Sri Lanka is currently facing its worst economic crisis since its independence and is the first country in the Asia-Pacific region to default on its external debt in over two decades. While the financial crisis is underpinned by political mismanagement, low tourism during COVID-19, and affected exports and payments due to the Ukraine-Russia war, growing Chinese debt in recent years is also considered to be a major factor in the country’s financial downfall. More so, with China withholding desired and critical support at this time, more questions are being raised over China’s relationship with Sri Lanka. This has provided India and to an extent, the West, with the perfect opportunity to strengthen its ties with the country and in turn limit China’s political and economic influence in the region.
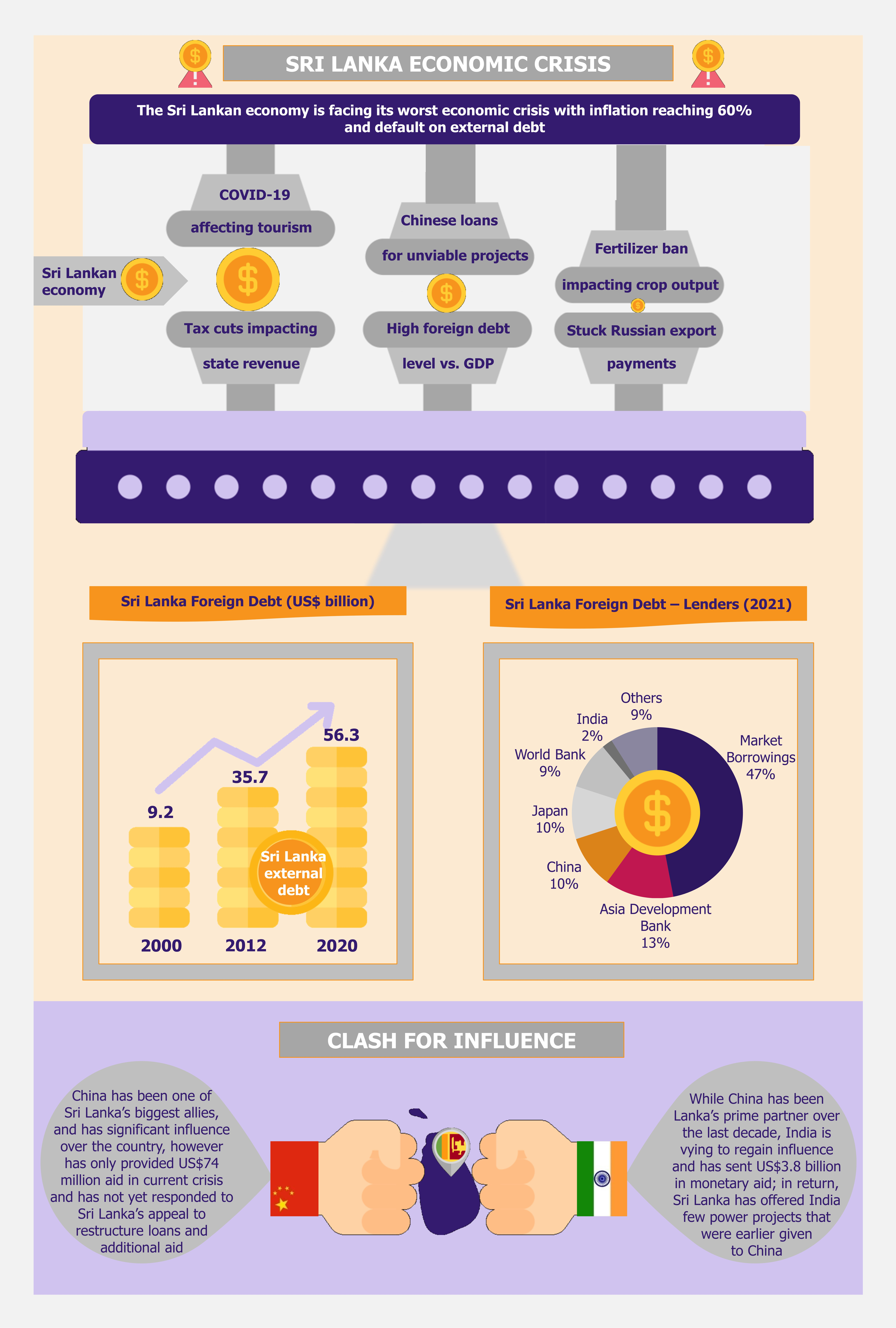
In April 2022, the Sri Lankan economy witnessed an absolute collapse owing to skyrocketing inflation, shortage of essential goods such as fuel, food, and medicines, and foreign debt to the tune of US$50 billion with just US$2 billion in foreign reserves. The financial turmoil further spiraled into a political crisis with the president, Gotabaya Rajapaksa, fleeing the country amidst strong public outcry.
There is no one cause for the freefall of the economy. However, the situation is largely underpinned by unforeseen factors such as halt in tourism earnings due to the pandemic, the Ukraine-Russia war, which resulted in blocked payments from Russia for tea exports, along with deep-rooted issues such as political corruption, favoritism, and weak policies.
An example of weak governance could be the 2019 tax cuts and 2021 ban on imports of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, which forced majority of farmers to go organic overnight. While the ban on pesticides import was aimed at saving US$400 million that were spent annually on import of fertilizers (in addition to reducing the adverse effect of pesticides on health and environment), the move backfired as the ban led to a substantial drop in crop production. As a result, Sri Lanka had to spend US$450 million on rice imports to cover up for the 20% drop in rice production levels. Moreover, it saw a decline in tea exports by 18% due to limited production. To offset this loss by farmers, the government had to spend several hundred million dollars as compensation and subsidies for farmers who lost their livelihoods. While the policy was removed after only five months for some sectors such as tea production, the damage was done causing a huge dent to the economy.
However, one of the key reasons for the country’s downfall is attributed to the government’s close alliance with China and to several economically unviable infrastructure projects that were green-lighted with China’s financial support and influence. Currently China is Sri Lanka’s biggest unilateral creditor.
The Rajpaksa family, which has dominated Sri Lankan politics for the last two decades, has been a close ally of China, and has favored investments from the country at the cost of relations with India and other nations that have for long warned Sri Lanka (and other Asian and African countries) about China’s debt-trap diplomacy. Over the last 15 years or so, Sri Lanka’s government has authorized several Chinese infrastructure projects including some that were considered economically unviable.
One such example is the Sri Lankan Hambantota Port that was built by China Harbor Engineering Company on a loan of about US$1.26 billion taken by Sri Lanka from China. The project, which was also touted to be commercially unviable from the very start by several experts and was cleared primarily because of close ties between China and the Rajpaksa family, was a commercial failure. In 2017, the port was handed over to the Chinese government for a 99-year lease due to default in loan payment. Similarly, the Hambantota airport is considered to be one of the emptiest airports in the world and has not been attracting traffic as anticipated, while the Nelum Kuluna towers (touted to be the tallest building in South Asia), stand empty. This has resulted in huge debt to the Chinese government from projects that failed to generate revenue for Sri Lanka. Sri Lanka owes 10% of its total foreign debt to China alone.
Now in the midst of its worst financial crisis and ridden of the old political regime, Sri Lanka is realizing the burden of the foreign debt it has to China. Especially at the moment, when the support received from its once most valued partner has been lukewarm at best.
China has largely maintained silence on the current economic crisis faced by Sri Lanka as well as on the political turmoil and fall of the Rajapaksa clan. It has adopted a ‘wait and watch’ approach, which is being criticized globally. More so, China has only provided minimal relief support to the nation in crisis. To put it into perspective, China has provided only US$74 million of aid and has sent a large shipment of rice to Sri Lanka in response to the large-scale monetary assistance requested by the Rajapaksas, before their departure. Moreover, China has turned a deaf ear to Sri Lankan government’s plead for loan restructuring and is yet to consider the request for an additional financial aid of US$4 billion (which encompasses US$1 billion loan, US$1.5 billion credit line for Chinese imports and US$1.5 billion in bilateral currency swap). Furthermore, China has not cleared its stance on IMF’s relief package for Sri Lanka. While IMF is designing a relief package for Sri Lanka, it needs consent from all its creditors to write off some loans so that the relief sum is used for economic revival instead of just servicing foreign debt. While Sri Lanka is urging the IMF and China to work together, it is going to be a long round of negotiations.
On the other hand, India has been increasing its influence on its neighbor and has provided US$3.8 billion in monetary relief to Sri Lanka. In addition, it is willingly working with IMF to restructure loans to provide debt relief to the country in need. It is also collaborating with Japan to assist Sri Lanka during the crisis. Sri Lanka is of strategic importance to India as it connects several of its key trade routes to Africa and Europe. With China having close ties with Sri Lanka in the past, it had built a strong foothold in the Indian Ocean, which was threatening to India and led to a geopolitical rivalry between India and China.
This financial crisis comes as an opportunity to India to replace China as Sri Lanka’s preferred partner. In March 2022, the Indian government signed a deal with Sri Lanka to develop hybrid power projects in northern parts of the country after China suspended a similar project in December 2021, stating security reasons. Around the same time, India was awarded a US$12 million contract to build wind farms on three small islands in the Palk Strait (which lies between southern India and Sri Lanka) after the project was taken away from a Chinese firm. In March 2022, India’s National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC) also signed an agreement with Ceylon Electricity Board (CEB) to jointly set up a solar power plant in Sampur, Sri Lanka.
Moreover, in July 2022, several investment proposals to strengthen the economic ties between India and Sri Lanka were discussed between officials from both countries. The key sectors that were identified for investments by India in Sri Lanka include renewable energy, hydrocarbon, ports and infrastructure, IT, and hospitality. The talks also encompassed the development of the Trincomalee Port on Sri Lanka’s northeastern coast and a proposal to use Indian Rupee for transactions in Sri Lanka. In August 2022, the Sri Lanka government also gave an approval to Lanka’s Indian Oil Corporation (LIOC, a subsidiary of India’s Indian Oil Corporation) to open 50 new fuel stations in the country. While LIOC already operates 216 fuel stations in Sri Lanka, it plans to invest US$5.5 million in the proposed expansion. In a separate deal in December 2021, LIOC gained control of 75 oil tanks in a strategically significant storage facility near Trincomalee.
For China, on the other hand, this crisis presents a precarious situation. While it holds 10% of Sri Lanka’s debt, the perception is that China is one of the key reasons for Sri Lanka’s downfall. With China’s other BRI partners, such as Pakistan, heading towards a similar fate, it is important for China to understand the grip it has in deciding the fate of countries over which it holds such significant power. At the same time, it will not like to lose the control it holds over this region to India that would gladly step in to displace China as the preferred partner.
EOS Perspective
The Sri Lankan crisis and its management is being closely observed by several global economies. While China has been Sri Lanka’s prominent partner over the last decade and a half, a new regime in Sri Lanka, China’s tepid response, and India’s support may lead to a shift in allegiances in the region. However, it is still early to offer any definite comments. China still holds significant influence in the region. This can be seen in the recent events, when in August 2022, China docked its ballistic missile and satellite tracking ship, Yuan Wang 5, (also termed ‘spy’ ship) at Sri Lanka’s Hambantota port for six days, despite significant resistance and raised security concerns by India. Therefore, while India is trying to get closer with Sri Lanka, it is very difficult to match China’s control over the region. That being said, there is definitely an opening to improve both political and business relations with Sri Lanka for India. While politically Sri Lanka is of strong geopolitical significance, the country can also prove to be a valuable economic partner with regards to growing trade as well as large scale power and infrastructure projects in the long run.