able to generate revenue and remain profitable.
Moreover, while the new users multiplied quickly, retaining them is easier said than done. Emphasis on service quality and overall delivery experience would be crucial to convert current free subscribers into paying customers.
Bearing in mind that the current momentary spike in demand for online tools is not directly proportional to increased business, EdTech companies need to revisit their business strategies to achieve long-term growth. As the competition increases, companies must tweak their commercial business model to adapt to changing customer requirements and fulfill the need for on-demand educational lessons.
Additionally, the importance of collaborative partnerships with educational institutions (for their need for customized curricula, creating teaching modules and courses to train teachers) and corporations (the need for upskilling employees on technical competencies) cannot be underestimated. Business models based on such partnerships are likely to open new avenues of revenue generation. This will also negate the per-student acquisition cost for EdTech players.
Nevertheless, though the growth path for the EdTech sector may have a few roadblocks, in hindsight, the overall outlook towards the sector’s growth in the near future appears to be optimistic.
Read our other Perspectives on coronavirus here