For several years, the US sanctions on Iran continued to have a detrimental impact on the economic growth of the country, with tourism sector being severely affected throughout the period under sanctions. The 2016 sanctions removal brought many visible changes to the development of the country, with hopes for tourism industry to benefit from the potential influx of travelers and new opportunities for the industry players.
Iran’s tourism was severely affected by the US sanctions
Iran was in a quivering state for more than 35 years owing to the never-ending political tensions with the USA post the 1979 Iranian Revolution. This led to no formal diplomatic relationships between the countries since 1980, and considerable sanctions imposed on Iran over the years. The impact of these sanctions was visible through a range of profound economic problems such as inflation, unemployment, poverty, and underdevelopment of virtually all industries in the country.
One sector that faced severe repercussions of the sanctions was Iran’s tourism industry. A negative image of the country was reinforced by the mainstream media as a flag-burning, west-hating nation, a fact that caused a major dent to Iran’s tourism industry. Adding to it, lack of resources to tackle this negative discourse had further left Iran in an international isolation over all these years. Despite being rich in culture, natural history and landscapes, a country with such an image could not persuade foreign tourists to visit.
Moreover, the US sanctions drastically affected Iran’s economy, which resulted in lack of proper resources to establish a well-equipped transportation sector, including airlines, trains, and buses, which in turn led to Iran becoming even less attractive to tourists. In addition, lack of proper hospitality infrastructure such as hotels, restaurants, roads, etc., further negatively impacted international tourists’ interest in Iran. Adding to it, the US sanctions also created greater tensions between Iran and the USA which led the US government to issue a travel advisory over all these years, which restricted its citizens to travel to Iran due to safety risks, such as getting kidnapped or arbitrary arrest and detention in the country. Thus, this resulted in almost no tourist from the western countries visiting Iran.
Iran’s tourism sector did witness a very modest growth over the years, largely thanks to pilgrimage tourism visiting the shrines and originating mostly from regional countries such as Iraq, Azerbaijan, and Turkey.
According to The World Bank data, the number of international tourists’ arrivals in Iran fluctuated, increasing from 2.7 million in 2006 to just 4.9 million visitors in 2014. Iran’s tourism industry was suffering particularly badly not only from the lack of arrivals of American tourists, but generally more affluent, well-spending tourists from western hemisphere, who were universally deterred by sanctions, poor state of the tourism infrastructure, as well as the negative image of the country created by international media.
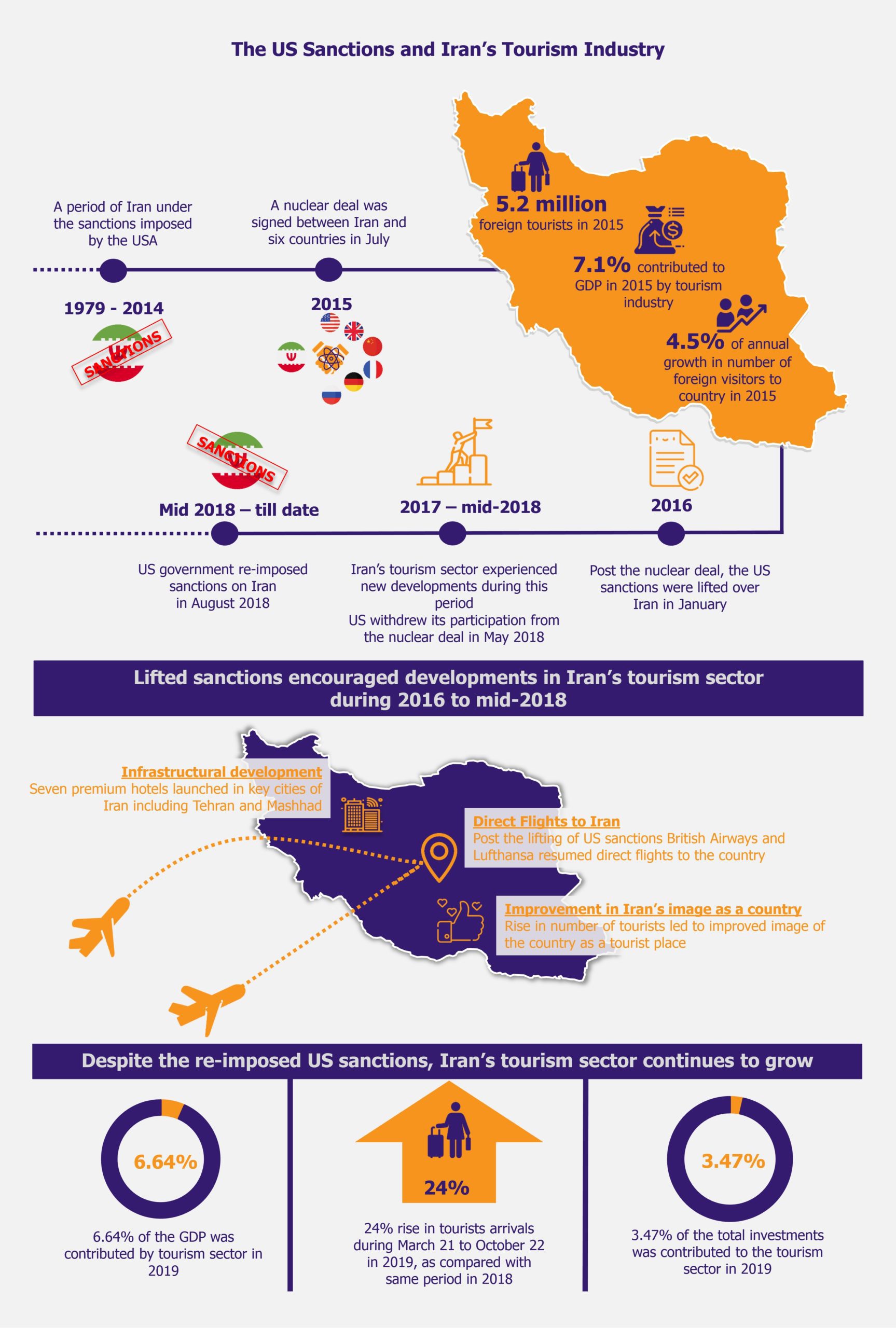
According to official figures by Iran’s Culture Heritage Organization, during the sanctions period, tourism sector contributed around 2.0% to the country’s GDP (an average of US$7.5 billion in a year), leading to sluggish infrastructural development throughout that period. Iranian tourism sector’s hopes for change and better growth started budding when Iran signed a nuclear deal with six countries in July 2015, an event that led to the US sanctions being finally lifted.
The nuclear deal came as a ray of hope
Even before the US government removed the sanctions, the country started witnessing a slight increase in the number of foreign visitors. This was thanks to the nuclear deal signed between Iran and a group of six countries (the permanent members of the United Nations Security Council – Russia, France, UK, USA, and China, plus Germany) and the EU in July 2015. The deal included Iran’s commitment to restricting its nuclear activities, agreeing to keep check on the uranium stockpile, among other agreements.
The deal immediately mellowed down Iran’s negative image and released a positive message of lowered risks associated with visiting the country. This gave a slight boost to the tourism sector with a moderate growth of 4.5% with 5.2 million foreign tourists visiting the country in 2015, the highest arrivals number till date.
Another upward push on the growth trajectory came the following year, when the US government removed sanctions from Iran in January 2016, as part of the nuclear deal. This was expected to have a major impact on tourism sector as it offered hope for much needed economic stimulation, along with investments and development in the economy, and tourism sector in particular.
Post lifting of sanctions, tourism sector rejoiced with developments
The nuclear deal and removal of sanctions brought growth to the tourism sector, owing to removal of restrictions on imports of financial and transportation-related services. As a result, some European airlines, such as British Airways and Lufthansa, resumed direct flights to the country. As visa requirements were increasingly relaxed, tourists from western countries started to arrive. This in turn slowly raised the demand for accommodation leading to skyrocketing prices of hotel rooms. These changes finally generated higher income for local businesses such as hotels, restaurants, tourist guides, local transportation providers, and other players in the market. Iranians excitedly welcomed foreign tourists, including the Americans, along with the positive outlook for the sector’s growth.
The Iranian government, following the sanctions removal, initiated efforts to attract foreign investments with a clear agenda of reducing Iran’s oil dependency and boost the country’s economy, by betting on increasing revenues from tourism sector.
The initiatives included the launch of a scheme called “100 Hotels, 100 Businesses” that outlined 174 projects to be introduced to investors interested in hotel construction. This is was an ambitious scheme led by the Iranian government focusing on bringing the hotel industry of the country back on track. This scheme aimed at attracting investments for the construction of 100 hotels across 31 provinces with priority given to most popular regions such as Tehran, Kashan, or Mashhad. Also, through this scheme, the government focused on initiating joint ventures with foreign companies, benefiting both the government and foreign investors.
The government also announced other major plans for the development of tourism industry. These included creating regulations to facilitate investment, creating brands of hotels and restaurants, promoting new types of tourism such as sports, climate, and industrial tourism, developing knowledge-based human resources, creating a comprehensive system of standards, balancing inbound and outbound tourism by improving political relations, and creating a system for the protection and restoration of historical and natural sites.
The Iranian government further assured about the transfer of capital and profits overseas as per the foreign investment law of the country and full protection for the investors against any non-commercial risks such war or border conflict, confiscation or corruption, etc.
The government also started working on changing the image of the country and its tourism industry in the eyes of potential foreign visitors. One major change to this was to allow increased access to the internet, e.g. over social media, for the local players, which gave the restrained westerners a far greater insight into the country without the filters added from the mainstream media.
These efforts undertaken by the Iranian government were welcomed by several foreign investors, as they brought a sense of encouragement and stability to prospects of investing in the country.
This soon led to emergence of international hotel chains, the first being Novotel (296 rooms) and Ibis (196 rooms) hotels by the French hospitality company Accor which came to Tehran already in 2015. The company’s chief executive Mr. Bazin, at the launch of the venture, was optimistic in bringing up the chain of budget hotels such as Ibis and mid and upmarket hotels such as Novotel, Sofitel, and Pullman in 20 cities of Iran, but with no particular timeline given. Another hotel that came up in 2017 was Spanish Melia in Caspian Sea in 2017, built in partnership of Melia and its Iranian partners in Tehran, where the Iranians invested more than US$250 million while the management is taken over by Melia. The hotel includes 319 luxurious rooms, two residential towers, a sports center, and other services in an area of 18,000 square meters. Similarly, the Abu Dhabi’s Rotana Management Corporation planned to open four hotels in Iran’s major cities, Tehran and Mashhad, two in each. One of the hotels (a five-star hotel with 275 rooms and suites in Mashhad) was built within one year in 2017.
Overall, investments in the tourism sector started growing at a moderate level post the removal of US sanctions. According to World Tourism and Travel Council (WTTC) data on the capital investments in Iran’s tourism sector, 2016 witnessed an investment of US$2.75 billion contributing 3.25% of all investments in the country, as compared to the investment of US$2.63 billion in 2015. Since then, capital investments have been growing and are estimated to reach US$3.75 billion in 2028 with a share of 4.86% of all investments.
As a result of increased investments and rise in tourism sector, the GDP of the country also witnessed a slight growth. According to WTTC data, tourism industry’s share in the country’s GDP increased to 7.1% in 2015 contributing US$26.04 billion, up from 6.5% (US$24.38 billion) in 2014. However, it stabilized in the following years (6.8% in 2016, 6.4% in 2017, and 6.5% in 2018), with expected contribution to GDP of 6.52% amounting to US$35.39 billion by 2028. With developments in the tourism sector, the ministry of tourism is hoping to host nearly 20 million tourists per year by 2025.
But as the country started seeing benefits of the sanctions removal, with its improved economy thanks to rise in export and import, infrastructural developments, increase of foreign investments from 2016 to mid-2018, and boost in tourism sector and many other industries, the US government shocked the country by re-imposing sanctions in August 2018. The re-imposition was a consequence of the USA withdrawing its participation from the nuclear deal in May 2018 over political differences. This brought a blow to the Iranian economy with restrictions over imports and exports, thus again leaving Iran in economic struggle due to recession through shrinking oil exports.
EOS Perspective
The economic trembles coming from crude oil export ban led the Iranian government to increase its focus on tourism industry to offset the lost revenues. While American tourists are again restricted to travel to Iran, the country is still witnessing an increased influx of tourists from other regions, including the Middle East and Asia, a fact that cushions the impact of re-imposed sanctions.
Although a blessing in disguise for Iran, one of major reasons for the rise in tourism despite the US sanctions was the almost threefold fall of Iranian currency against US dollar which made travelling to Iran a low-cost affair for many foreign tourists, especially in comparison to other Middle Eastern destinations. This has contributed to the foreign tourists’ influx especially from the western countries – tourists with budget constraints as well as tourist arriving for medical tourism purposes. At the same time, the fall in rial value against the US dollar increased travel expenses for Iranians going overseas. This has constrained the outbound tourism, resulting in a decrease of 6.5% during 2018 (March 21- June 21 of Iranian Calendar).
The weakening of the currency was just one of the reasons that contributed to the slight growth in the Iran’s tourism sector, despite the US sanctions. The country continued to communicate its selling points and positive image to foreign audiences. Iran has been working on reinforcing its position as destination of religious pilgrimages, place with improved infrastructure, natural landscape, and cultural history. Through these messages on social media, the country seems to have attracted various sorts of tourists, from leisure travelers to artists to businessmen and more, resulting in growth of the industry.
According to deputy minister of the Cultural Heritage, Handicrafts and Tourism of Iran, the number of tourists’ arrivals increased by 24% during the first seven months of 2019 (starting from March 21 as per Iranian Calendar) compared to the same period previous year. In terms of tourists’ arrivals numbers, between March 2018 to March 2019, Iran witnessed 7.8 million foreign tourists visiting the country as compared to 4.7 million tourists from March 2017 to March 2018.
Encouraged by the growth in the sector, Iranian government undertook further initiatives to ensure the inflow of foreign visitors continues (and increases). In August 2019, a functionalized center was established in Cultural Heritage, Handicrafts and Tourism Organization, with a task to make decisions on reducing the negative impact of the US sanctions on tourism industry.
Following the US State Department’s warning (issued in May 2018) against travelling to Iran, citing it being an unsafe travel destination, the risk of fall of other western tourists’ arrivals increased. The Iranian government, to compensate for the fall, focused more on attracting tourists from regional countries. For instance, visa fees for Iraqi tourists (accounting for 24% of inbound tourists in 2018) were removed, while visas for Omanis were waived off.
Iran is also looking for tourists in more remote markets, especially in countries that are known to frequently stand against the USA in the international area. China is one such market which Iran is hoping to attract leisure tourism from by allowing visa-free entry of the Chinese nationals into Iran as of July 2019. Iran has an ambitious plan to increase the number of Chinese visitors from just over 50,000 in 2018 to 2 million in 2020.
Furthermore, in order to encourage foreign tourists to visit Iran, the Iranian government decided not to stamp their passports to help them avoid issues with subsequent attempts to travel to the USA. Additionally, the government is also trying to spur medical tourism by developing health tourism hubs, especially in Shiraz with a vision to increase the tourists travel for medical purposes as well.
These measures have been quite successful in promoting Iranian tourism growth, even though the American and other western visitors have (to some extent) been replaced with arrivals from the Middle Eastern and Asian countries. However, looking at the current situation of unrest, with the killing of Iranian general Qassem Soleimani in January 2020 by US military, and Iran responding to this with missile attacks on the US military troops in Iraq less than a week later, the conflict between the two countries is nowhere near its end. This political unrest, if continues, has a potential to again severely affect Iran’s tourism industry, as the country will be unable to grow the sector without reliance on western visitors. Tourists’ sentiments are tightly linked to political climate; therefore, it can be expected that only improved relations with the USA, and through this a better image, will allow Iran to truly develop its tourism industry and its economic situation in general.